Remote telephones – Xblue Networks X-50 User Manual
Page 18
Introduction
18
XBLUE Networks
2
LA
N
v
s. WA
N
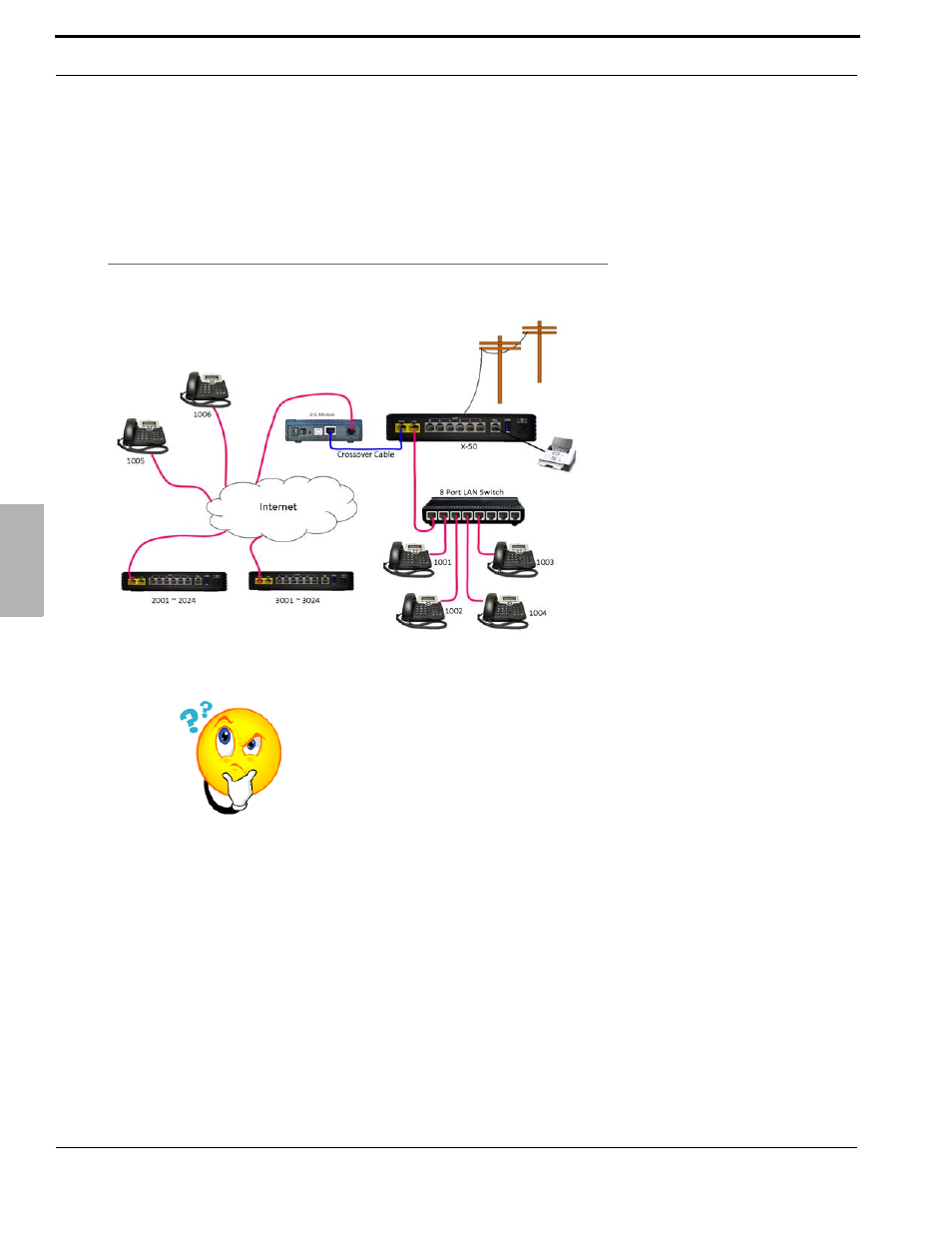
Remote Telephones
When connecting remote workers to the X-50 VoIP Telephone System it must have a fixed or static class A or B
IP Address. When creating a voice network (Campus Environment) the “Master” X-50 VoIP Telephone System
also must have a fixed or static class A or B IP Address. All other systems on the voice network can use Dynamic IP
addresses. This may require the ISP’s Gateway to be programmed as a Bridge or a concurrent bridge.
Remote telephones are directed
to the static IP Address of the
WAN port, which will have a
Class A or Class B IP Address.
Once registered, the WAN port
of the X-50 keeps the
telephone endpoints active by
sending “keep alive” packets to
each of the remote telephone
endpoints.
The Remote telephone should
set the Session Timer to 20
seconds.
What does that say?
The Internet Service Provider (ISP) will program their DSL/Cable
modem to be a bridge or a concurrent bridge allowing the X-50 VoIP
Telephone System to join the network parallel to the ISP’s DSL/Cable
modem. If needed, this also allows the X-50 VoIP Telephone System
to become the main router on the Local Area Network (LAN).
When connecting remote workers to a X-50 system, it must have a
static IP Address. When creating a voice network or “Campus
Environment”, only one of the X-50 systems must have a static IP
Address.
Any X-50 with a static Class A or B IP Address will support remote
workers, even if they are a node on a voice network.
