Condenser maintenance, Effect of condenser on head pressure, How to purge noncondensable gases – Carrier 30HH User Manual
Page 44: Inspecting shell and tube condensers, Cleaning shell and tube condensers, Cleaning shell and coil condenser, The gravity flow method of cleaning, 30hh,hj, Carrier, Maintenance
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
30HH,HJ
MAINTENANCE
Carrier
Ü I
CONDENSER MAINTENANCE
Effect of Condenser on Head Pressure
The normal head pressure for an installation is
determined when the job is engineered. Too great
a variation from normal may be caused by:
1.
Incorrect adjustment of the water regulating
valve. (See Water Regulating Valve - Check
Controls.)
2. Noncond'ensable gases.
3. incorrect refrigerant charge.
4. Scaled condenser tubes.
How to Purge Noncondensable Gases
Purge noncondensable gases thru the purge cock
on top of the condenser or receiver.
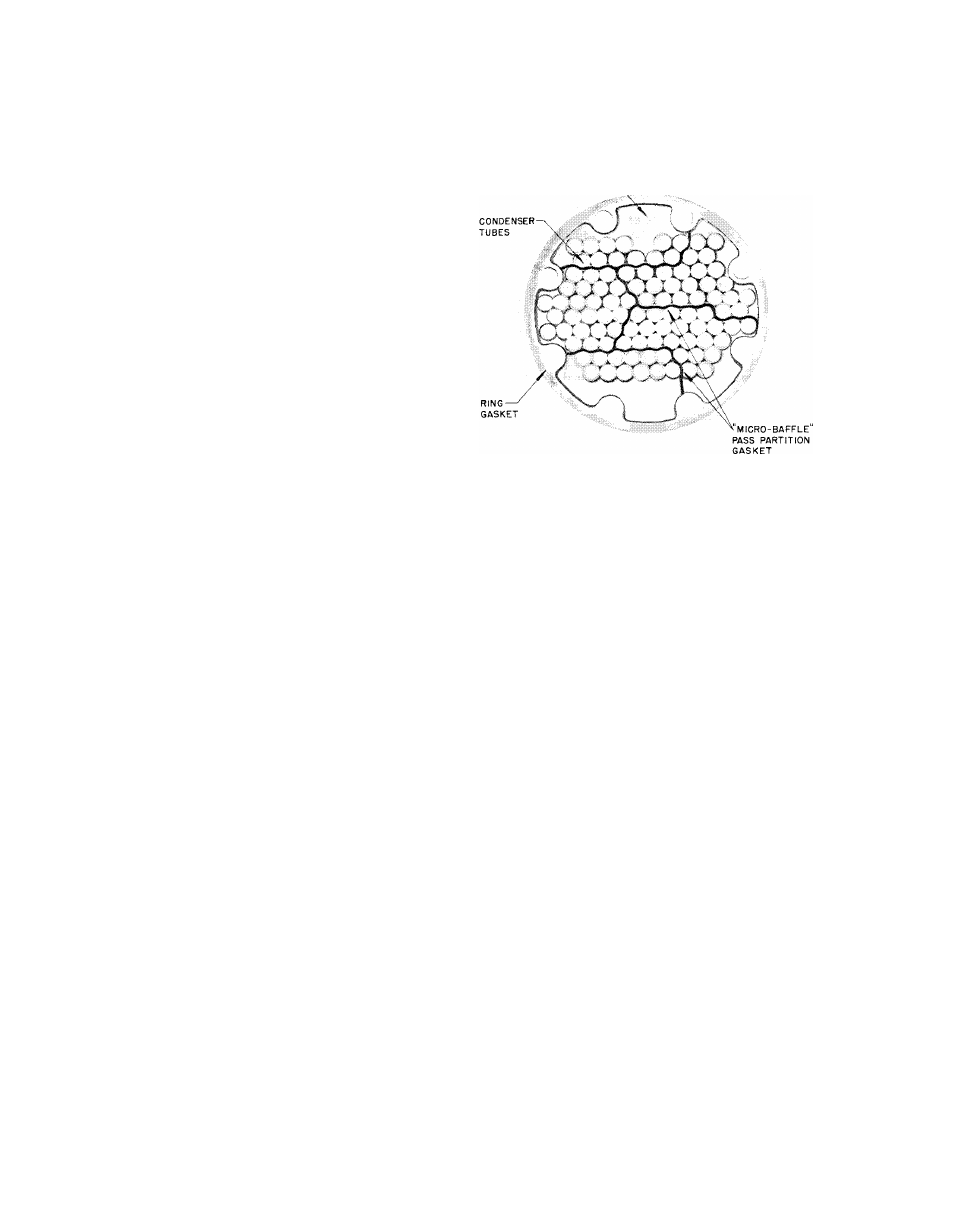
TUBE SHEET
Fig. 43 - Location of Pass Partition (Typical
Inspecting Shell and Tube Condensers
The shell and tube condensers used on 30HH055,
065 chillers can be inspected on the water side
by removing the heads. It is not necessary to
pump down. The necessary steps are as follows;
1. Shut off the machine.
2.
Shut off condenser water supply and discon
nect the inlet and outlet piping.
3.
Backseat
the
angle
valve
connecting
the
water regulating valve capillary to the con
denser
and
disconnect
the
tubing
from
the
valve.
4.
Remove tne drain plugs from the bottoms of
the heads and the vent plug from the top of
the front head and drain the water.
5. Remove the head bolts and heads.
A "Micro-Baffle" pass partition gasket made of
soft
metal
seals
the
water
passes
(Fig.
43).
When replacing a damaged gasket be sure to get
a new one in the correct position.
Cleaning Shell and Tube Condensers
To clean the tubes on 30HH055,065 chillers, use
a
special
nylon
brush
(available
from
local
Carrier
Distributor)
or
a
similar
brush
at
tached to a rod. If hard scale has formed, the
coils should be cleaned chemically. Do not use
brushes that will scrape and scratch the tube's.
Experience has shown that once the tubing has
been scratched, corrosion takes place which re
sults in pitting of the tubes. This is less likely
to occur with chemical cleaning.
Flush water thru the coils while brushing. The
results are best if the brush is turned with a
slow speed electric drill.
It is also possible to clean the tubes by using air
pressure to force rubber plugs thru the tubing.
After the tubes are cleaned, install the heads,
connect the water lines, and flush the condenser
to remove any remaining sediment.
Cleaning Shell and Coil Condenser
The simplest method of cleaning shell and coil
condensers is with inhibited acid. Use an inhib
ited
hydrochloric
acid
solution such
as
"Oakite
32." Handle the acid with the usual precautions
because it will stain the hands and clothing and
attack concrete. If the inhibitor is not present^
it will attack steel. Where splashing may occur,
cover the surfaces with burlap or boards. Gas
coming from the vent pipe during cleaning is not
harmful,
but
take
care
to
prevent liquid
from
being carrier over by the gas. The solution acts
more readily if it is warm, but a cold solution
and a longer time does just as thorough a job.
The Gravity Flow Method of Cleaning
The gravity flow method of cleaning is shown in
Fig. 44. Do not add the solution more rapidly
38
