Dhcp overview, Introduction to dhcp, Dhcp address allocation – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 39: Allocation mechanisms
28
DHCP overview
NOTE:
The term
interface in the DHCP features refers to Layer 3 interfaces, including VLAN interfaces and
route-mode (or Layer 3) Ethernet ports. You can set an Ethernet port to operate in route mode by using the
port link-mode route command (see the
Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide).
Introduction to DHCP
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) provides a framework to assign configuration
information to network devices.
DHCP uses the client/server model.
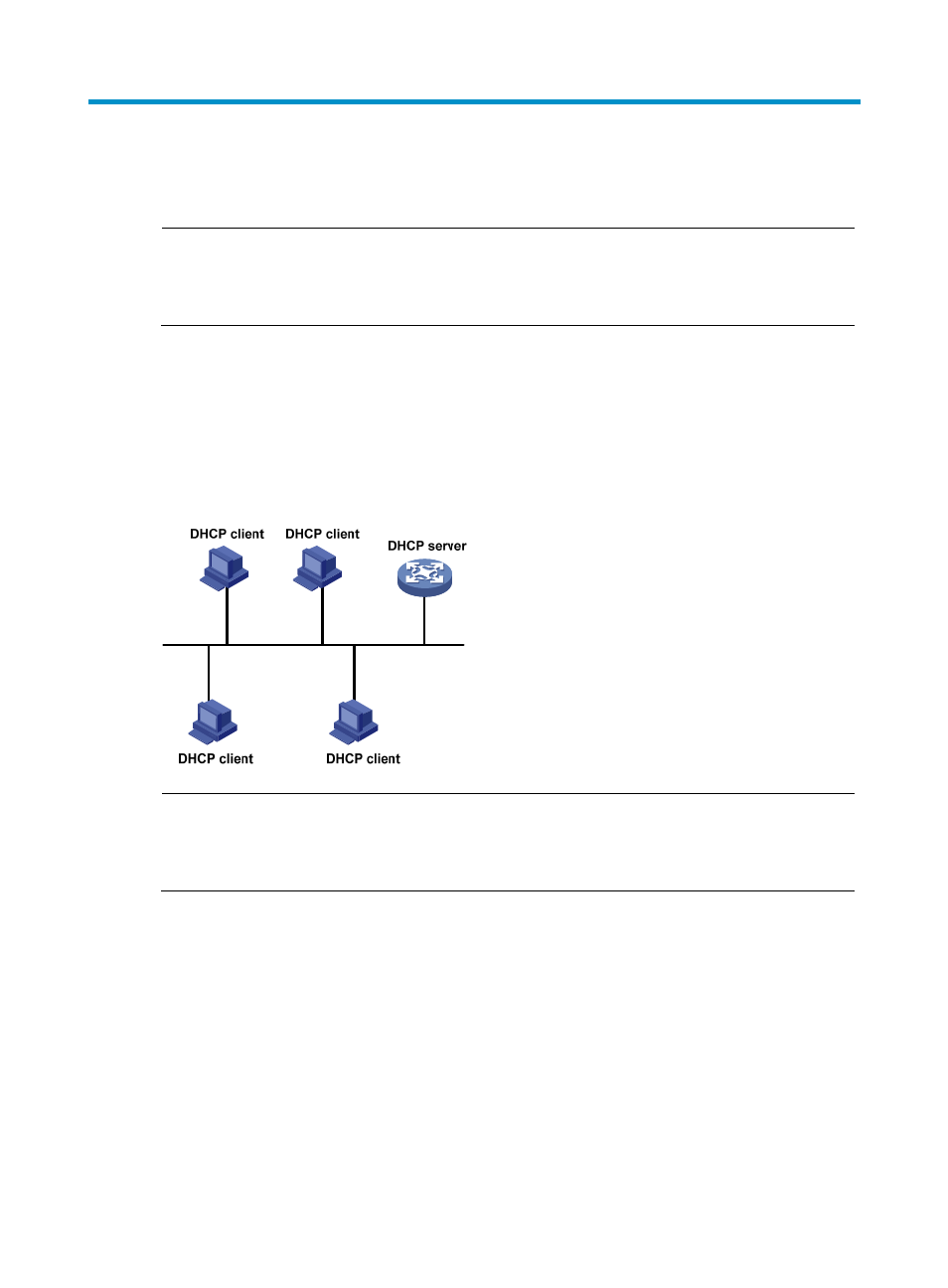
shows a typical DHCP application.
Figure 16 A typical DHCP application
NOTE:
A DHCP client can obtain an IP address and other configuration parameters from a DHCP server on
another subnet via a DHCP relay agent. For more information about the DHCP relay agent, see the
chapter “DHCP relay agent configuration.”
DHCP address allocation
Allocation mechanisms
DHCP supports the following mechanisms for IP address allocation.
•
Static allocation: The network administrator assigns an IP address to a client like a WWW server,
and DHCP conveys the assigned address to the client.
•
Automatic allocation: DHCP assigns a permanent IP address to a client.
•
Dynamic allocation: DHCP assigns an IP address to a client for a limited period of time, which is
called a lease. Most DHCP clients obtain their addresses in this way.
