Table 126 firmware specifications – ZyXEL Communications V501-T1 User Manual
Page 236
Appendix A Product Specifications
V500 Series User’s Guide
236
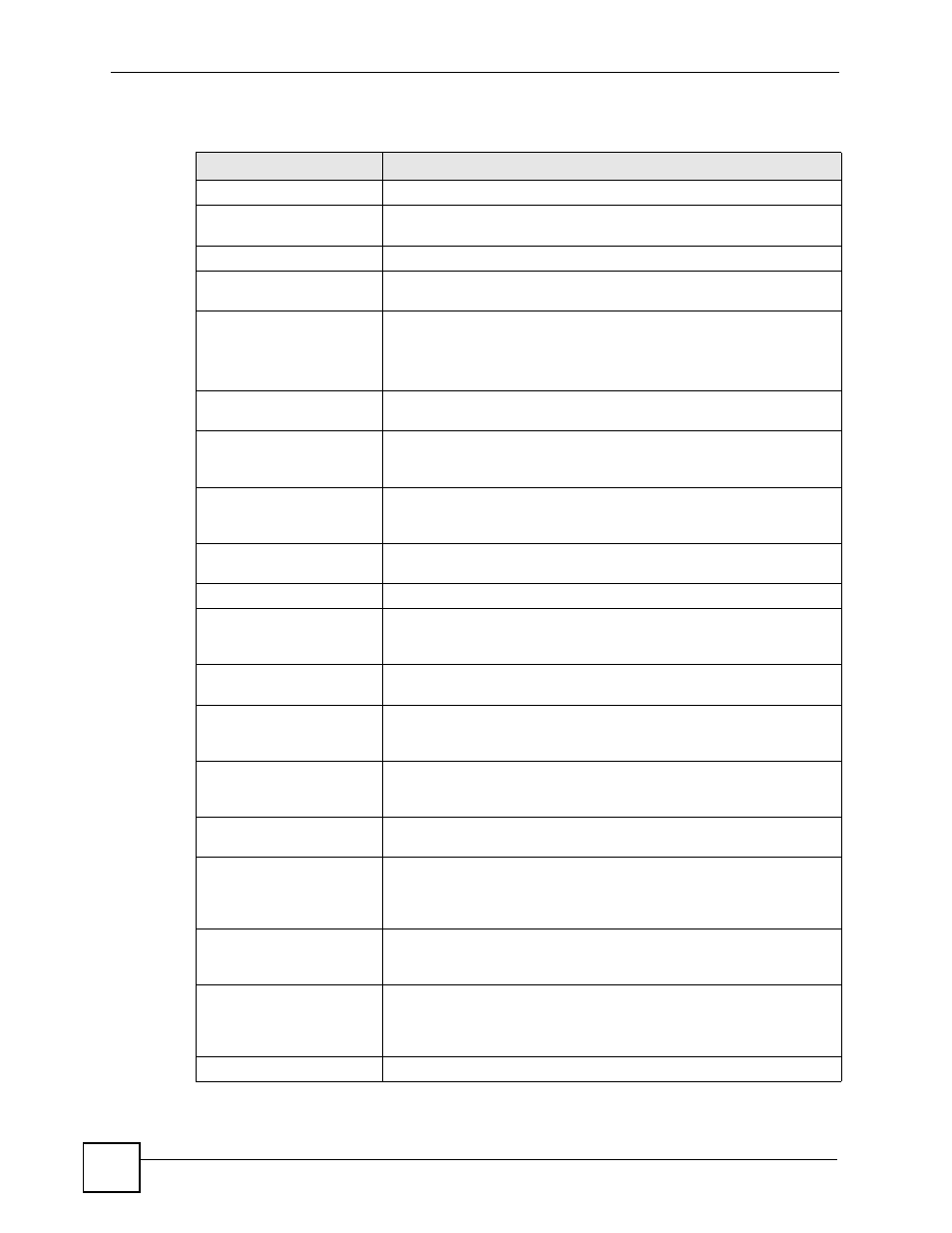
Table 126 Firmware Specifications
FEATURE
DESCRIPTION
Default DHCP status
Client
Default management IP
address
192.168.5.1
Default Password
1234
Device Management
Use the V500’s LCD screen menus or the web configurator to easily
configure the rich range of features.
Firmware Upgrade
Download new firmware (when available) from the ZyXEL web site and
use the web configurator, an FTP or a TFTP tool to put it on the V500.
Note: Only upload firmware for your specific model!
Configuration Backup &
Restoration
Make a copy of the V500’s configuration. You can put it back on the
V500 later if you decide to revert back to an earl
i
er configuration.
Network Address
Translation (NAT)
Each computer on your network must have its own unique IP address.
Use NAT to convert your public IP address(es) to multiple private IP
addresses for
the computers on your network.
Time and Date
Get the current time and date from an external server when you turn on
your V500. You can also set the time manually. These dates and times
are then used in logs.
Logging and Tracing
Use packet tracing and logs for troubleshooting. You can send logs from
the V500 to an external syslog server.
PPPoE
PPPoE mimics a dial-up Internet access connection.
Remote Management
This allows you to decide whether a service (HTTP or FTP traffic for
example) from a computer on a network (LAN or WAN for example) can
access the V500.
Embedded FTP and TFTP
Servers
The embedded FTP and TFTP servers enable fast firmware upgrades
as well as configuration file backups and restoration.
Auto-provisioning support
When auto-provisioning is used, the V500 downloads its settings
automatically from the auto-provisioning server, meaning you do not
have to input them manually.
Dynamic Jitter Buffer
The built-in adaptive buffer helps to smooth out the variations in delay
(jitter) for voice traffic. This helps ensure good voice quality for your
conversations.
Voice Activity Detection/
Silence Suppression
Voice Activity Detection (VAD) reduces the bandwidth that a call uses by
not transmitting when you are not speaking.
Comfort Noise Generation
Your device generates background noise to fill moments of silence when
the other device in a call stops transmitting because the other party is
not speaking (as total silence could easily be mistaken for a lost
connection).
Echo Cancellation
You device supports G.168, an ITU-T standard for eliminating the echo
caused by the sound of your voice reverberating in the telephone
receiver while you talk.
QoS (Quality of Service)
Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms help to provide better service on a
per-flow basis. Your device supports Type of Service (ToS) tagging. This
allows the device to tag voice frames so they can be prioritized over the
network.
Voice Codecs
G.711a/u, G.722, G.722.2, G.723.1, G.726 (16/24/32/40), G.729a/b
