Troubleshooting ipsec tunnels – D-Link DFL-2500 User Manual
Page 238
•
If certificates have been used, check that the correct certificates have been used and that they
haven't expired.
•
Use ICMP Ping to confirm that the tunnel is working. With roaming clients this is best done by
Pinging the internal IP address of the local network interface on the D-Link Firewall from a
client (in LAN to LAN setups pinging could be done in any direction). If NetDefendOS is to
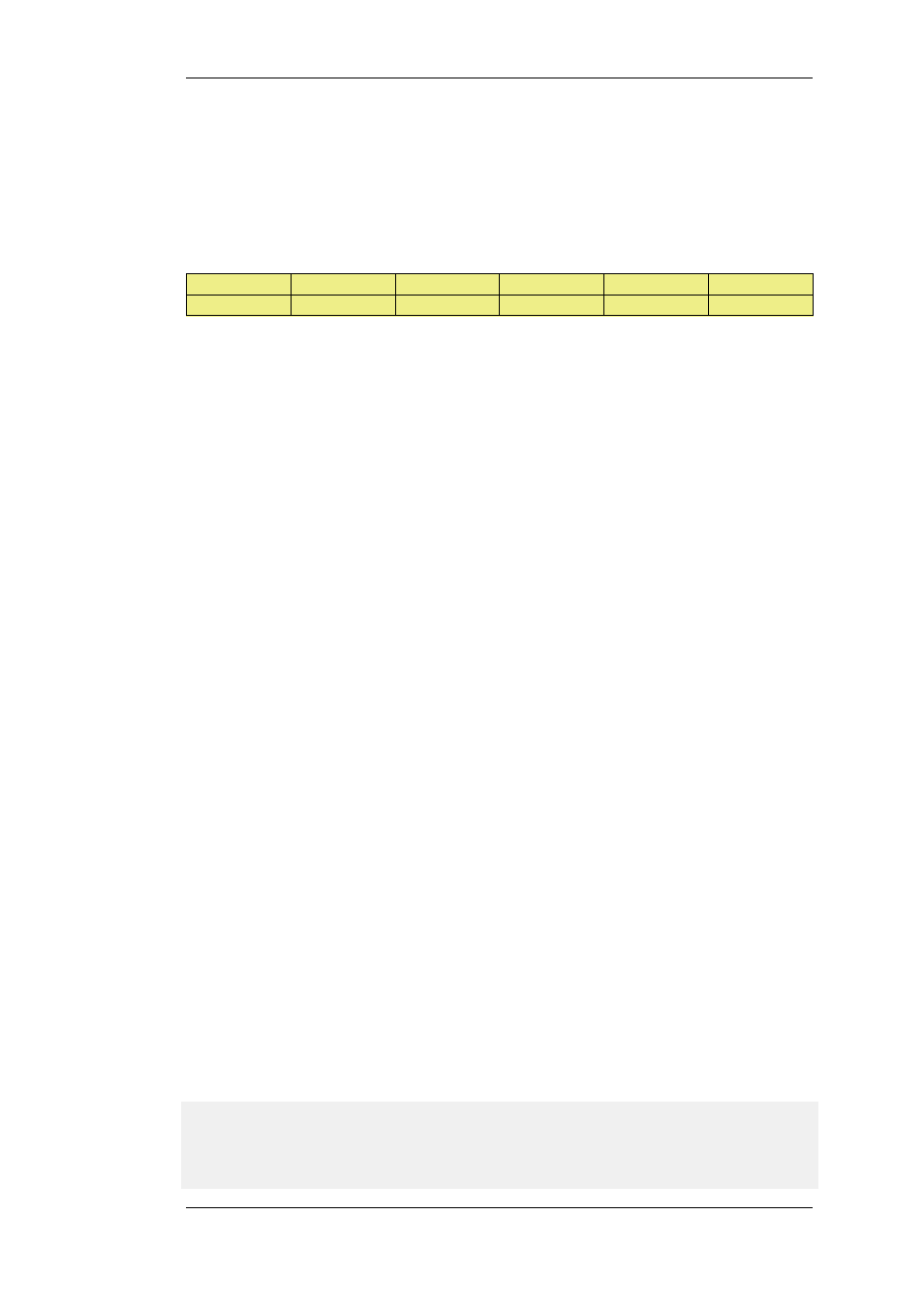
able to respond to a Ping then the following rule must exist in the IP rule set.
Action
Src Interface
Src Network
Dest Interface
Dest Network
Service
Allow
vpn_tunnel
all-nets
core
all-nets
ICMP
•
Ensure that another IPsec Tunnel definition isn't preventing the correct definition being
reached. The tunnel list is scanned from top to bottom and a tunnel in a higher position with the
Remote Network set to all-nets and the Remote Gateway set to none could prevent the correct
tunnel being reached. The symptom of this problem is often an Incorrect Pre-shared Key
message.
•
Try and avoid duplication of IP addresses between the remote network being accessed by a
client and the internal network to which a roaming client belongs.
If a roaming client becomes temporarily part of a network such as a Wi-Fi network at an airport,
the client will get an IP address from the Wi-Fi network's DHCP server. If that IP also belongs
to the network behind the D-Link Firewall accessible through a tunnel, then Windows will still
continue to assume that the IP address is to be found on the client's local network. Windows
therefore won't correctly route packets bound for the remote network through the tunnel but
instead route them to the local network.
The solution to this problem of local/remote IP address duplication is to create a new route in the
client's Windows routing table that explicitly routes the IP address to the tunnel.
•
If roaming client user authentication is not asking the users for their username/password then
ensure that the following advanced settings are enabled:
•
IPsecBeforeRules for pure IPsec roaming clients.
•
PPP_L2TPBeforeRules for L2TP roaming clients.
•
PPP_PPTPBeforeRules for PPTP roaming clients.
These settings should be enabled by default and they ensure that user authentication traffic
between NetDefendOS and the client can bypass the IP rule set. If the appropriate setting is not
enabled then an explicit rule needs to be added to the IP rule set to allow the authentication
traffic to pass between roaming clients and NetDefendOS. This rule will have a destination
interface of core.
Troubleshooting IPsec Tunnels
A number of commands can be used to diagnose IPsec tunnels:
The ipsecstat console command
ipsecstat can be used to show that IPsec tunnels have correctly established. A representative
example of output is:
> ipsecstat
--- IPsec SAs:
Displaying one line per SA-bundle
9.2.7. VPN Troubleshooting
Chapter 9. VPN
238
