Attiny26(l) – Rainbow Electronics ATtiny26L User Manual
Page 72
72
ATtiny26(L)
1477B–AVR–04/02
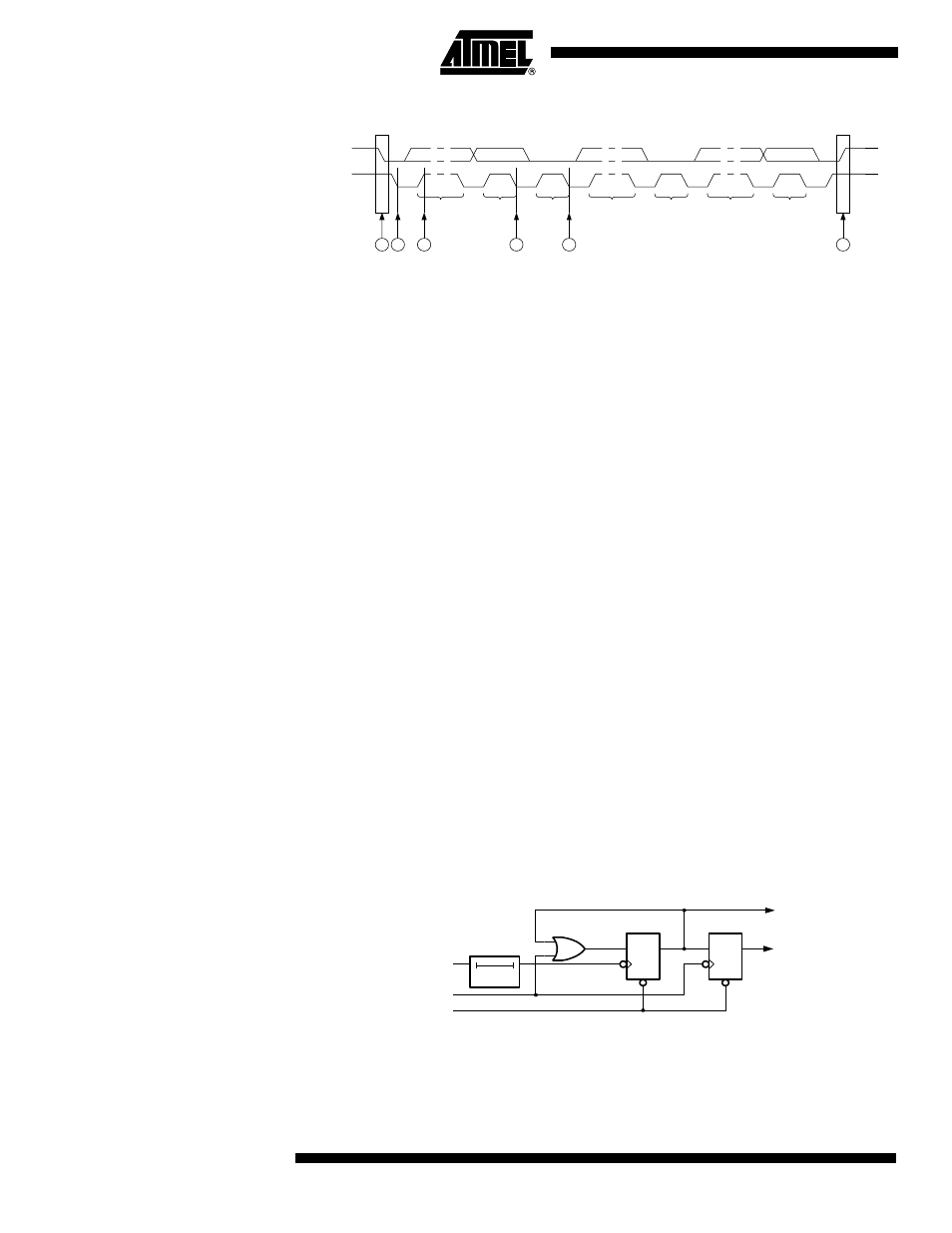
Figure 43. Two-wire Mode, Typical Timing Diagram
Referring to the timing diagram (Figure 43.), a bus transfer involves the following steps:
1.
The a start condition is generated by the master by forcing the SDA low line
while the SCL line is high (A). SDA can be forced low either by writing a zero to
bit 7 of the Shift Register, or by setting the PORTB0 bit to zero. Note that DDRB0
must be set to one for the output to be enabled. The slave device’s start detector
logic (Figure 44.) detects the start condition and sets the USISIF flag. The flag
can generate an interrupt if necessary.
2.
In addition, the start detector will hold the SCL line low after the master has
forced an negative edge on this line (B). This allows the slave to wake up from
sleep or complete its other tasks, before setting up the Shift Register to receive
the address by clearing the start condition flag and reset the counter.
3.
The master set the first bit to be transferred and releases the SCL line (C). The
slave samples the data and shift it into the serial register at the positive edge of
the SCL clock.
4.
After eight bits are transferred containing slave address and data direction (read
or write), the slave counter overflows and the SCL line is forced low (D). If the
slave is not the one the master has addressed it releases the SCL line and waits
for a new start condition.
5.
If the slave is addressed it holds the SDA line low during the acknowledgment
cycle before holding the SCL line low again (i.e., the Counter Register must be
set to 14 before releasing SCL at (D)). Depending of the R/W bit the master or
slave enables its output. If the bit is set, a master read operation is in progress
(i.e., the slave drives the SDA line) The slave can hold the SCL line low after the
acknowledge (E).
6.
Multiple bytes can now be transmitted, all in same direction, until a stop condition
is given by the master (F). Or a new start condition is given.
If the slave is not able to receive more data it does not acknowledge the data byte it has
last received. When the master does a read operation it must terminate the operation by
force the acknowledge bit low after the last byte transmitted.
Figure 44. Start Condition Detector, Logic Diagram
P
S
ADDRESS
1 - 7
8
9
R/W
ACK
ACK
1 - 8
9
DATA
ACK
1 - 8
9
DATA
SDA
SCL
A
B
D
E
C
F
SDA
SCL
Write( USISIF)
CLOCK
HOLD
USISIF
D Q
CLR
D Q
CLR
