Orbital Antares User Manual
Page 85
Antares
®
OSP-3
User’s Guide
Section 8.0
– Non-Standard Services
Release 1.1
July 2013
74
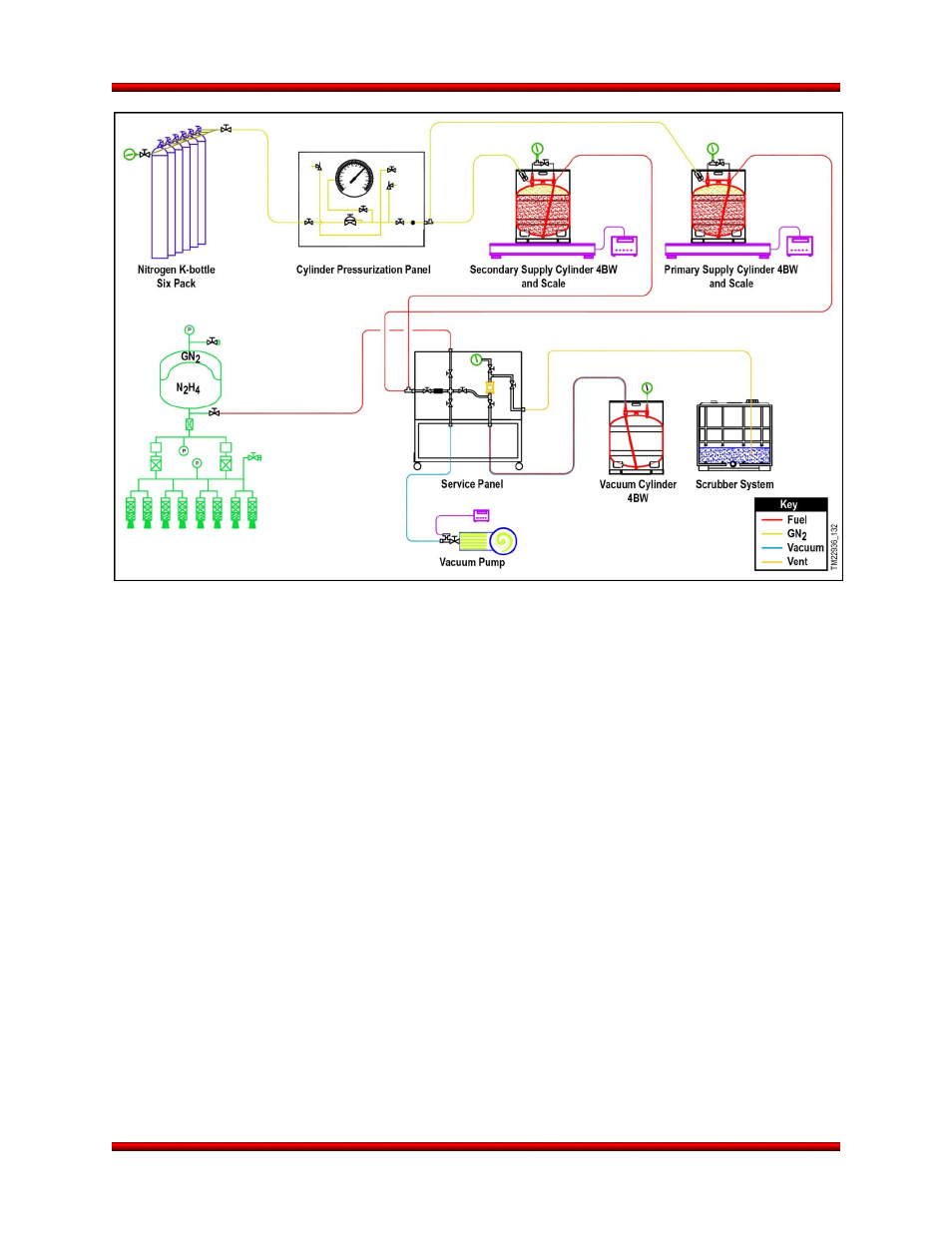
Figure 8.15-1. Typical Propellant Loading Schematic
8.17. Poly-Pico Orbital Deployer (P-POD)
Orbital offers to fly a single P-POD canister mounted to the Stage 2 motor as an enhanced Antares ser-
vice for 120 or 130 configurations. For this service, Orbital provides all required hardware to mount the
canister to the motor, monitor the P-POD door status throughout the mission, and provide two (redun-
dant) electrical pulses to initiate the door actuator, enabling the CubeSats to be ejected after the primary
payload is deployed. This enhancement also includes the necessary mission integration support as well
as required documentation and verification of the interface as part of the vehicle processing.
This enhancement can be exercised multiple times to support multiple P-POD canisters. The maximum
number of canisters is determined on a mission-specific basis.
8.18. Suborbital Performance
Suborbital Performance enhancements will be designed on a mission specific basis.
8.19. Alternate Launch Locations
For missions requiring greater performance to high inclination orbits, Orbital offers the KLC in Kodiak,
Alaska as an alternate Antares launch site. The performance associated with launches from KLC is in-
cluded in Section 3.4. Orbital designed the Antares launch systems for compatibility with multiple ranges,
including KLC, and has been working with the Alaska Aerospace Corporation (AAC) for two years on the
design, siting, and logistic support of an Antares launch pad in Alaska. AAC and their construction man-
agement personnel have been to the Antares Wallops launch site to finalize the Antares requirements for
Alaska. The key lessons learned from Orbital’s WFF pad construction are being incorporated into the
Antares launch site design in Alaska. Orbital provides recent and relevant capabilities to support Antares
