Driveline clamp cone yoke operating instructions, Blade servicing, Maintenance – Alamo FC-0016 User Manual
Page 148
MAINTENANCE
A96B 03/06
Maintenance Section 5-6
© 2006 Alamo Group Inc.
MAINTENANCE
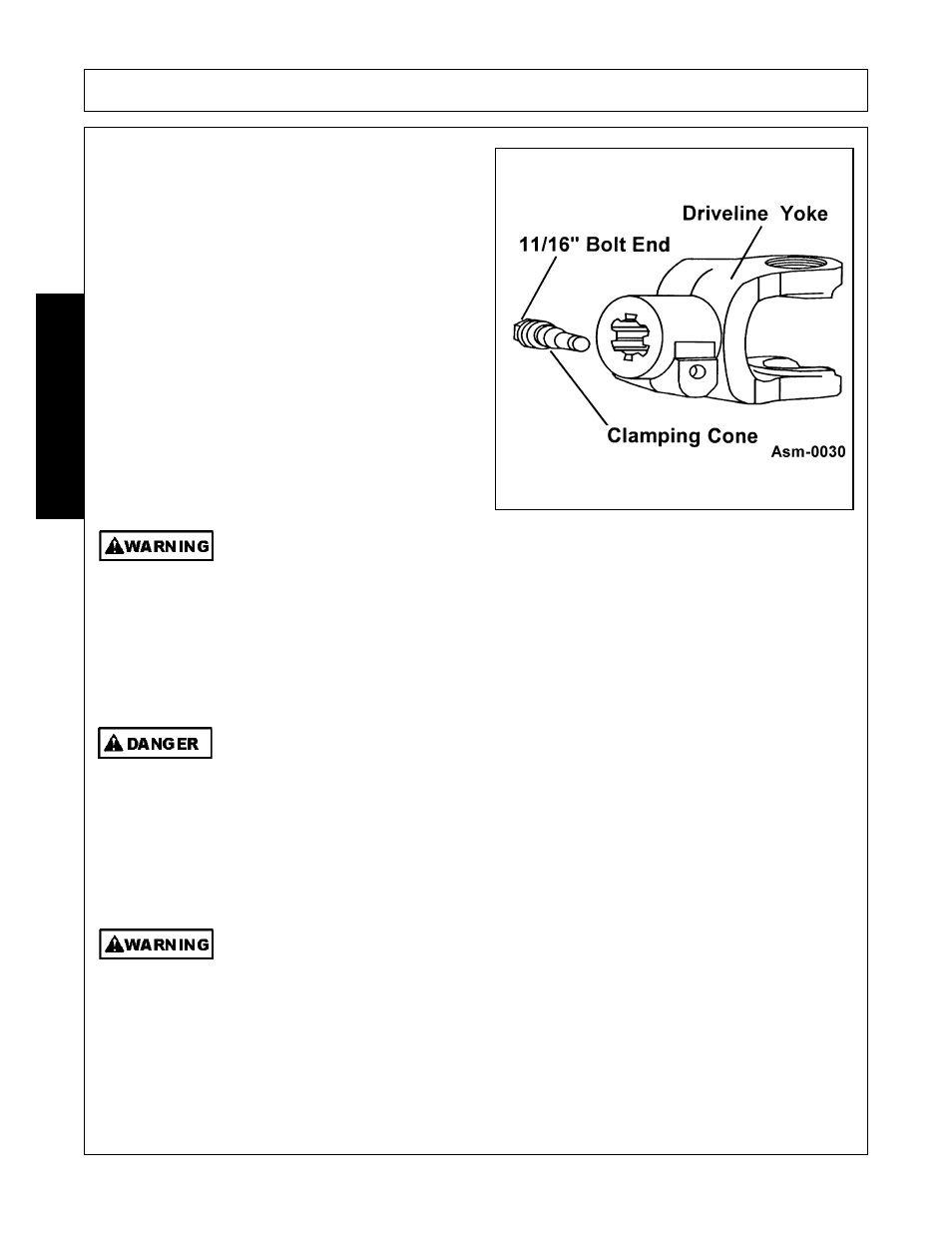
DRIVELINE CLAMP CONE YOKE
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Loosen the yoke clamp cone with a 11/16” (17mm)
wrench and remove the cone from yoke. Slide yoke onto
the shaft and align hole for clamping cone with annular
groove of gearbox shaft. Reinstall cone and tighten
(75lb-ft. torque). Push and pull the driveline to ensure it
is securely attached to the shaft. Regularly check the
driveline yoke to ensure a tight connection. To remove
the yoke, remove the connecting cone and pull yoke off
the shaft. If the cone cannot be easily removed by hand,
drive it out from the other side using a hammer and
punch.
NOTE: The clamping cone is serviced only as a
complete assembly. Do not attempt to disassemble the
clamping cone.
When attaching PTO yoke to tractor PTO shaft, it is important that spring-activated locking
collar slides freely and locking balls are seated in groove on PTO shaft. A loose shaft could
slip off and result in personal injury or damage to cutter.
BLADE SERVICING
Inspect blades before each use to determine that they are properly installed and in good condition. Replace
any blade that is bent, excessively nicked, worn, or has any other damage. Small nicks can be ground out
when sharpening.
Replace bent or broken blade with new blades. NEVER ATTEMPT TO STRAIGHTEN OR
WELD ON BLADES SINCE THIS WILL LIKELY CRACK OR OTHERWISE DAMAGE THE
BLADE WITH SUBSEQUENT FAILURE AND POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY FROM
THROWN BLADES.
(SGM-10)
IMPORTANT! When sharpening blades, grind each blade the same amount to maintain balance. The
difference in blade weights should not exceed 1 ounce. Unbalanced blades will cause excessive vibration
which can damage gear box bearings. Vibration may also cause structural cracks in cutter housing.
Use only original equipment blades on this cutter. They are made of special heat-treated
alloy steel. Substitute blades may not meet specifications and may fail in a hazardous
manner that could cause injury.
