Packet format, Sending control codes, Sending a dle as data – Watlow CLS200, MLS300 and CAS200 User Manual
Page 12: Codes in a packet, Dle stx, Packet format codes in a packet
6 Communications Specification
Chapter 1: ANAFAZE/AB Protocol
Packet Format
Messages are transmitted in the form of packets. Command and reply
packets specify the source and destination addresses, whether to read or
write, the block of data to read or write, etc.
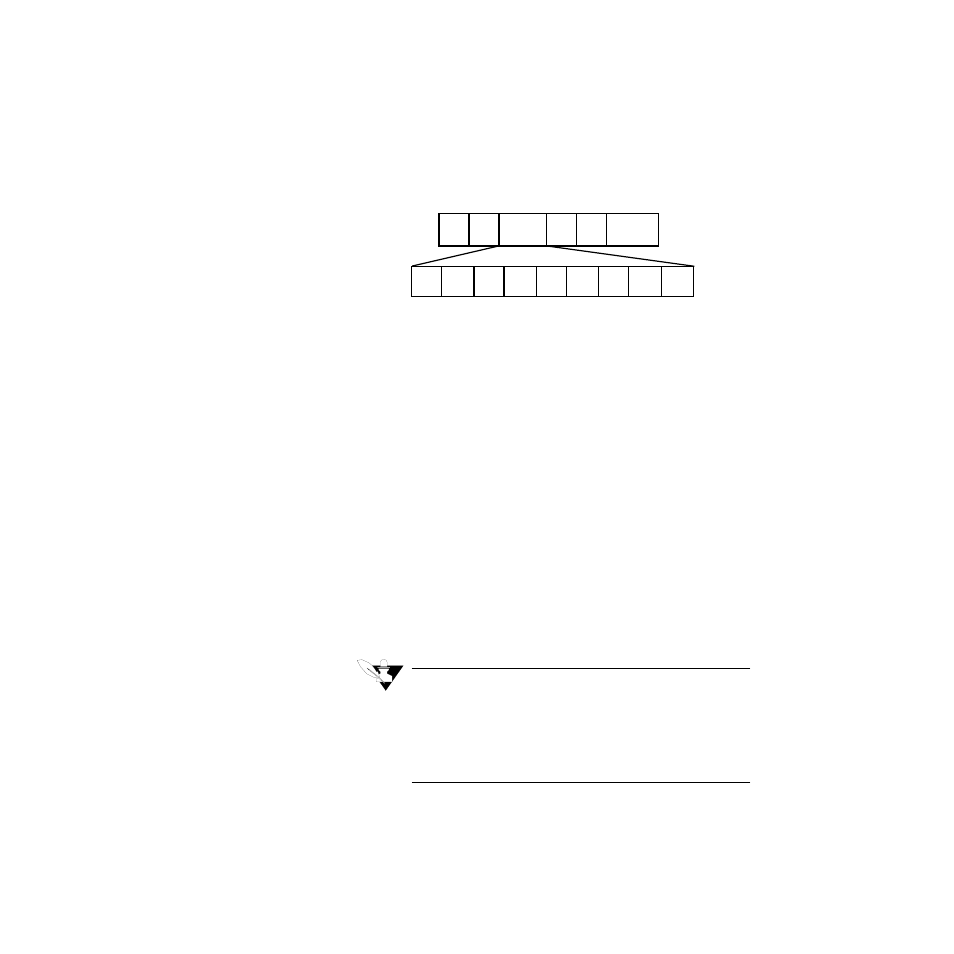
A packet contains a sequence of binary bytes formatted this way:
Sending Control Codes
To send a control code, send a DLE before the control code to
distinguish it from data.
Sending a DLE as Data
When you send a byte with an x10, (a DLE), the controller and software
interpret it as a command. Therefore, to send a DLE as data, send
another DLE immediately before it (DLE DLE).
Codes in a Packet
This section describes the sequence of bytes in a packet, in the order the
host software or controller sends them.
DLE STX
•
The DLE STX byte signals the beginning of a transmission. Every
packet of information starts with the control codes DLE STX.
DST
•
The DST byte is the address of the destination device (usually a con-
troller; the first Watlow Anafaze controller is at x08).
NOTE
When host software communicates with an MLS, a CLS, or
a CAS in ANAFAZE or AB protocol, it does not send the
controller’s actual address. Since the protocol reserves
device addresses 0 to 7, the host software sends the value
(controller address + 7), instead of the actual device
address.
SRC
•
The SRC byte is the device address of the packet’s source. The host
software is usually designated address x00.
DLE
STX
DLE
ETX
BCC/CRC
DST
SRC
CMD
STS
TNSL
TNSH
ADDL ADDH
DATA
