Translation of multiple ip addresses (m:n) – D-Link DFL-2500 User Manual
Page 213
•
NetDefendOS translates the address in accordance with rule 1 and forwards the packet in accordance with
rule 2:
10.0.0.3:1038 => 10.0.0.2:80
•
wwwsrv processes the packet and replies:
10.0.0.2:80 => 10.0.0.3:1038
This reply arrives directly to PC1 without passing through the D-Link Firewall. This causes problems. The reason
this will not work is because PC1 expects a reply from 195.55.66.77:80, not 10.0.0.2:80. The unexpected reply is
discarded and PC1 continues to wait for a response from 195.55.66.77:80, which will never arrive.
Making a minor change to the rule set in the same way as described above, will solve the problem. In this
example, for no particular reason, we choose to use option 2:
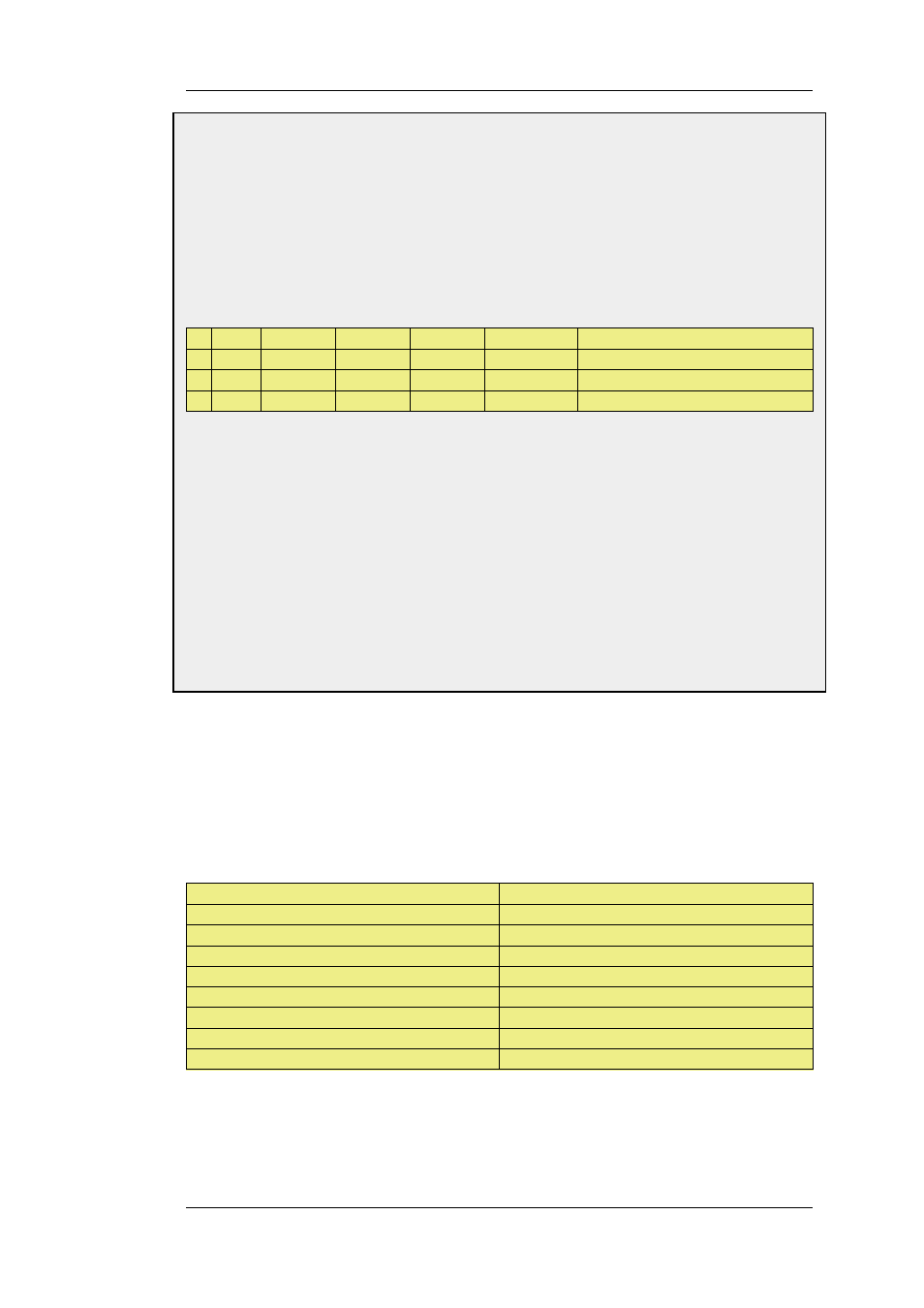
#
Action Src Iface
Src Net
Dest Iface
Dest Net
Parameters
1
SAT
any
all-nets
core
wan_ip
http SETDEST wwwsrv 80
2
NAT
lan
lannet
any
all-nets
All
3
Allow
any
all-nets
core
wan_ip
http
•
PC1 sends a packet to wan_ip to reach "www.ourcompany.com":
10.0.0.3:1038 => 195.55.66.77:80
•
NetDefendOS address translates this statically in accordance with rule 1 and dynamically in accordance with
rule 2:
10.0.0.1:32789 => 10.0.0.2:80
•
wwwsrv processes the packet and replies:
10.0.0.2:80 => 10.0.0.1:32789
•
The reply arrives and both address translations are restored:
195.55.66.77:80 => 10.0.0.3:1038
This way, the reply arrives at PC1 from the expected address.
Another possible solution to this problem is to allow internal clients to speak directly to 10.0.0.2, which would
completely avoid all the problems associated with address translation. However, this is not always practical.
7.3.2. Translation of Multiple IP Addresses (M:N)
A single SAT rule can be used to translate an entire range of IP addresses. In this case, the result is a
transposition where the first original IP address will be translated to the first IP address in the
translation list and so on.
For instance, a SAT policy specifying that connections to the 194.1.2.16/29 network should be
translated to 192.168.0.50 will result in transpositions as per the table below:
Original Address
Translated Address
194.1.2.16
192.168.0.50
194.1.2.17
192.168.0.51
194.1.2.18
192.168.0.52
194.1.2.19
192.168.0.53
194.1.2.20
192.168.0.54
194.1.2.21
192.168.0.55
194.1.2.22
192.168.0.56
194.1.2.23
192.168.0.57
In other words:
•
Attempts to communicate with 194.1.2.16 will result in a connection to 192.168.0.50.
•
Attempts to communicate with 194.1.2.22 will result in a connection to 192.168.0.56.
7.3.2. Translation of Multiple IP
Addresses (M:N)
Chapter 7. Address Translation
213
