Guralp Systems CMG-CD24 User Manual
Page 71
Operator's Guide
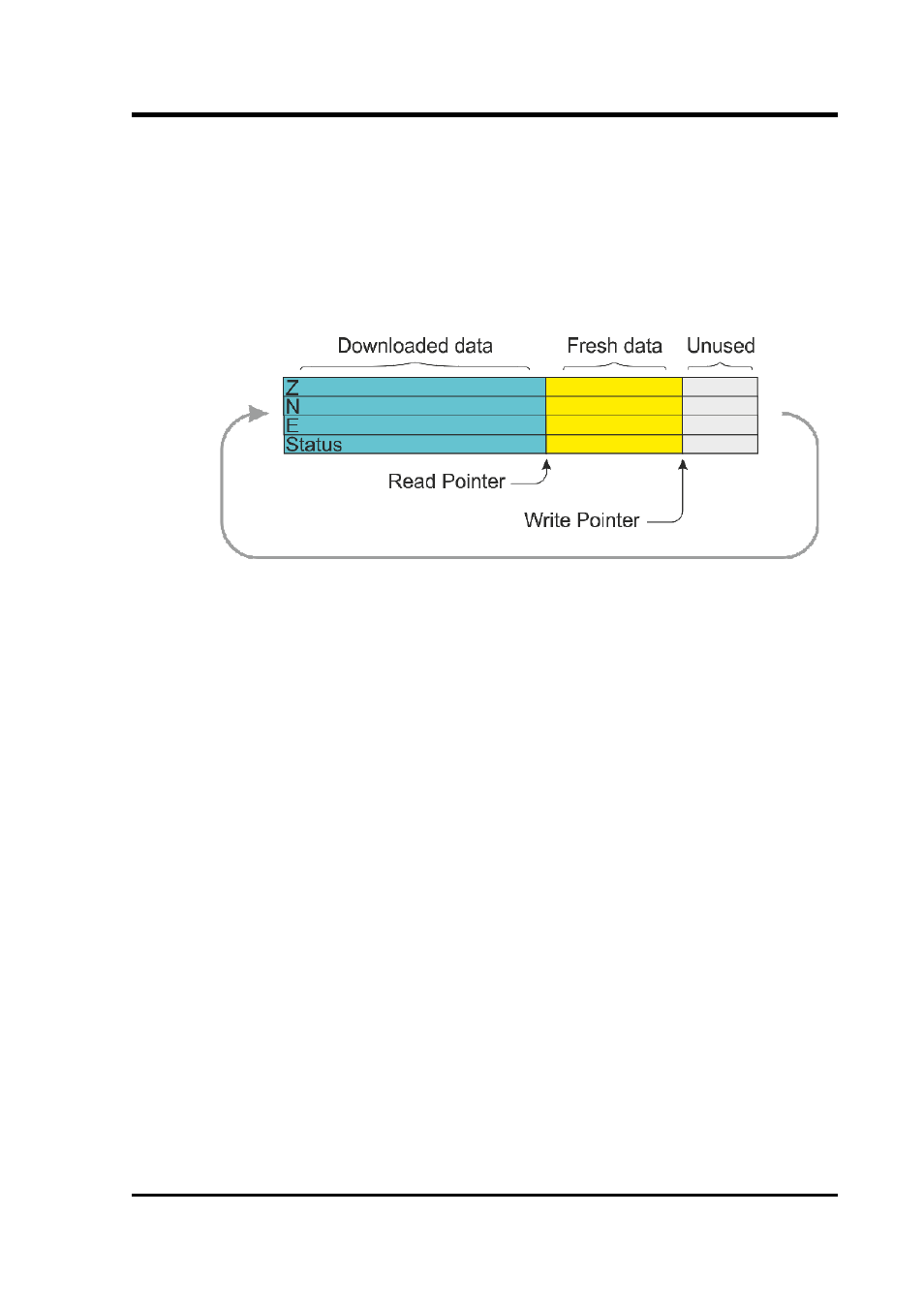
The flash memory is used as a ring buffer. Two pointers into the
memory keep track of where data were last read (the “Read Pointer”)
and last written (the “Write pointer”). When either pointer reaches the
end of physical memory, it wraps round back to the beginning. The
behaviour when the write pointer reaches the read pointer (i.e. when
the memory becomes full of data, none of which have been
downloaded) is governed by the commands RE-USE/RECYCLE and
WRITE-ONCE.
Which data are downloaded depends on various parameters you can
set, which allow you to select a particular stream, streams of a
specified sample rate, or streams within a certain time window. You
can set parameters separately, or place the definitions before the
DOWNLOAD command, e.g.
ALL-FLASH HPA0N1 STREAM DOWNLOAD
2004 12 01 00 00 FROM-TIME ALL-DATA DOWNLOAD
100 S/S ALL-TIMES DOWNLOAD
ALL-DATA ALL-TIMES DOWNLOAD
Before DOWNLOAD will work, it needs to know
●
the desired time period, which is specified with ALL-FLASH,
ALL-TIMES, or FROM-TIME and/or TO-TIME, and
●
the streams you want to download, which are specified with
ALL-DATA, S/S, or STATUS-ONLY.
The parameters are illustrated in the diagram below and fully
described in the following sections. If you miss out a parameter,
DOWNLOAD will use the value you last used.
March 2011
71
