Ipv4 over ipv4 tunneling, Introduction, Encapsulation and de-encapsulation – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 161
150
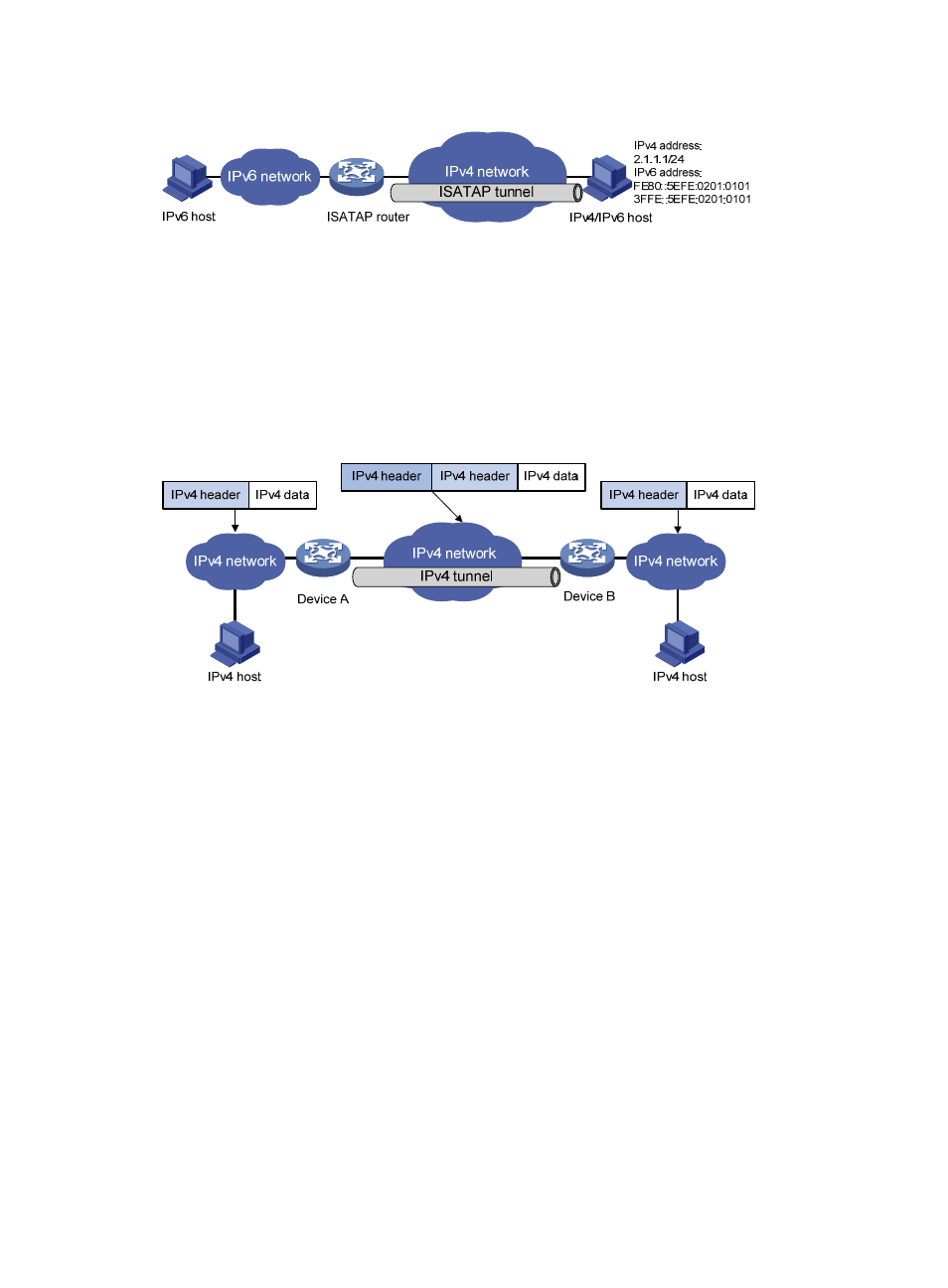
Figure 66 Principle of ISATAP tunneling
IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling
Introduction
IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling (specified in RFC 1853) is developed for IP data packet encapsulation so that
data can be transferred from one IPv4 network to another IPv4 network.
Encapsulation and de-encapsulation
Figure 67 Principle of IPv4 over IPv4 tunneling
Packets traveling through a tunnel undergo encapsulation and de-encapsulation processes, as shown in
•
Encapsulation
The encapsulation follows these steps.
1.
Device A receives an IP packet from an IPv4 host and submits it to the IP protocol stack.
2.
The IP protocol stack determines how to forward the packet according to the destination address
in the IP header. If the packet is destined for the IPv4 host connected to Device B, Device A delivers
the packet to the tunnel interface.
3.
The ttunnel interface encapsulates the packet into an IPv4 packet and submitted to the IP protocol
stack for processing. The IP protocol stack determines the outgoing interface of the tunnel
according to the IP header, and sends the packet out.
•
De-encapsulation
The de-encapsulation follows these steps.
1.
After receiving the packet, Device A delivers it to the IP protocol stack, which then checks the
protocol number in the IP header.
2.
If the protocol number is IPv4 (indicating an IPv4 packet is encapsulated within the packet), the IP
packet is sent to the tunnel module for de-encapsulation.
3.
The de-encapsulated IP packet is sent back to the IP protocol stack for processing.
