3 design and function, 1 the heat pump in general, Design and function 3.1 the heat pump in general – REMKO HTS 90 ALU User Manual
Page 28: Remko hts, 3design and function
3
Design and function
3.1 The heat pump in general
Arguments for REMKO inverter heat pumps
n
Lower heating costs in comparison to oil and
gas
n
Heat pumps represent a contribution to envi-
ronmental protection
n
Lower CO
2
emissions in comparison to oil and
gas heating
n
All models are able to cool as well as heat
n
Low noise-level of the outdoor module
n
Flexible installation due to split system design
n
Negligible maintenance costs.
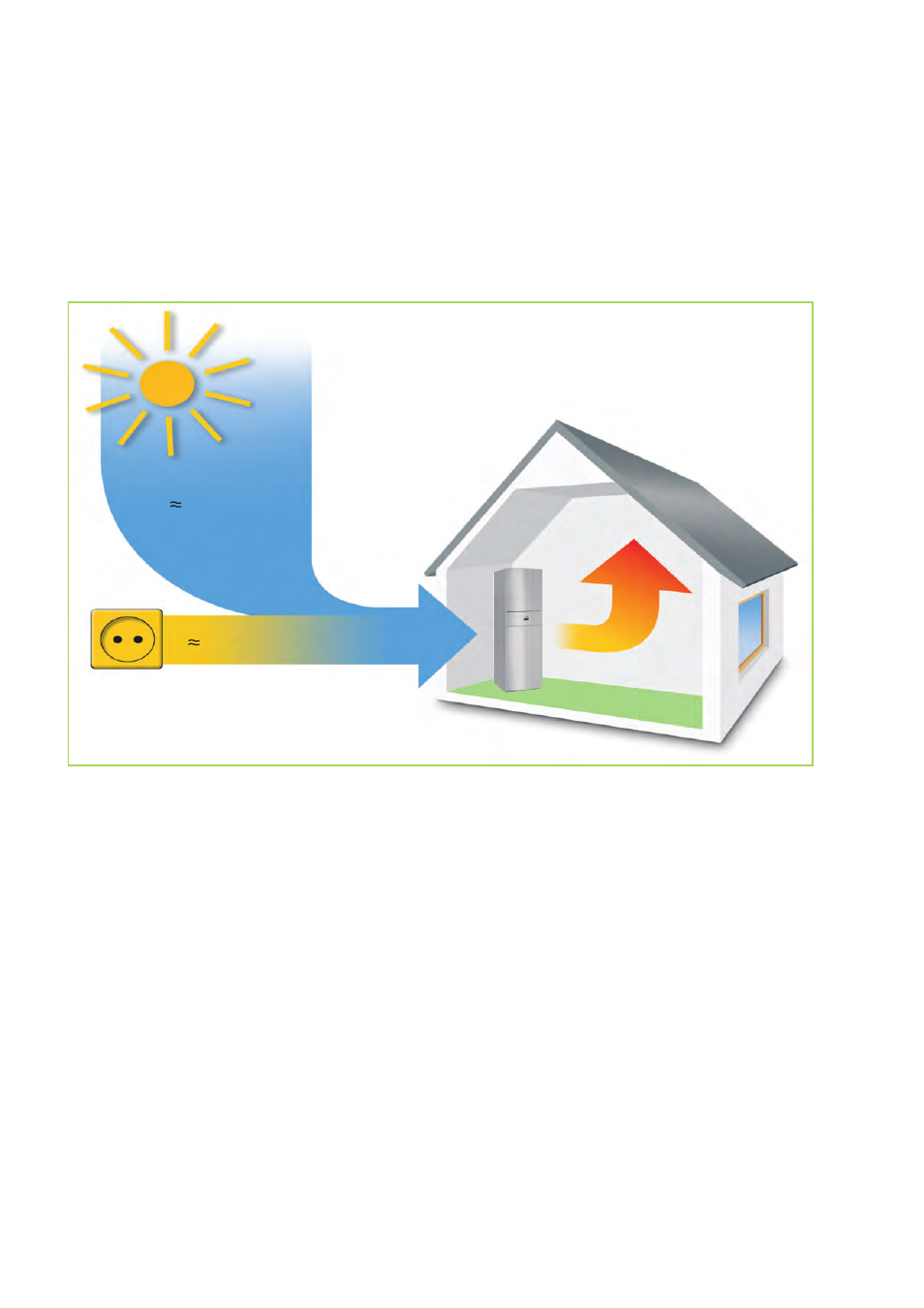
75%* of the heat
comes from the air,
free of charge
75%
freesolar energy
from the air
*
25%
electrical drive energy
*
Heating
Fig. 7: Free heat
* The relationship can vary depending on outdoor temperature and operating conditions.
Economical and environmentally-conscious
heating
The burning of fossil-based energy sources in
order to generate power creates severe conse-
quences for the environment. A high percentage of
fossil fuels is also problematic due to the limited
resources of oil and gas and the price increases
resulting from this. For this reason, many people
today are thinking both economically and environ-
mentally-consciously in terms of heating. The
application of heat pump technology enables both
of these concepts to be combined. It makes use of
the energy which is permanently available in the
air, water and soil and converts it into usable
heating energy by means of inputting electrical
energy. Yet in order to generate heat equivalent to
4kWh, only about 1kWh of electricity is required.
The rest is made available free-of-charge by the
environment.
Heat source
There are essentially three heat sources from
which heat pumps can derive energy: air, soil and
groundwater. The air heat pumps have the
advantage that their source of power, i.e. air, is
available everywhere in unlimited quantities and
it is free of charge to harness. A disadvantage is
that the outside air is at its coldest when the heat
requirement is greatest.
Brine heat pumps extract energy from the soil. This
is undertaken in serpentine pipe networks which
are laid approx. 1m deep or placed by means of
drilling. Their disadvantage lies in the large sur-
face areas required for the serpentine pipe net-
works or the high price of drilling. Long-term
cooling of the soil is also a possibility.
REMKO HTS
28
