Driver valve, Switch closed, Switch open – High Country Tek emc-3L User Manual
Page 99
SUPPLY
-
+
COIL
VALVE
POWER
DRIVER
VALVE
+POWER
+COIL
-COIL
PWR COM
SWITCH
PWM
DIODE
SWITCH CLOSED
CURRENT
+
-
FIG. 2
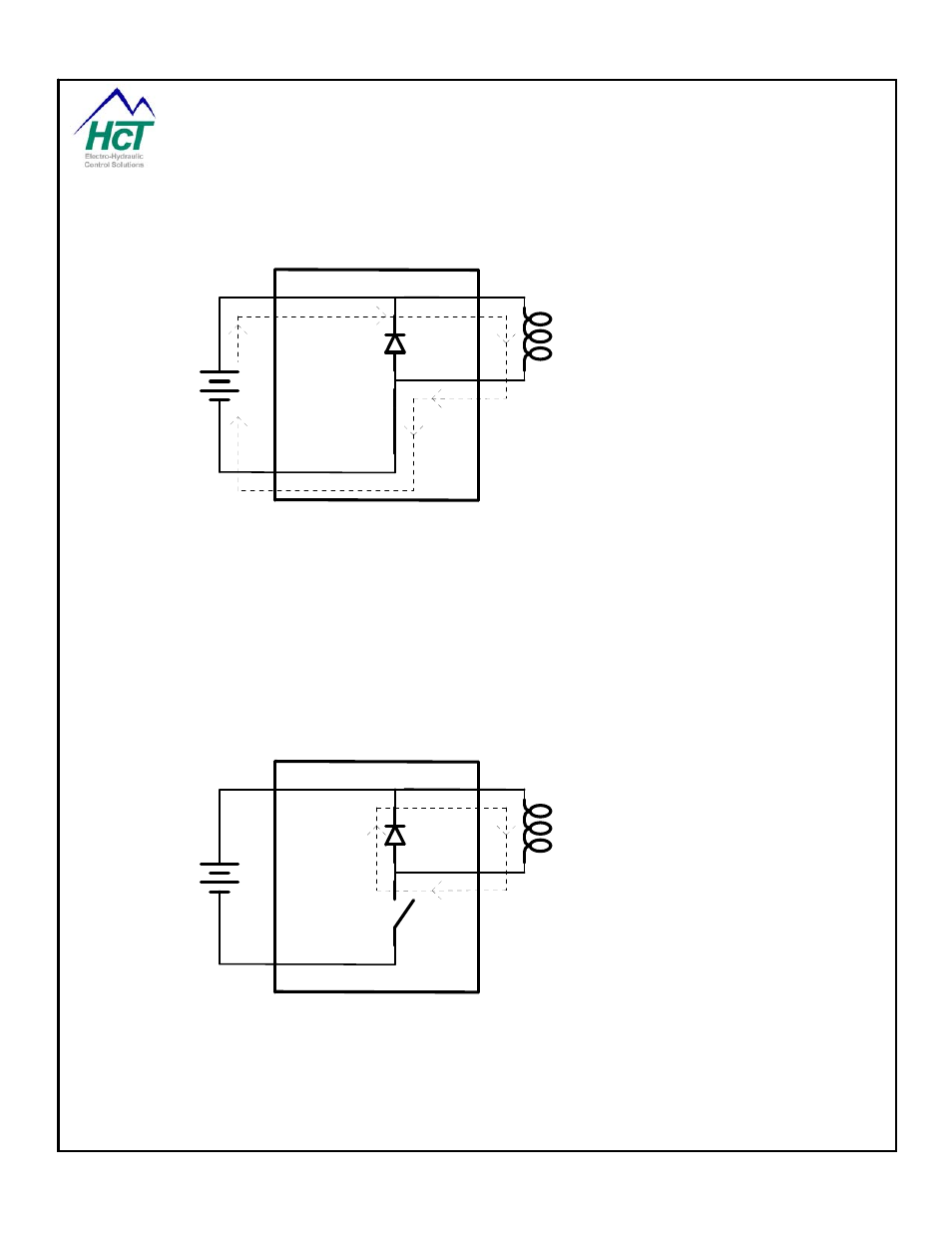
A simplified explanation of coil inductance is required to explain the preceding sentence. The coil's magnetic
field stores more energy as the current increases, much as a flywheel stores mechanical energy as the
rotational speed increases. Inductance is the measure of the electrical inertia that acts to oppose increasing or
decreasing the coil current. PWM takes advantage of this inductive effect by switching power to the coil on and
off. When the valve driver's switch (PWM switch) is closed, full power supply voltage appears across the coil
and attempts to increase the current flow to the maximum (FIG. 2). The coil prevents an instant change in
current by appearing to have a larger resistance than it really does. This resistance decreases with time, so the
current increases as long as the switch is closed. This continues until the rated current of the coil is reached, or
the switch is opened. When the valve driver opens the switch the coil will attempt to maintain its current flow.
SUPPLY
-
+
COIL
VALVE
POWER
DRIVER
VALVE
+POWER
+COIL
-COIL
PWR COM
SWITCH
PWM
DIODE
SWITCH OPEN
CURRENT
+
-
FIG. 3
The coil reverses its voltage, acts as a generator and drives its current through the diode (called a fly back
diode) (FIG. 3). The diode requires a voltage of about -0.5 volts to make this current flow. The direction of
current flow through the coil does not reverse. The current flows out of the low side of the coil through the
diode. The current decreases as long as the switch is open, with no power drawn from the power supply. The
coil current flowing through the diode provides the force required to maintain the position of the spool. The
current will be almost constant if the PWM frequency is high enough. At high PWM frequencies there is not
enough time for the current to change much before the switch changes state again, and reverses the last
change. The average value of coil current is relative to the PWM duty cycle, i.e. proportional to the time the
P/N: 021-00163, Rev. A.0 - for V5.2 Tools
Page | 99
