Vivotek NR9682-v2 64-Channel NVR (No HDD) User Manual
Page 56
VIVOTEK - A Leading Provider of Multimedia Communication Solutions
56 - User's Manual
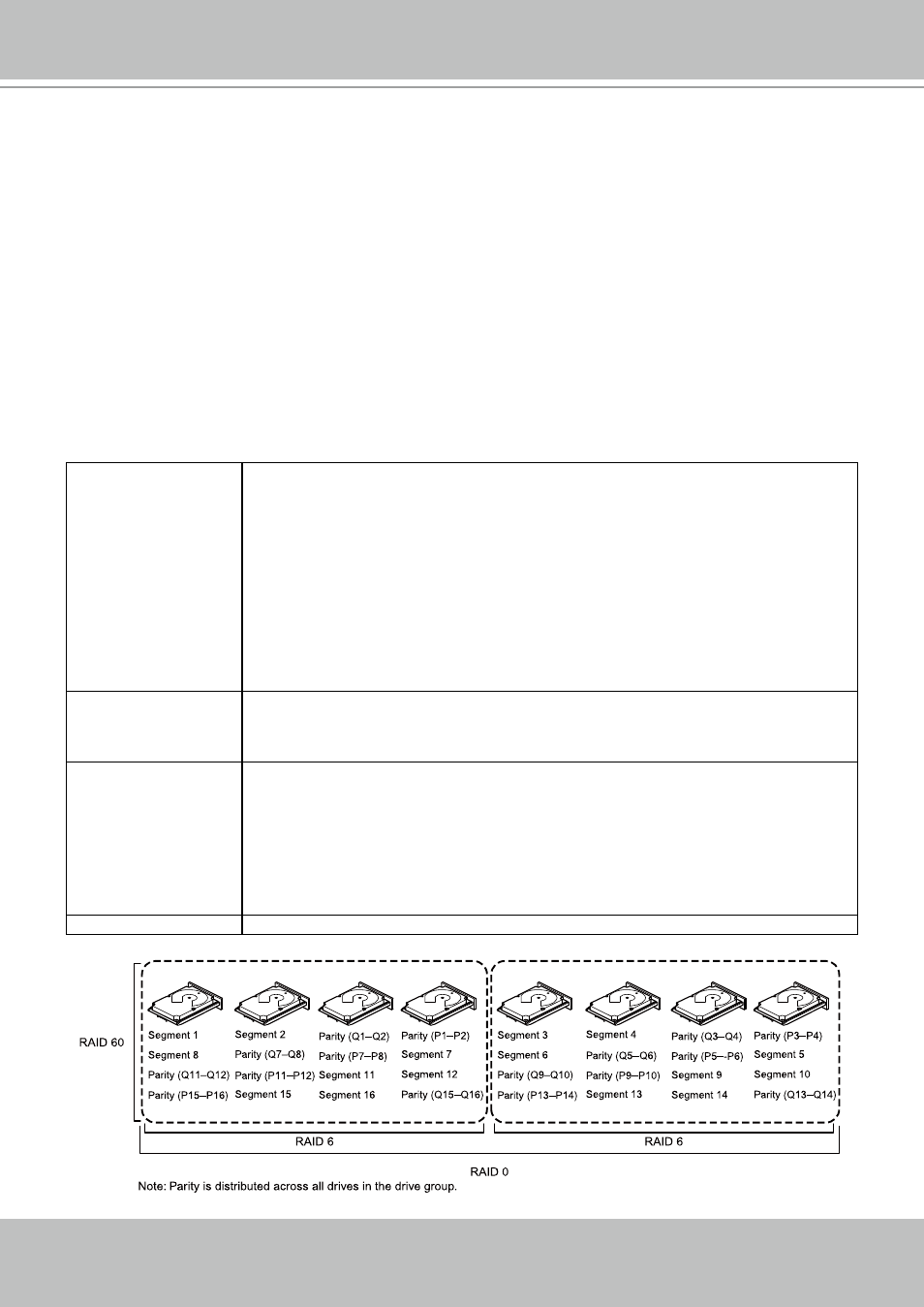
RAID 60
A RAID 60 drive group provides the features of both RAID 0 and RAID 6 drive groups, and
includes both parity and disk striping across multiple drive groups. A RAID6 drive group supports
two independent parity blocks per stripe. A RAID 60 virtual drive can survive the loss of two
drives in each of the RAID6 drive group sets without losing data. A RAID60 drive group is best
implemented on two RAID6 drive groups with data striped across both drive groups.
A RAID60 drive group breaks up data into smaller blocks and then stripes the blocks of data to
each RAID6 disk set. A RAID6 drive group breaks up data into smaller blocks, calculates parity
by performing an exclusive-OR operation on the blocks, and then performs write operations to
the blocks of data and writes the parity to each drive in the drive group. The size of each block is
determined by the stripe size parameter, which is set during the creation of the RAID set.
A RAID60 drive group can support up to 8spans and tolerate up to 16 drive failures, though less
than total driv
e capacity is available. Two drive failures can be tolerated in each RAID 6 level
drive group.
Uses
Provides a high level of data protection through the use of a second parity block in each
stripe. Use a RAID60 drive group for data that requires a very high level of protection
from loss.
In the case of a failure of one drive or two drives in a RAID set in a virtual drive, the RAID
controller uses the parity blocks to re-create all of the missing information. If two drives in
a RAID 6 set in a RAID60 virtual drive fail, two drive Rebuild operations are required, one
for each drive. These Rebuild operations can occur at the same time.
Use for online customer service that requires fault tolerance. Use for any application that
has high read request rates but low write request rates. Also used when a virtual drive of
greater than 32 drives is needed.
Strong points
Provides data redundancy, high read rates, and good performance in most environments.
Each RAID6 set can survive the loss of two drives or the loss of a drive while another
drive is being rebuilt.Provides the highest level of protection against drive failures of all of
the RAID levels.
Weak points
Not well-suited for small block write or random write operations. A RAID 60 virtual
drive must generate two sets of parity data for each write operation, which results in
a significant decrease in performance during write operations.Drive performance is
reduced during a drive Rebuild operation. Environments with few processes do not
perform as well because the RAID overhead is not offset by the performance gains in
handling simultaneous processes.
A RAID6 drive group costs more because of the extra capacity required by using two
parity blocks per stripe.
Drives
A minimum of 6.
