Write block, How data is transferred – ProSoft Technology MVI69-101S User Manual
Page 81
Reference MVI69-101S
♦ CompactLogix or MicroLogix Platform
IEC 60870-5-101 Slave Communication Module
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Page 81 of 149
March 16, 2009
If Block Transfer Size = 240:
Write Block
These blocks of data transfer information from the CompactLogix or MicroLogix
processor to the module and source the input (monitored) data to be used by the
remote client. The structure of the output image used to transfer this data is
shown in the following table.
Offset Description
Length
0
Write Block ID
1
1 to n
Write Data
n
where n = 60, 120, or 240 depending on the Block Transfer Size parameter (refer
to the configuration file).
The Write Block ID is an index value used to determine the location in the
module's database where the data will be placed. Each transfer can move up to
200 words (block offsets 1 to 200) of data.
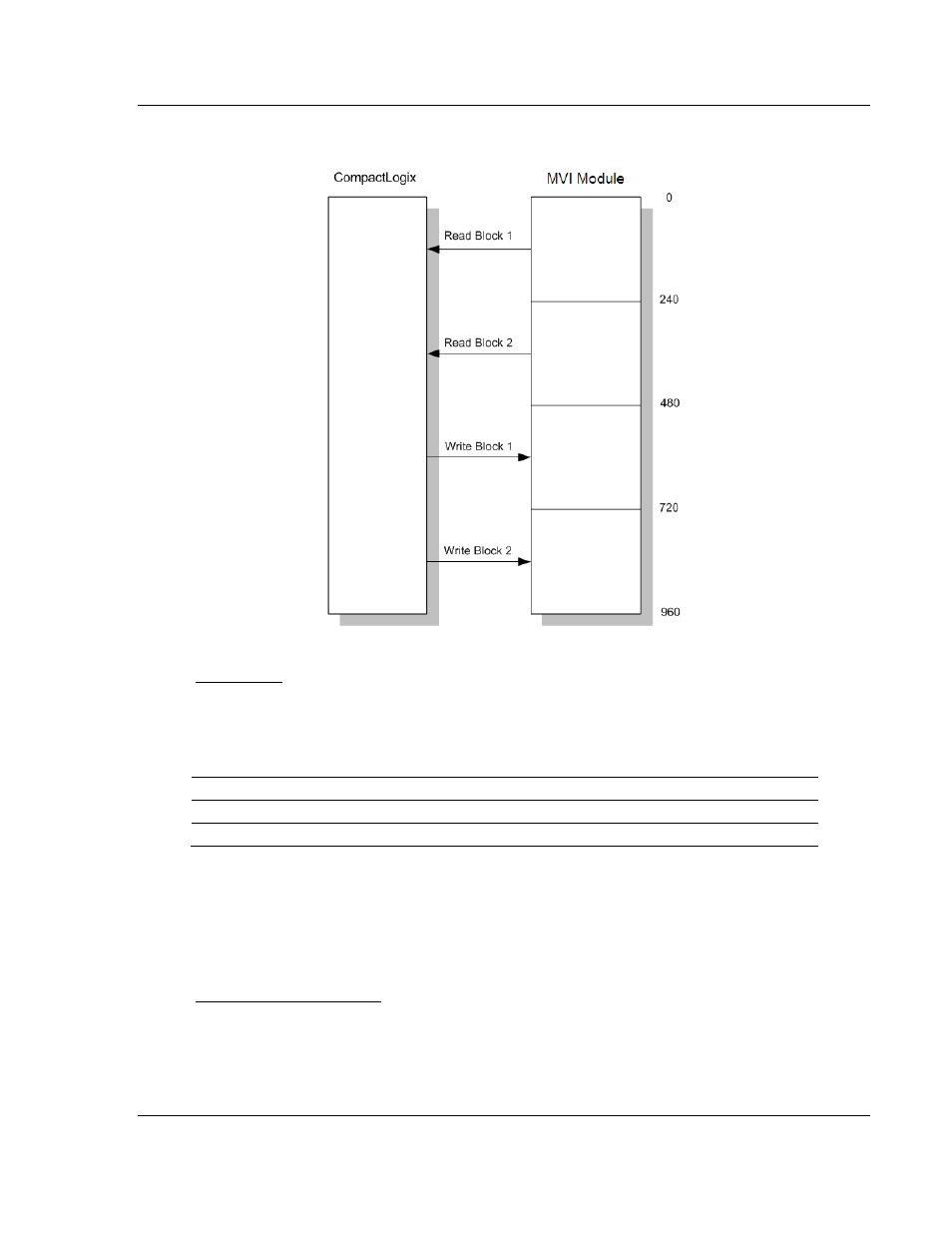
How Data is Transferred
In order to understand how the data is transferred between the processor and the
module, you must understand the Read Data and Write Data area concept in the
module's database. The module's database can be partially, or totally divided into
Read Data Areas and Write Data Areas.
