Configuring dldp, Overview, Background – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 46
35
Configuring DLDP
Overview
Background
Unidirectional links occur when one end of a link can receive packets from the other end, but the other
end cannot receive packets sent by the first end. Unidirectional links result in problems such as loops in
an STP-enabled network.
For example, the link between Switch A and Switch B is bidirectional when they are connected through
a fiber pair, with one fiber used for sending packets from A to B and the other for sending packets from
B to A. This link is a two-way link. If one of these fibers gets broken, the link becomes unidirectional
(one-way link).
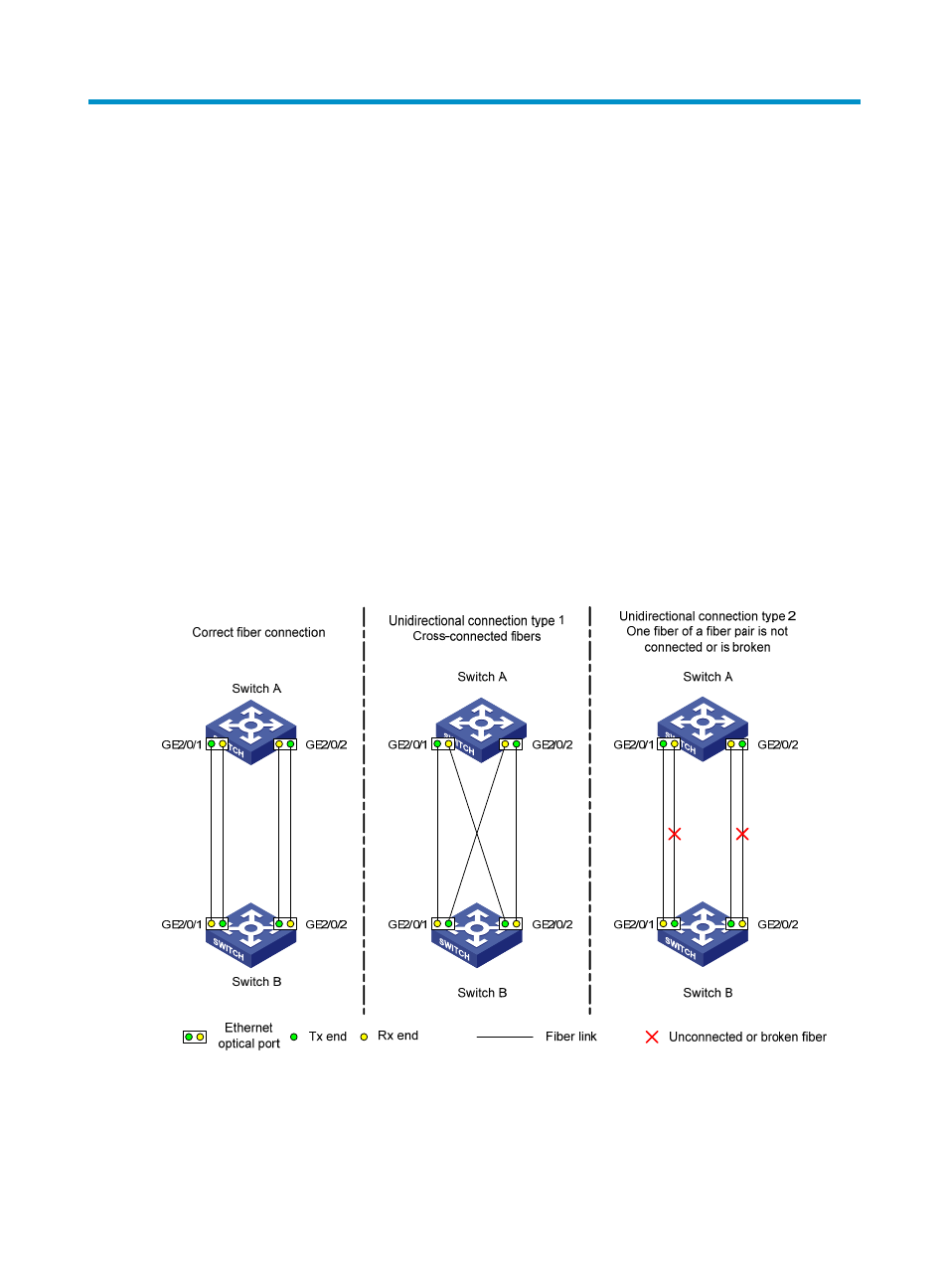
There are two types of unidirectional fiber links. One occurs when fibers are cross-connected. The other
occurs when a fiber is not connected, or when one fiber of a fiber pair gets broken.
shows a
correct fiber connection and the two types of unidirectional fiber connection.
Figure 7 Correct and incorrect fiber connections
The Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP) detects unidirectional links (fiber links or twisted-pair links) and
can be configured to shut down the related port automatically or prompt users to take actions to avoid
network problems.
