Modbus-rtu data table summary – Watlow CLS200, MLS300 and CAS200 User Manual
Page 39
Chapter 2: Modbus-RTU Protocol
Communications Specification 33
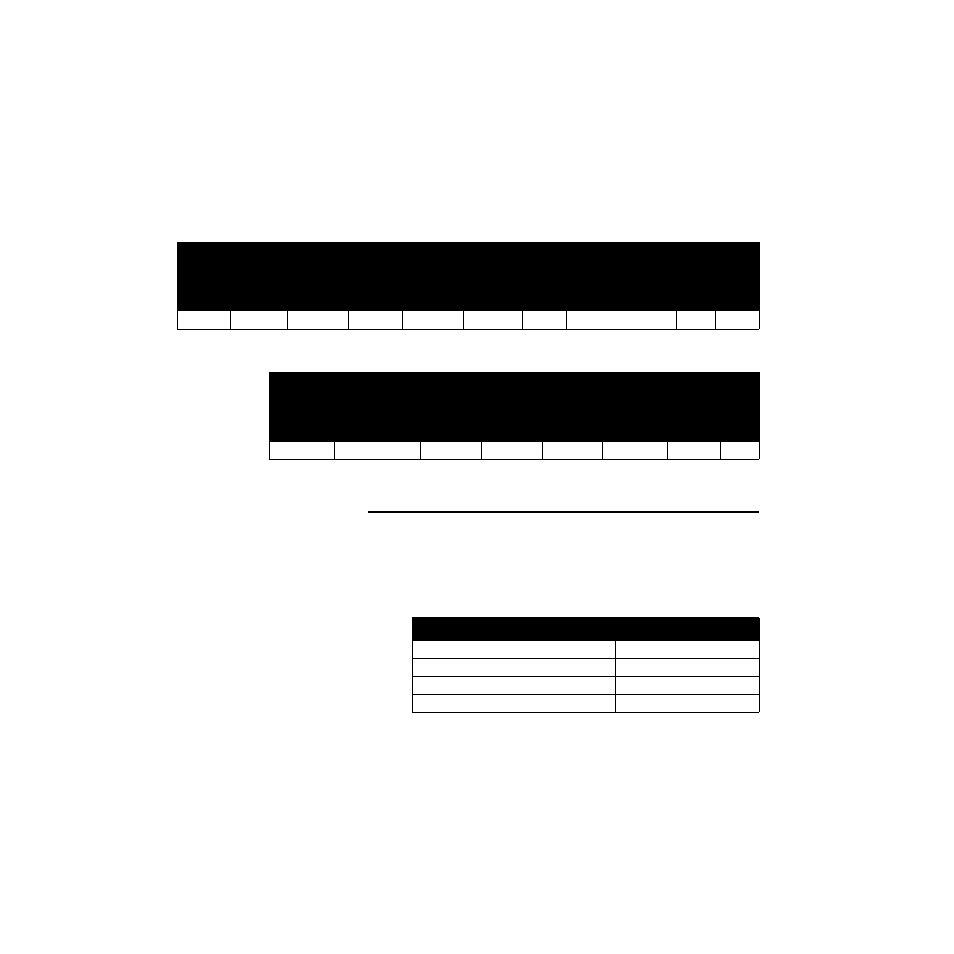
Sample Packet for Host Transmission, a Multipoint Write
The data must be written to sequential locations.
Helpful hint: The string is longer for multiple write; checking the
BYTE COUNT can help in determining if a command timeout is valid.
Example 6: Writing TI loops 3 (100) and 4 (150), controller
10.
Sample Packet for Slave Transmission, a multipoint write.
Modbus-RTU Data Table Summary
Each addressable register holds two bytes of data. Each parameter value
requires only one register to store any of these types of data. The data
type for each parameter is indicated in the tables on the following pages.
Because each loop is individually configurable, the number of instances
of many parameters depends on the number of loops in the controller.
Therefore, the number of registers for these parameters is listed in the
tables on the following pages in terms of the number of loops in the
controller.
Slave
Address
in Hex
Function
in Hex
Address
High
in Hex
Address
Low
in Hex
Number
of
Registers
High
in Hex
Number
of
Registers
Low
in Hex
Byte
Count
in Hex
Data
in Hex
CRC
High
in
Hex
CRC
Low
in Hex
0A
10
00
86
00
02
04
00 64 00 96
9F
70
Slave
Address
in Hex
Function
in Hex
Address
High
in Hex
Address
Low
in Hex
Number
of
Registers
High
in Hex
Number of
Registers
Low
in Hex
CRC
High
in Hex
CRC
Low
in
Hex
0A
10
00
86
00
02
A1
5A
Data Type and Symbol
Data Size
Unsigned char (UC)
1 byte
Signed char (SC)
1 byte
Unsigned int (UI)
2 bytes
Signed int (SI)
2 bytes
