A storage overview, Arrays and logical drives, Storage overview – HP StorageWorks 1510i Modular Smart Array User Manual
Page 85
A Storage overview
• Arrays and logical drives
• Fault-tolerance levels
• Comparison of RAID Methods
• Choosing a RAID level
Arrays and logical drives
The capacity and performance of a single physical hard drive is adequate for home users. However,
business users demand higher storage capacities, higher data transfer rates, and greater protection
against data loss when a hard drive fails.
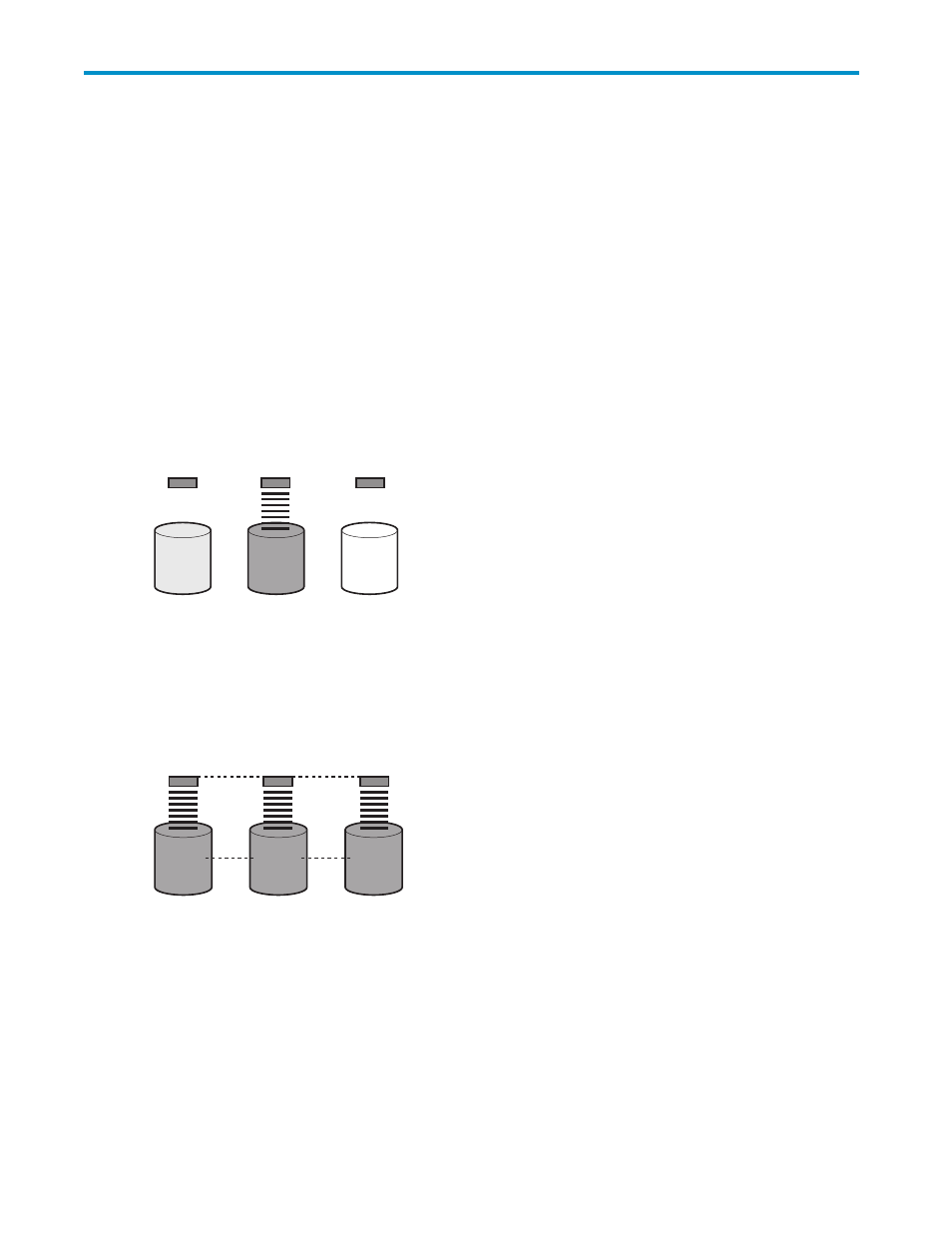
Connecting extra physical drives to a system increases the total storage capacity (
), but has
no effect on the efficiency of read/write operations. Data is still transferred to only one physical drive
at a time.
R/W
D1
D2
D3
15310
Figure 15 Multiple physical drives (D1, D2, and D3) in a system
An array controller combines several physical drives into one or more virtual units called logical drives,
which have superior performance, capacity, and/or fault tolerant features than separate physical drives.
The read/write heads of all included physical drives are active simultaneously, reducing the total time
required for data transfer.
L1
R/W
D1
D2
D3
15311
Figure 16 Multiple physical drives (D1, D2, and D3) configured into one logical drive (L1)
Because the read/write heads are active simultaneously, the same amount of data is written to each drive
during any given time interval. Each unit of data is called a block, and adjacent blocks form a set of
data stripes across all physical drives in that logical drive (
).
HP Storage Management Utility user guide
85
