Assigning virtual mac addresses – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 146
135
NOTE:
To configure the VRRP load balancing function in IRF mode, you must configure the bridge MAC address
to be permanently preserved (default setting). For more information about IRF mode, see
IRF
Configuration Guide.
Assigning virtual MAC addresses
When VRRP is operating in load balancing mode, the master assigns virtual MAC addresses to the
routers in the VRRP group and answers the ARP requests or ND requests from different hosts. The backup
routers, however, do not answer the ARP requests or ND requests from the hosts.
In an IPv4 network, a load-balanced VRRP group works as follows:
1.
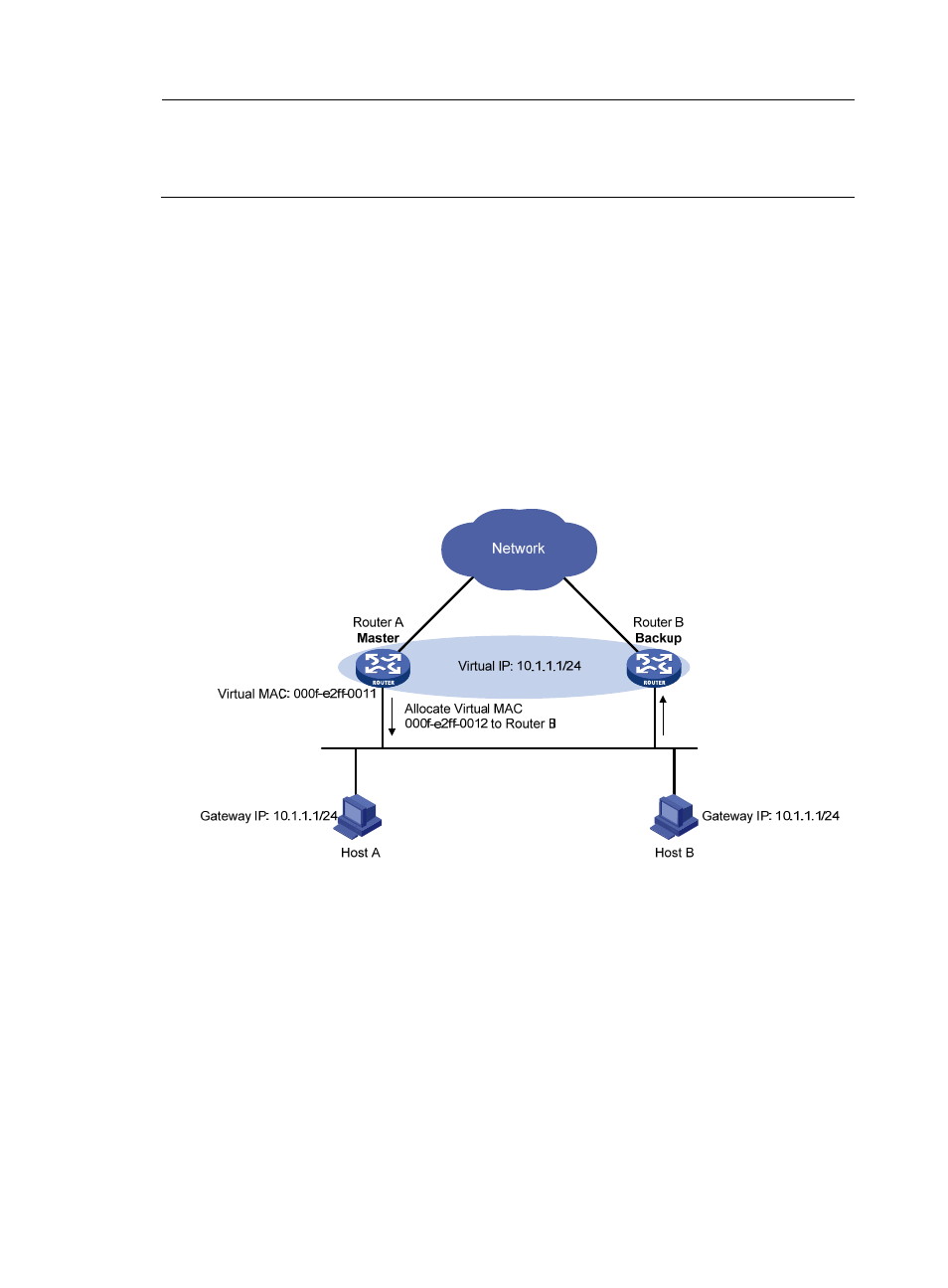
The master assigns virtual MAC addresses to the routers (including the master itself and the
backups) in the VRRP group. For example, as shown in
, the virtual IP address of the VRRP
group is 10.1.1.1/24; Router A is the master; Router B and Router C are the backups. Router A
assigns 000f-e2ff-0011 to itself, and 000f-e2ff-0012 to Router B.
Figure 35 Allocating virtual MAC addresses
2.
After receiving an ARP request destined for the virtual IP address of the VRRP group from a host, the
master, based on the load balancing algorithm, uses a corresponding virtual MAC address to
answer the ARP request. For example, as shown
, when Host A sends an ARP request to
retrieve the MAC address of gateway 10.1.1.1, the master (Router A), after receiving the request,
returns the virtual MAC address of Router A to Host A; when Host B sends an ARP request to
retrieve the MAC address of gateway 10.1.1.1, the master (Router A), after receiving the request,
returns the virtual MAC address of Router B to Host B.
