Hitachi NJI-350B User Manual
Page 164
Chapter 5 Instruction Specifications
5-114
Syntax of SB n, RTS, INT n and RTI
SB 1
RTS
SB 2
RTS
RTS
RTS
RTS
SB 10
SB 11
SB 12
END
INT 1
RTI
INT 2
RTI
Program
SB n
RTS
Program
INT n
RT1
CAL 1
CAL 1
END
SB 2
CAL 1
RTS
SB 1
RTS
INI 0
CAL 1
RTI
SB 1
JMP 1
SB 2
SB 3
JMP 1
LBL 1
RTS
SB 1
JMP 1
SB 2
JMP 1
SB 3
LBL 1
RTS
INT 0
JMP 1
INT 1
INT 2
JMP 1
LBL 1
RTI
INT 0
JMP 1
INT 2
JMP 1
INT 1
RTI
SB 1
CAL 20
RTS
SB 20
CAL 30
RTS
SB 30
CAL 40
RTS
RTS
CAL 50
SB 40
SB 50
RTS
1st level 2nd level 3rd level 4th level 5th level
END
SB 20
RTS
SB 1
RTS
SB 40
RTS
SB 30
RTS
SB 50
RTS
INT 0
RTI
LBL 1
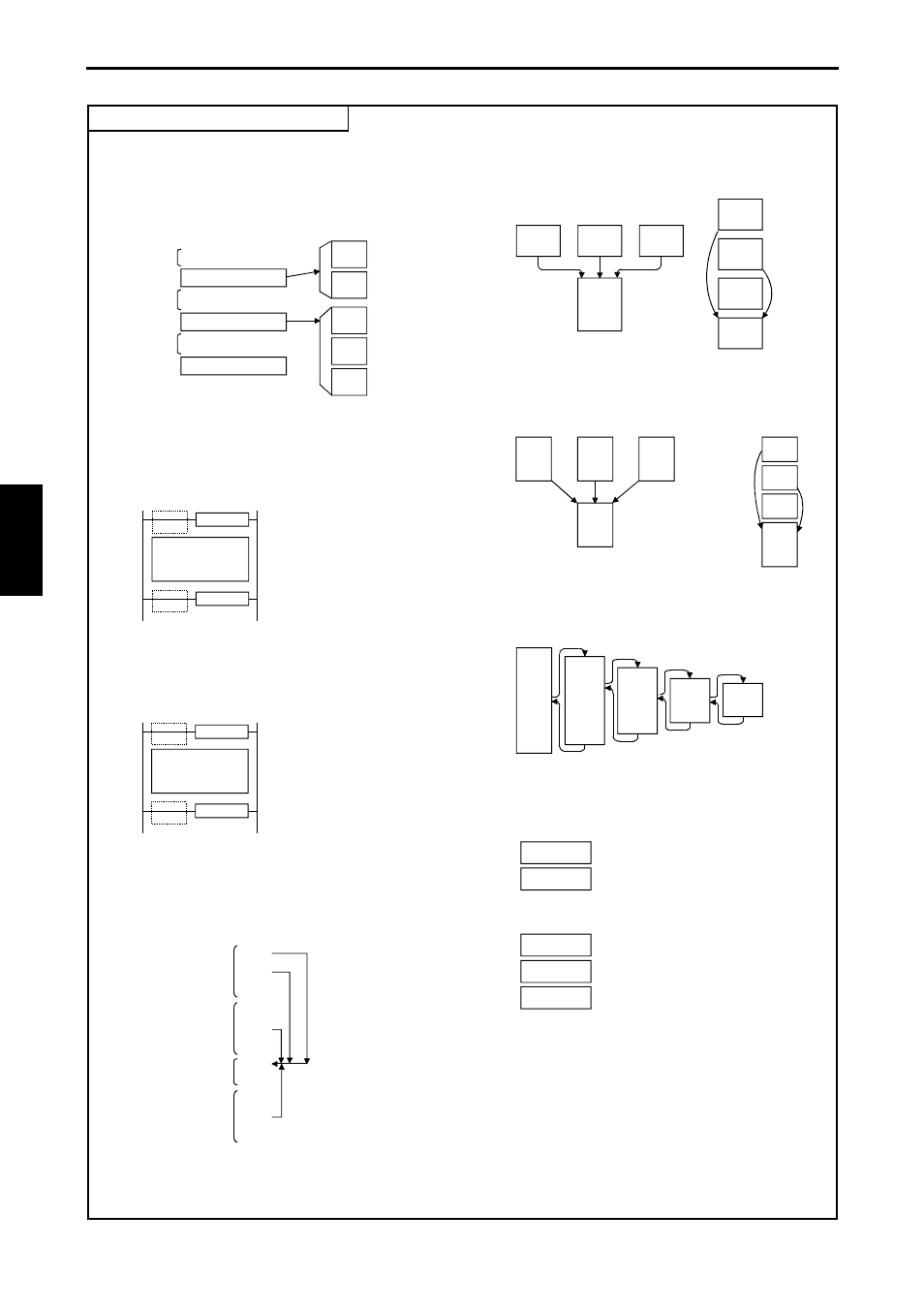
1] A subroutine can be programmed between a normal scan
and interrupt scan, between two interrupt scans, or after
the final interrupt scan.
Normal scan
Interrupt
scan
Interrupt
scan
Program head
Subroutine area
Subroutine area
Subroutine area
Program end
Subroutine 1
Subroutine 2
Subroutine 10
Subroutine 11
Subroutine 12
5] It is also possible to program a subroutine with
multiple entry points and one exit.
2] Program the subroutine start (SB n) and subroutine
end (RTS) instructions without specifying startup
conditions.
Startup
condition
• The RTS startup condition error
will occur during operation pre-
processing.
6] It is also possible to program a interrupt scan with
many entry points and one exit.
7] Nesting of subroutines is allowed up to 5 levels.
Startup
condition
Startup
condition
Startup
condition
(1) As shown to the left, the subroutine
program order and nesting order
have no relationship.
4] The same subroutine can be called from a normal scan,
interrupt scan or subroutine.
Program head
Program head
3] Program the interrupt scan start (INT n) and scan complete
(RTI) instructions without specifying startup conditions.
Normal scan
Interrupt scan
Subroutine 2
Subroutine 1
RT
I
