Mep list, Cfd functions, Continuity check – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 32
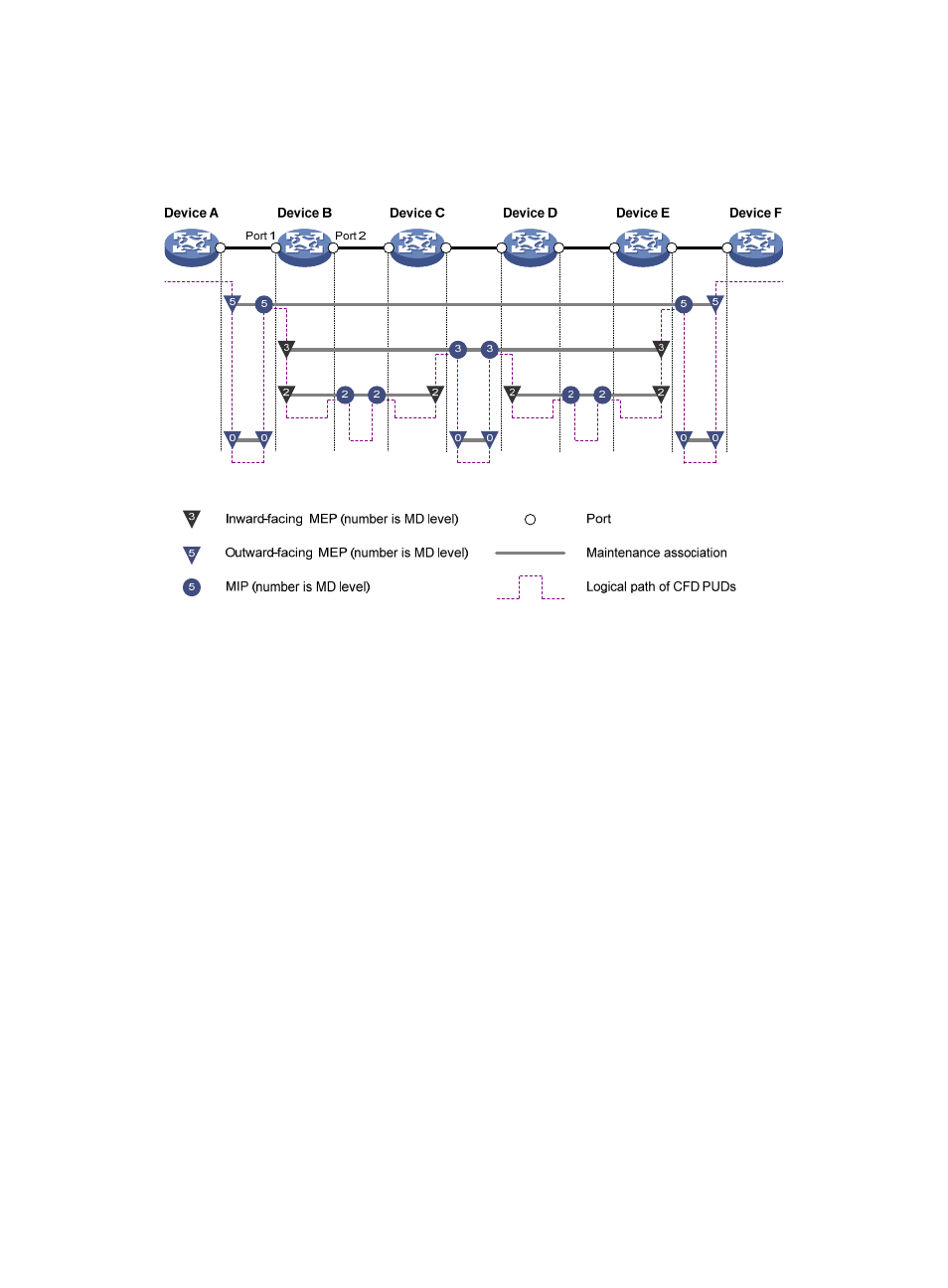
21
configured on the ports of device A through device F. Port 1 of device B is configured with the following
MPs—a level 5 MIP, a level 3 inward-facing MEP, a level 2 inward-facing MEP, and a level 0
outward-facing MEP.
Figure 5 CFD grading example
MEP list
A MEP list is a collection of local MEPs allowed to be configured and the remote MEPs to be monitored
in the same MA. It lists all the MEPs configured on different devices in the same MA. The MEPs all have
unique MEP IDs. When a MEP receives from a remote device a continuity check message (CCM) that
carries a MEP ID not included in the MEP list of the MA, it drops the message.
CFD functions
CFD works effectively only in correctly-configured networks. Its functions, which are implemented through
the MPs, include:
•
Continuity check (CC)
•
Loopback (LB)
•
Linktrace (LT)
•
Alarm indication signal (AIS)
•
Test (TST)
Continuity check
Connectivity faults are usually caused by device faults or configuration errors. Continuity check checks
the connectivity between MEPs. This function is implemented through periodic sending of continuity
check messages (CCMs) by the MEPs. A CCM sent by one MEP is intended to be received by all the other
MEPs in the same MA. If a MEP fails to receive the CCMs within 3.5 times the sending interval, the link
is considered as faulty and a log is generated. When multiple MEPs send CCMs at the same time, the
multipoint-to-multipoint link check is achieved. CCM frames are multicast frames.
