Ipv6 basics configuration, Ipv6 overview, Ipv6 features – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 111: Header format simplification, Larger address space
100
IPv6 basics configuration
NOTE:
The term
interface in this document refers to Layer 3 interfaces, including VLAN interfaces and route-mode
(or Layer 3) Ethernet ports. You can set an Ethernet port to operate in route mode by using the port
link-mode route command (see
Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide).
IPv6 overview
Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6), also called IP next generation (IPng), was designed by the Internet
Engineering Task Force (IETF) as the successor to Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4). The significant
difference between IPv6 and IPv4 is that IPv6 increases the IP address size from 32 bits to 128 bits.
IPv6 features
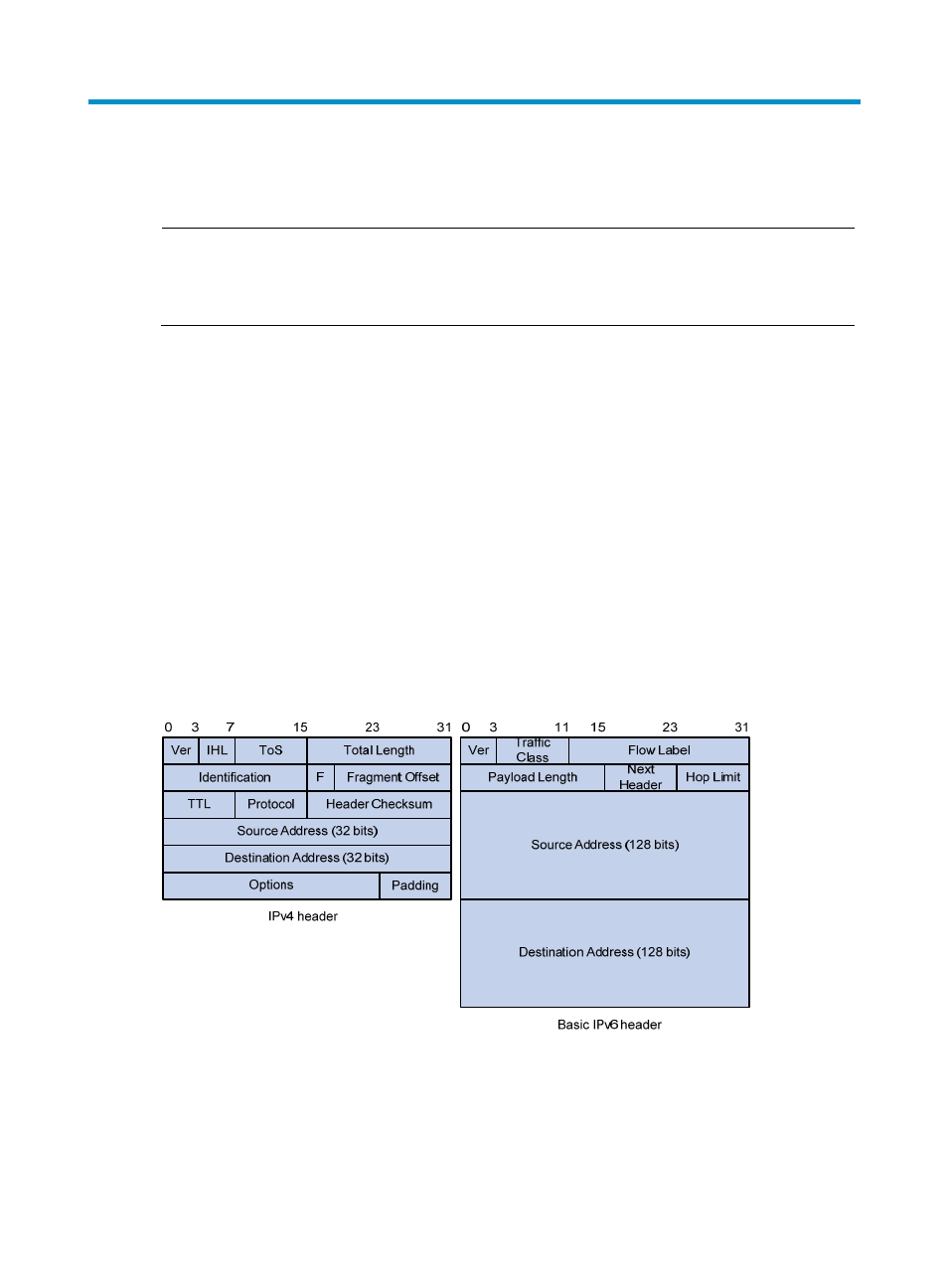
Header format simplification
IPv6 removes several IPv4 header fields or moves them to the IPv6 extension headers to reduce the length
of the basic IPv6 packet header. The basic IPv6 packet header has a fixed length of 40 bytes to simplify
IPv6 packet handling and to improve forwarding efficiency. Although IPv6 address size is four times
larger than IPv4 address size, the basic IPv6 packet header size is only twice the size of the option-less
IPv4 packet header.
Figure 44 IPv4 packet header format and basic IPv6 packet header format
Larger address space
The source and destination IPv6 addresses are 128 bits (or 16 bytes) long. IPv6 can provide 3.4 x 10
38
addresses to meet the requirements of hierarchical address division and the allocation of public and
private addresses.
