Tunnel types – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 159
148
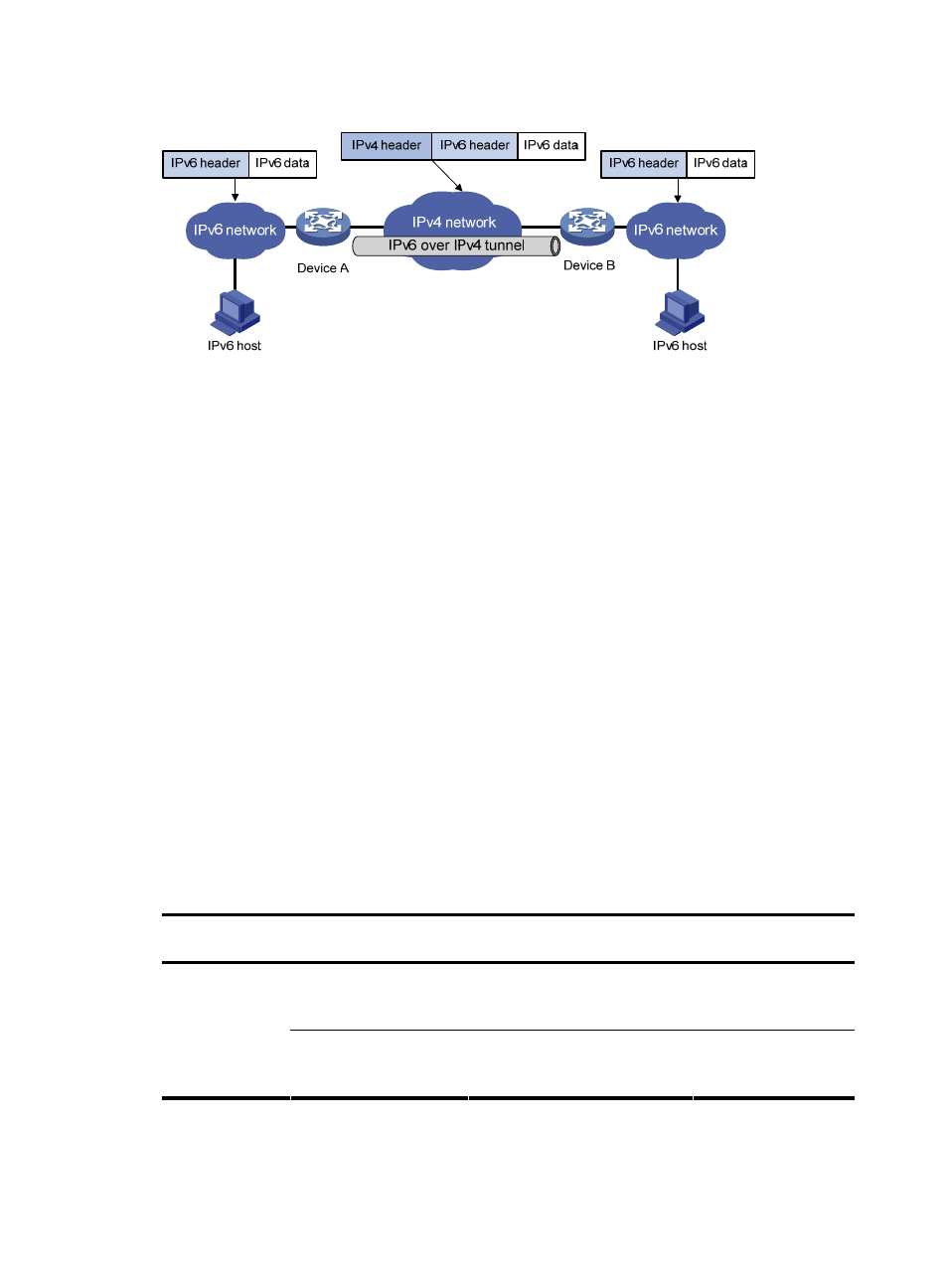
Figure 65 IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel
The IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel processes packets in the following ways.
1.
A host in the IPv6 network sends an IPv6 packet to Device A at the tunnel source.
2.
After determining from the routing table that the packet needs to be forwarded through the tunnel,
Device A encapsulates the IPv6 packet with an IPv4 header and forwards it through the physical
interface of the tunnel.
3.
Upon receiving the packet, Device B de-encapsulates the packet.
4.
Device B forwards the packet according to the destination address in the de-encapsulated IPv6
packet. If the destination address is the device itself, Device B forwards the IPv6 packet to the
upper-layer protocol for processing.
Tunnel types
IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels are divided into manually configured tunnels and automatic tunnels, depending
on how the IPv4 address of the tunnel destination is acquired.
•
Manually configured tunnel: The destination address of the tunnel cannot be automatically
acquired through the destination IPv6 address of an IPv6 packet at the tunnel source, and must be
manually configured.
•
Automatic tunnel: The destination address of the tunnel is an IPv6 address with an IPv4 address
embedded, and the IPv4 address can be automatically acquired through the destination IPv6
address of an IPv6 packet at the tunnel source.
According to the way an IPv6 packet is encapsulated, IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels are divided into the
following modes.
Table 11 IPv6 over IPv4 tunnel modes and key parameters
Tunnel type
Tunnel mode
Tunnel source/destination
address
Tunnel interface
address type
IPv6 manual tunneling
The source/destination IP address
is a manually configured IPv4
address.
IPv6 address
Manually
configured tunnel
IPv6-over-IPv4 GRE
tunneling
The source/destination IP address
is a manually configured IPv4
address.
IPv6 address
