Raid 5—distributed data guarding, Information (px,y), 4 raid 1, raid 1+0 features – HP StorageWorks 1510i Modular Smart Array User Manual
Page 88: Figure 20
S1
S2
S1
S2
D1
D5
B5
B1
B1
B5
D2
D6
B6
B2
B2
B6
D3
D7
B7
B3
B3
B7
D4
D8
B8
B4
B4
B8
15315
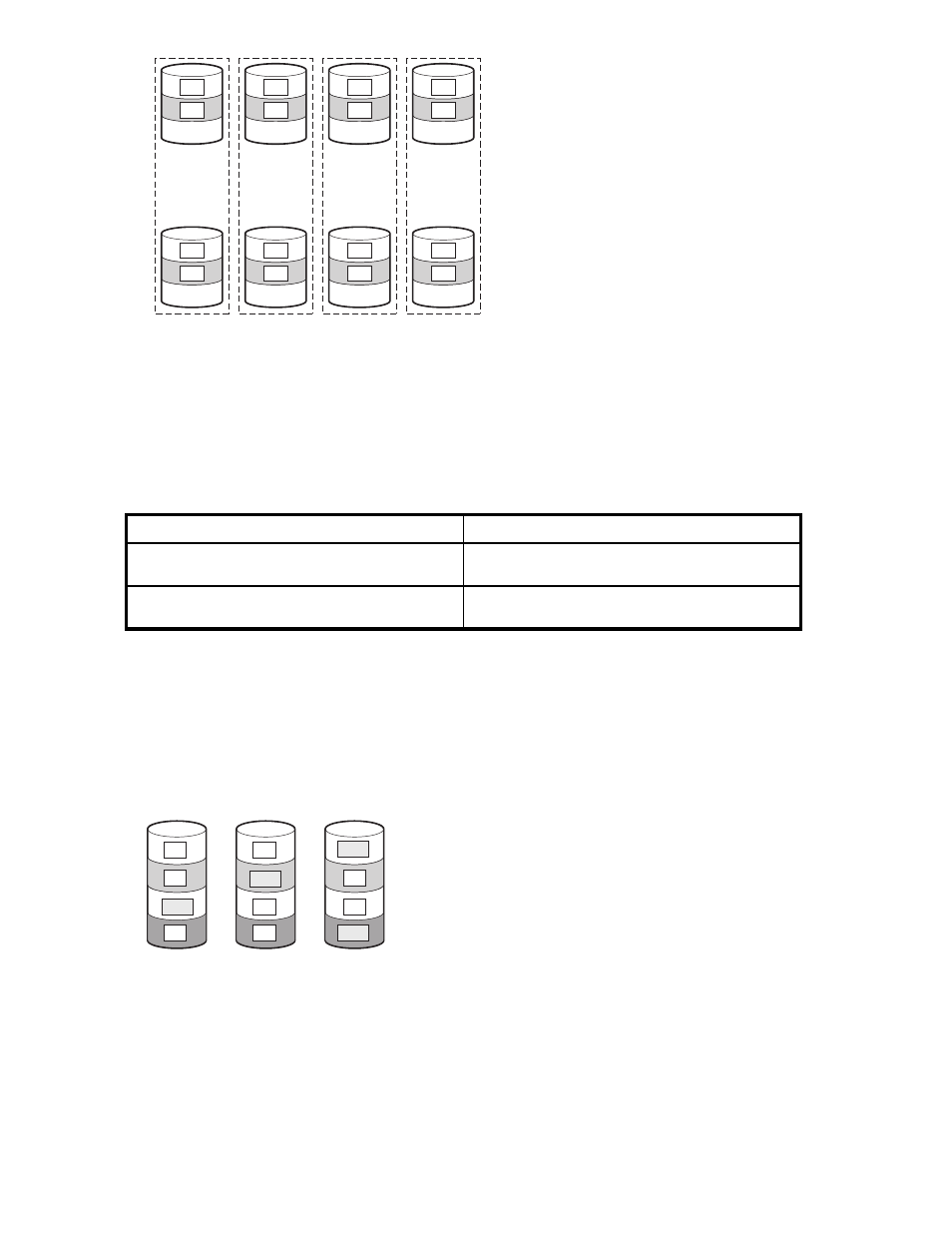
Figure 20 RAID 1+0 array, with eight physical hard drives (D1 through D8)
In each mirrored pair, the physical drive that is not busy answering other requests answers any read
request sent to the array. (This behavior is called load balancing.) If a physical drive fails, the remaining
drive in the mirrored pair can still provide all the necessary data. Several drives in the array can fail
without incurring data loss, as long as no two failed drives belong to the same mirrored pair.
RAID 1+0 is useful when high performance and data protection are more important than the cost of
physical drives.
Table 4 RAID 1, RAID 1+0 features
Advantages
Disadvantages
Highest read and write performance of any
fault-tolerant configuration.
Expensive (half of the drives are used for fault
tolerance).
No loss of data as long as no failed drive is mirrored
to another failed drive.
Only half of total drive capacity usable for data
storage.
RAID 5—distributed data guarding
In this method, a block of parity data is calculated for each stripe from the data that is in all other blocks
within that stripe. The blocks of parity data are distributed across every physical drive within the logical
drive (
). When a physical drive fails, data that was on the failed drive can be calculated from
the data on the remaining drives and the parity data. This recovered data is written to the assigned spare
or to a replacement drive in a process called a rebuild.
S1
S2
S3
S4
B1
B3
P5,6
P3,4
P1,2
P7,8
B7
D1
D2
D3
B2
B5
B8
B4
B6
15316
Figure 21 RAID 5 array, with three physical hard drives (D1, D2, D3) showing
distributed parity information (Px,y)
This configuration is useful when cost, performance, and data availability are equally important.
88
Storage overview
