OWON MSO Series User Manual
Page 51
46
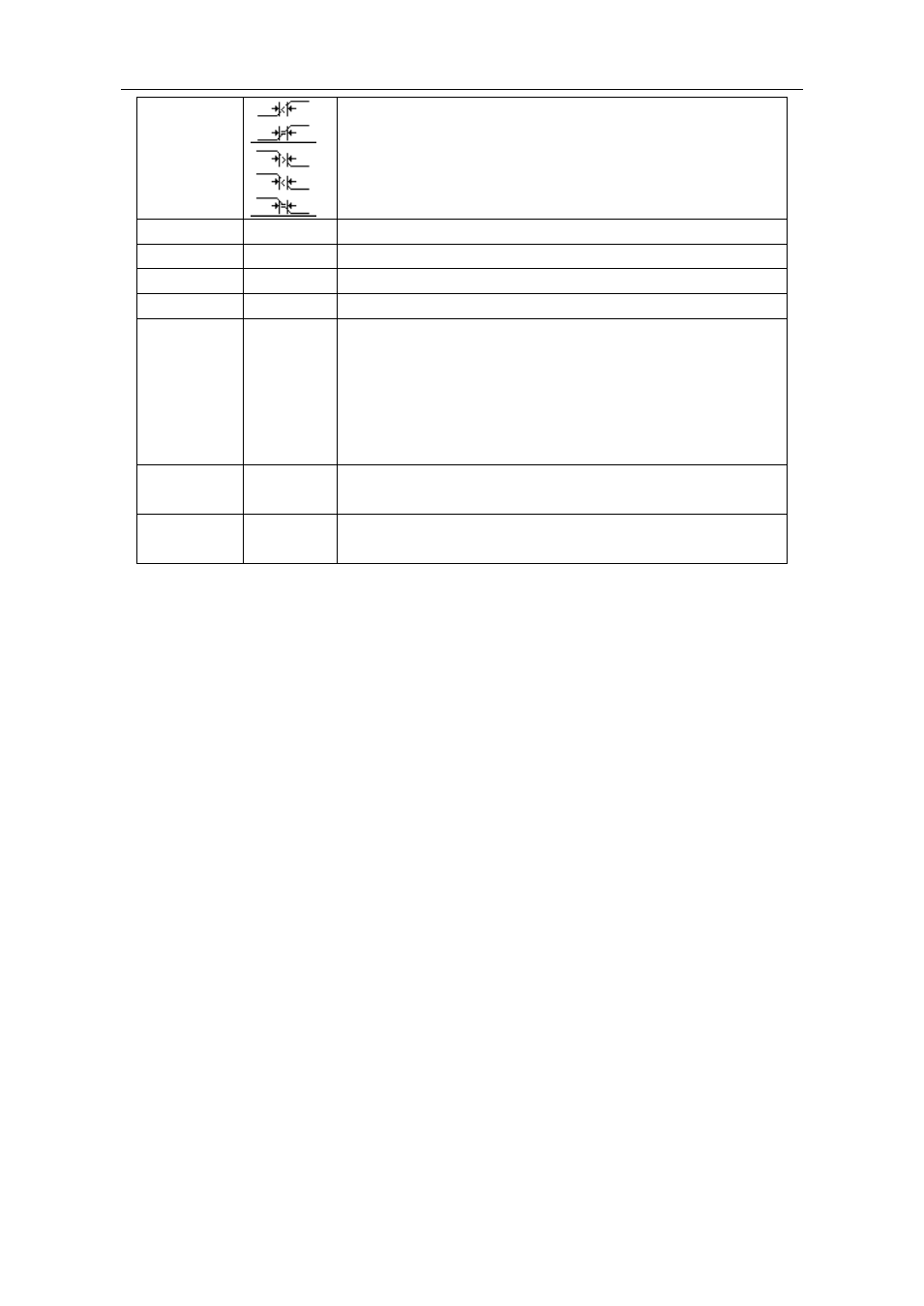
Condition
Rising Edge and less than.
Rising Edge and equal to .
Falling Edge and more than
Negative pulse and less than
Negative pulse and equal to
settings
24ns~10s
Turn "TRIG LEVEL" knob to set slope time
High level
Turn "TRIG LEVEL" knob to set the
High level
Low level
Turn "TRIG LEVEL" knob to set
Low level
Slew rate
Slew rate=(
High level- Low level)/ Settings
Coupling
AC
DC
HF
LF
Block the direct current component.
Unblock all components.
Block the high-frequency signal and only unblock the
low-frequency component.
Block the low-frequency signal and only unblock the high
-frequency component.
Holdoff
100ns~
10s
Set interval by using TRIG LEVEL control, value range
from 100ns~10s.
Holdoff
Reset
Reset hold time to default value (100ns).
Term interpretation
1. Source: Trigger can occur from several sources: Input channels (CH1, CH2), AC Line,
Ext, Ext/5.
Input :It is the most commonly used trigger source. The channel will work when
selected as a trigger source whatever displayed or not.
Ext Trig: The instrument can trigger from a third source while acquiring data from
CH1 and CH2. For example, you might want to trigger from an external clock or with a
signal from another part of the test circuit. The Ext, Ext/ 5 trigger sources use the
external trigger signal connected to the EXT TRIG connector. Ext uses the signal
directly; it has a trigger level range of +1.6 V to -1.6 V. The EXT/ 5 trigger source
attenuates the signal by 5X, which extends the trigger level range to +8 V to -8 V. This
allows the oscilloscope to trigger on a larger signal
AC Line: AC power can be used to display signals related to the power line frequency,
such as lighting equipment and power supply devices. The oscilloscope gets triggered
on its power cord, so you do not have to input an AC trigger signal. When AC Line is
selected as trigger source, the oscilloscope automatically set coupling to DC, set trigger
level to 0V.
2.
Trigger Mode:
The trigger mode determines how the oscilloscope behaves in the absence of a trigger
event. The oscilloscope provides three trigger modes: Auto, Normal, and Single.
Auto: This sweep mode allows the oscilloscope to acquire waveforms even when it
does not detect a trigger condition. If no trigger condition occurs while the oscilloscope
is waiting for a specific period (as determined by the time-base setting), it will force
itself to trigger.
