Fortinet FortiGate 100 User Manual
Page 198
198
Fortinet Inc.
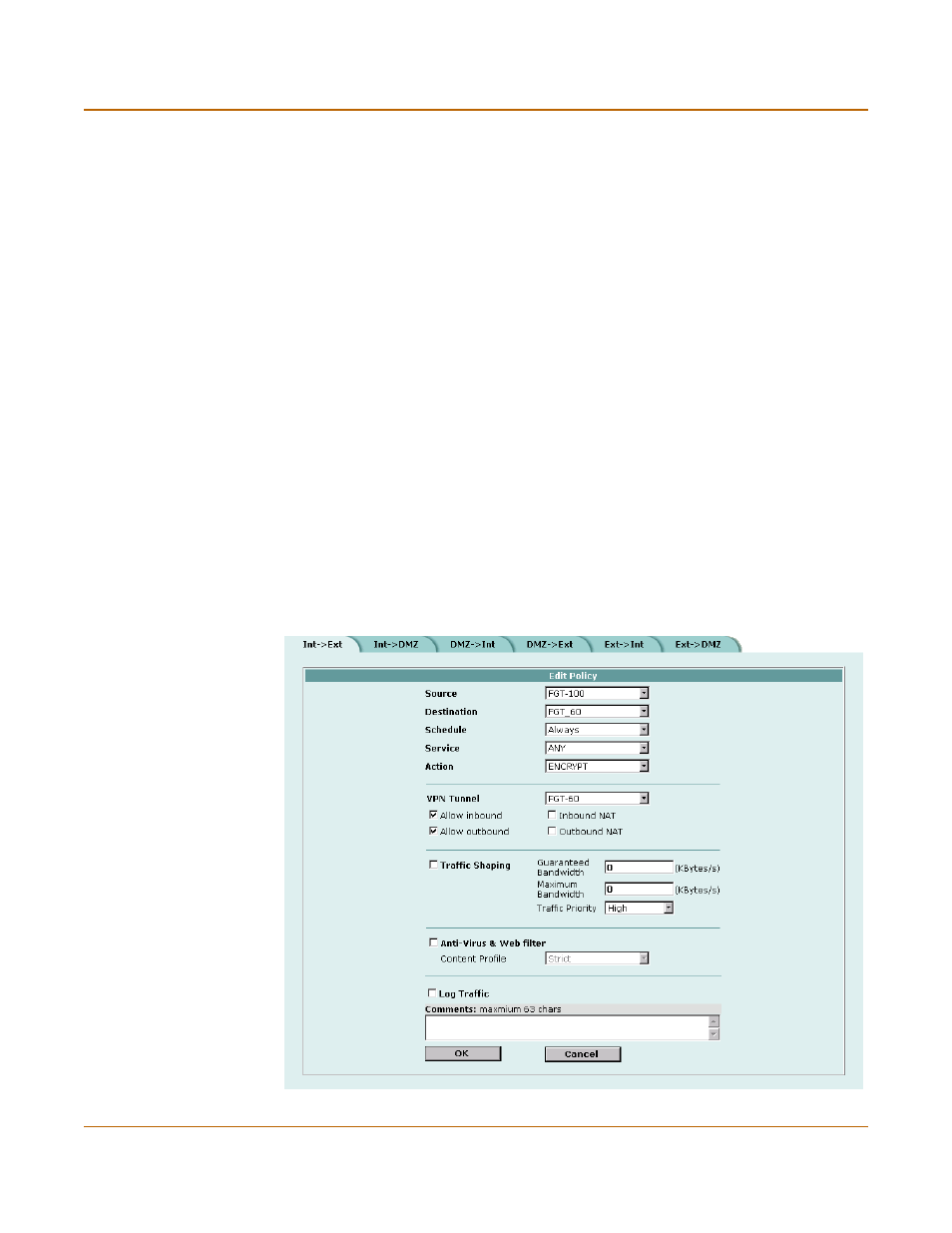
Adding an encrypt policy
IPSec VPN
Refer to the FortiGate Installation and Configuration Guide to configure the remaining
policy settings.
9
Select OK to save the encrypt policy.
To make sure that the encrypt policy is matched for VPN connections, arrange the
encrypt policy above other policies with similar source and destination addresses and
services in the policy list.
Figure 25: Adding an encrypt policy
Inbound NAT
The FortiGate unit translates the source address of incoming packets to the
IP address of the FortiGate interface connected to the source address
network. Typically, this is an internal interface of the FortiGate unit.
Inbound NAT makes it impossible for local hosts to see the IP addresses of
remote hosts (hosts located on the network behind the remote VPN
gateway).
Outbound NAT The FortiGate unit translates the source address of outgoing packets to the
IP address of the FortiGate interface connected to the destination address
network. Typically, this is an external interface of the FortiGate unit.
Outbound NAT makes it impossible for remote hosts to see the IP
addresses of local hosts (hosts located on the network behind the local VPN
gateway).
If Outbound NAT is implemented, it is subject to these limitations:
— Configure Outbound NAT only at one end of the tunnel.
— The end which does not implement Outbound NAT requires an Int->Ext
policy which specifies the other end’s external interface as the Destination.
(This will be a public IP address.)
— The tunnel, and the traffic within the tunnel, can only be initiated at the
end which implements Outbound NAT.
