Dhcp message format – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 41
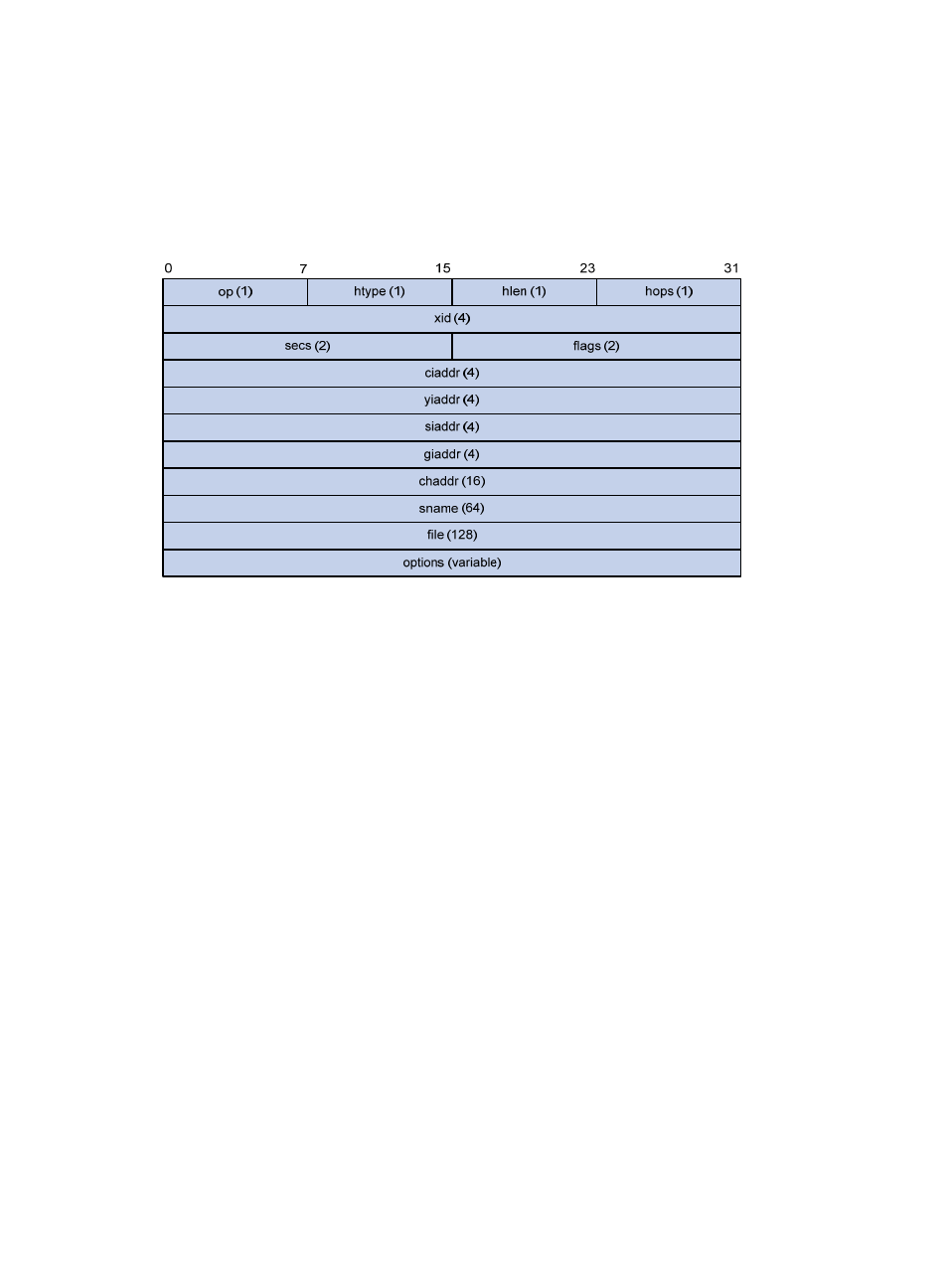
30
DHCP message format
shows the DHCP message format, which is based on the BOOTP message format although
DHCP uses some of the fields in significantly different ways. The numbers in parentheses indicate the size
of each field in bytes.
Figure 18 DHCP message format
•
op: Message type defined in option field. 1 = REQUEST, 2 = REPLY
•
htype, hlen: Hardware address type and length of a DHCP client.
•
hops: Number of relay agents a request message traveled.
•
xid: Transaction ID, a random number chosen by the client to identify an IP address allocation.
•
secs: Filled in by the client, the number of seconds elapsed since the client began address
acquisition or renewal process. Currently this field is reserved and set to 0.
•
flags: The leftmost bit is defined as the BROADCAST (B) flag. If this flag is set to 0, the DHCP server
sent a reply back by unicast; if this flag is set to 1, the DHCP server sent a reply back by broadcast.
The remaining bits of the flags field are reserved for future use.
•
ciaddr: Client IP address if the client has an IP address that is valid and usable; otherwise, set to
zero.
•
yiaddr: 'your' (client) IP address, assigned by the server.
•
siaddr: Server IP address, from which the client obtained configuration parameters.
•
giaddr: (Gateway) IP address of the first relay agent a request message traveled.
•
chaddr: Client hardware address.
•
sname: Server host name, from which the client obtained configuration parameters.
•
file: Bootfile name and path information, defined by the server to the client.
•
options: Optional parameters field that is variable in length, which includes the message type,
lease duration, subnet mask, domain name server IP address, WINS IP address, and other
information.
