Raid 6—advanced data guarding, Comparison of raid methods, Parity information (px,y)(qx,y) – HP StorageWorks 1510i Modular Smart Array User Manual
Page 89: 5 raid 5 features, 6 raid 6 (adg) features
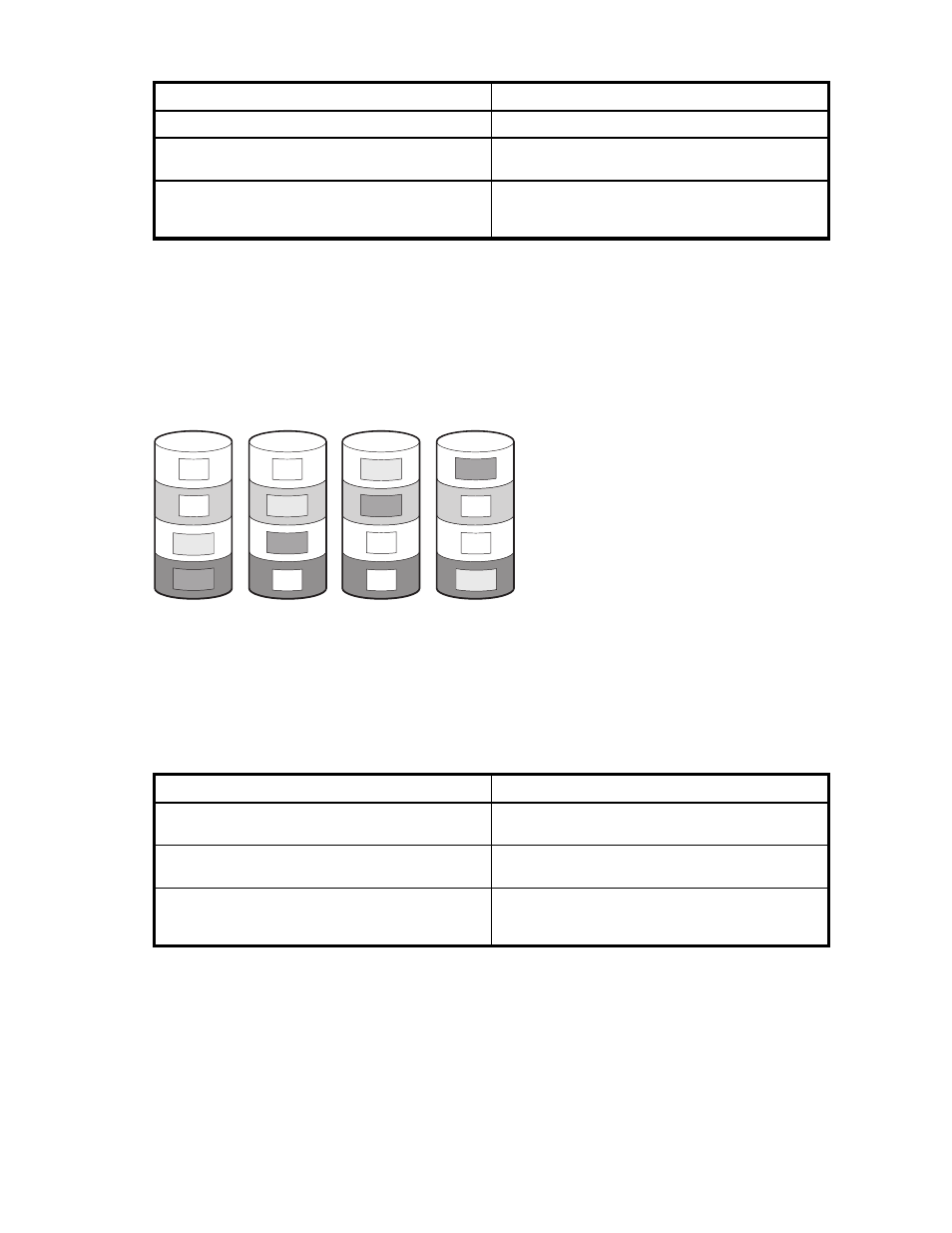
Table 5 RAID 5 features
Advantages
Disadvantages
High read performance.
Relatively low write performance.
No loss of data if one physical drive fails.
Loss of data if a second drive fails before data from
the first failed drive is rebuilt.
More usable drive capacity than RAID 1+0, because
parity information requires the storage space
equivalent to one physical drive.
RAID 6—advanced data guarding
RAID 6 (also called RAID ADG) is similar to RAID 5, because both methods generate and store parity
information to protect against data loss caused by drive failure. With RAID 6, however, two different
sets of parity data are distributed across the physical drives, allowing data to be preserved even if
two drives fail. Each set of parity data uses up a capacity equivalent to that of one of the constituent
drives, as shown in
B1
B3
P5,6
Q7,8
D1
D2
D3
D4
B2
B7
P3,4
Q5,6
B5
B8
P1,2
Q3,4
B4
B6
P7,8
Q1,2
15317
Figure 22 RAID 6 (ADG) array, with four physical hard drives (D1, D2, D3, D4) showing
distributed parity information (Px,y)(Qx,y)
This method is most useful when data loss is unacceptable, but cost is also an important factor. The
probability that data loss will occur when arrays are configured with RAID 6 (ADG) is less than when they
are configured with RAID 5.
Table 6 RAID 6 (ADG) features
Advantages
Disadvantages
High read performance.
Relatively low write performance (lower than RAID 5),
because of the need to create two sets of parity data.
High data availability—Any two drives can fail
without loss of critical data.
More drive capacity is usable than with RAID
1+0—Parity information requires only the storage
equivalent to two physical drives.
Comparison of RAID Methods
summarizes important features of the different RAID levels.
HP Storage Management Utility user guide
89
