Watlow CLS200, MLS300 and CAS200 User Manual
Page 57
Chapter 3: Controller Parameter Descriptions
Communications Specification 51
When using the Anafaze protocol, when an Alarm_Status bit has
changed, and there are no higher–priority status codes to return, the
controller will return an Ex (see the STS section in Chapter 1), in the
high nibble of the next communications status byte it sends to the host
software. The software should upload the Alarm_Status integers or
words for all loops to determine which alarms have changed and in
which loops.
Host software can read this parameter, but should not write to it.
NOTE
An alarm clears when its alarm condition is no longer
present. If an alarm clears, and it has not already been
acknowledged, it remains an unacknowledged alarm until
the operator acknowledges it (by pressing the controller’s
Alarm Ack key or through software).
Do not use host software to alter the status of the
Alarm_Status bits.
When Alarm_Status Trips
An alarm trips only if the Alarm_Mask bit, Alarm_Enable bit, and the
alarm condition are all TRUE. For example, the high process alarm trips
if the Alarm_Mask bit and Alarm_Enable bit are all true, and the process
exceeds the high process alarm setpoint value.
When Alarm_Status Clears
An alarm clears when the condition that caused it clears, or when the
Alarm_Mask bit is set to FALSE. For example, the high process alarm
clears if the process goes below the high process alarm setpoint.
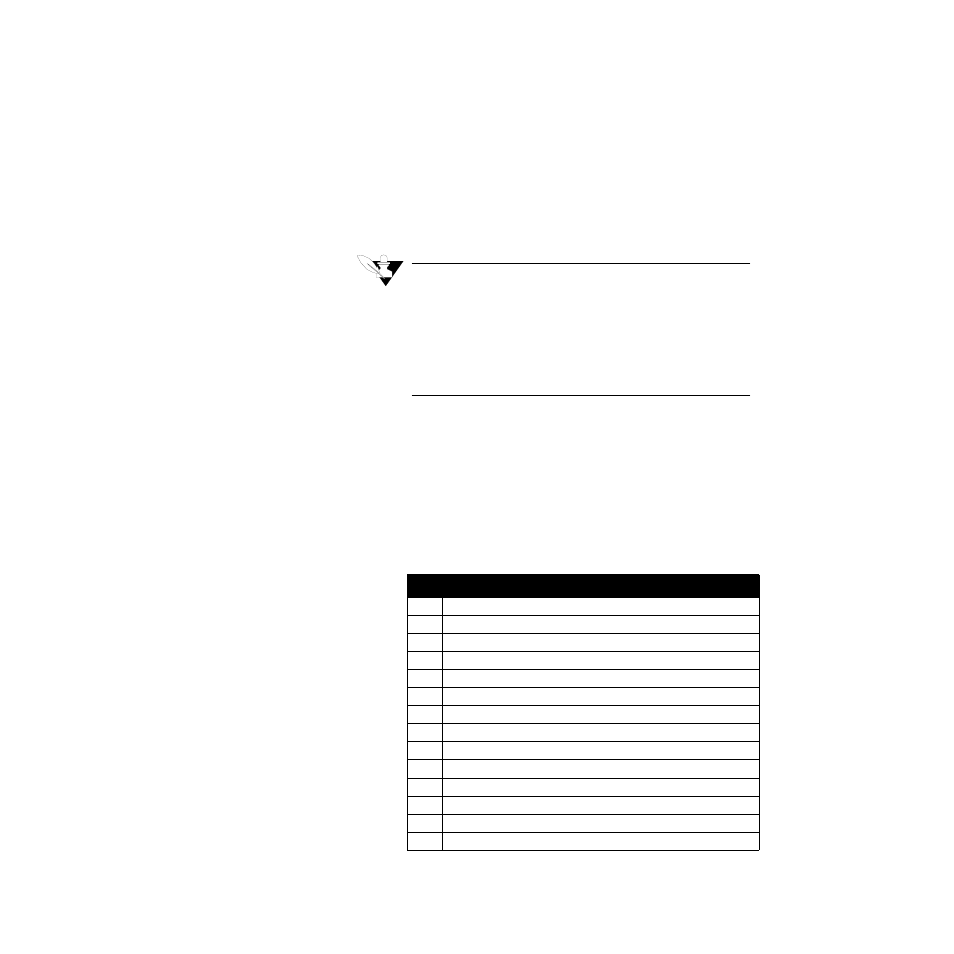
Bit
Alarm Name
0
Spare
1
Spare
2
Low deviation
3
High deviation
4
Low process
5
High process
6
T/C Reversed
7
T/C Short
8
T/C break (or open)
9
RTD open (not in 16CLS and CAS)
10
RTD short (not in 16CLS and CAS)
11
N/A
12
Ambient Warning (version 3.4 and later)
13
Ambient Cal Error
