Specifying the device program id – Echelon LonTal Stack User Manual
Page 100
88
Using the LonTalk Interface Developer Utility
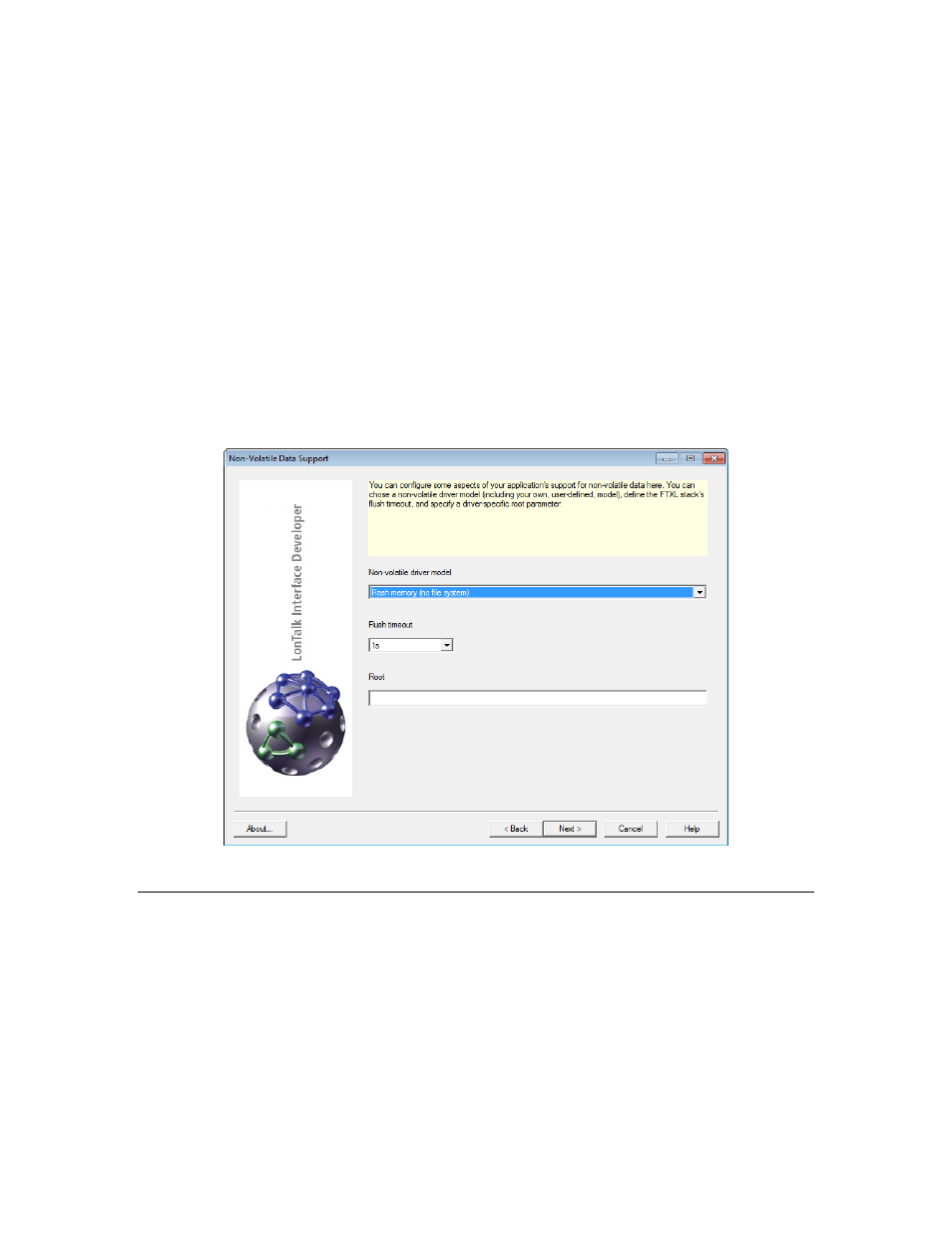
The non-volatile data flush timeout value determines how long the LonTalk host
stack waits to receive additional updates before writing them to the non-volatile
data.
The non-volatile root name is used to configure the non-volatile data support
driver. If you use the flash file system, the non-volatile root name is used as a
file system directory name in which to create non-volatile data files. If you use
the direct flash model, the name represents a host processor flash device name.
If you use unstructured flash memory, leave the Root field blank.
Within the host processor development environment, the system.h file defines
the root name. For the examples that are included with the LonTalk Stack, the
root name is /dev/cfi_flash, which is the root directory for the flash file system.
The source files that handle non-volatile data (FtxlNvdFlashDirect.c,
FtxlNvdFlashFs.c, and FtxlNvdUserDefined.c) use conditional compilation
based on the selected model to include the appropriate code. If you select a
user-defined model, the related callback handler functions are not defined and
cause a linker error if they are not implemented.
Click Next.
Specifying the Device Program ID
From the Program ID Selection page of the utility, you specify the device
program ID or use the L
ON
M
ARK
Standard Program ID Calculator to specify the
device program ID. The program ID is a 16-digit hexadecimal number that
uniquely identifies the device interface for your device.
The program ID can be formatted as a standard or non-standard program ID.
When formatted as a standard program ID, the 16 hexadecimal digits are
organized into six fields that identify the manufacturer, classification, usage,
channel type, and model number of the device. The L
ON
M
ARK
Standard Program
ID Calculator simplifies the selection of the appropriate values for these fields by
