3 reference voltage of the 71m6541, 4 voltage-divider, Table 2-2: temperature-related error sources – Maxim Integrated 71M6541 Demo Board User Manual
Page 50: Cib c c va c c ia c va p
71M6541 Demo Board REV 3.0 User’s Manual
50
Rev 4.0
2.4.3.3 Reference Voltage of the 71M6541
At a later time, it will be shown how the compensation coefficients for the reference voltage of the 71M6541 can
be derived. For the moment, let us assume that we know these coefficients, and that they are
PPMC
4X
= -820
and
PPMC2
4X
= -680.
2.4.3.4 Voltage-Divider
In most cases, especially when identical resistor types are used for all resistors of the voltage-divider ladder, the
TC of the voltage-divider will be of minor influence on the TC of the meter.
If desired, the voltage-divider can be characterized similar to the shunt resistor as shown above. Let us assume,
applying 240 Vrms to a meter and recording the RMS voltage displayed by the meter at -40°C, room tempera-
ture, +55°C, and at +85°C, we obtain the values in the center column of Table 2-2.
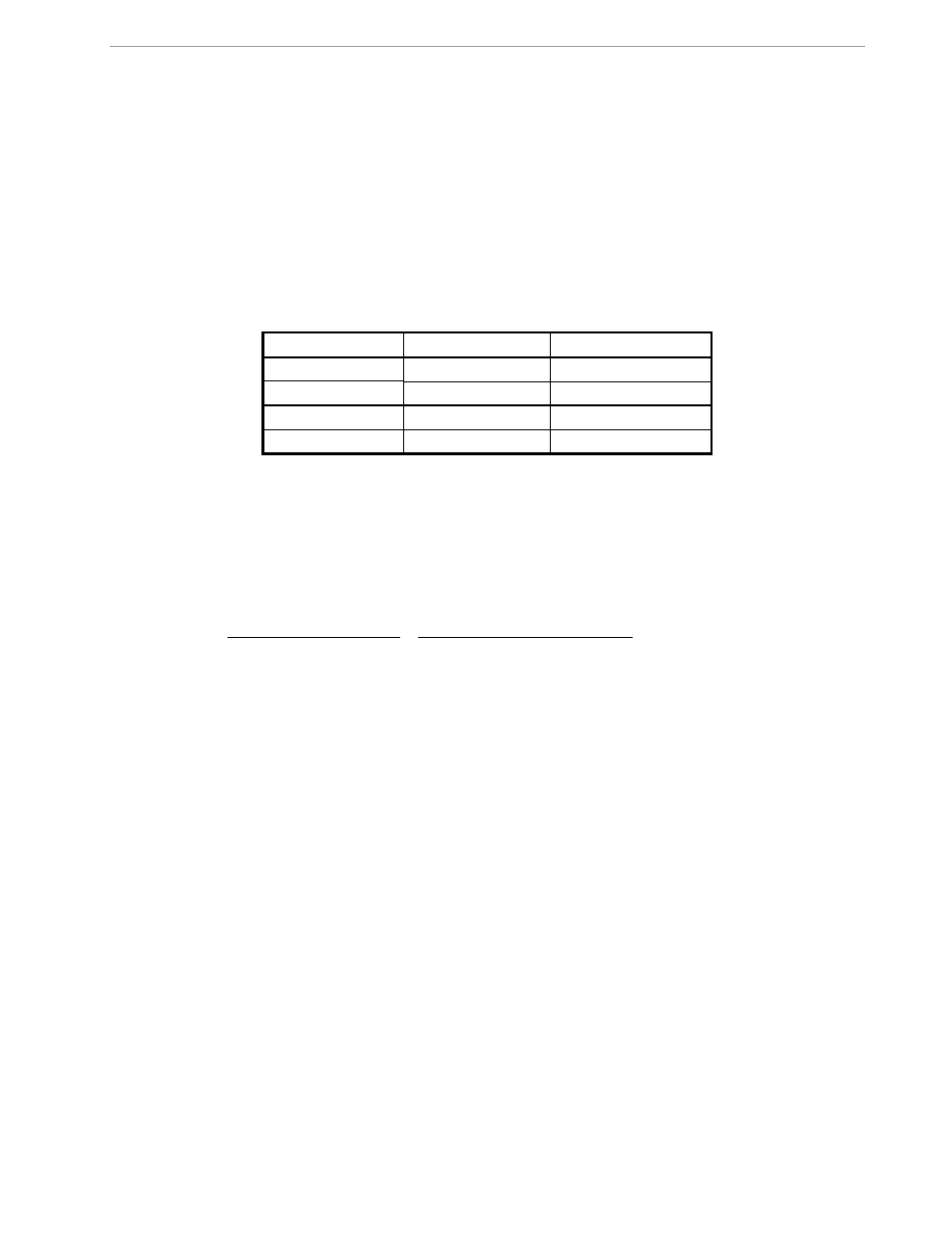
Table 2-2: Temperature-Related Error Sources
Temperature [°C]
Displayed Voltage
Normalized Voltage
-40
246.48
240.458
25
246.01
240.0
55
245.78
239.78
85
245.56
239.57
After normalizing with the factor 240/246.01 to accommodate for the initial error, we obtain the values in the
third column. We determine the voltage deviation between highest and lowest temperature to be -0.88 V, which
is equivalent to -3671 PPM, or -29.4 PPM/°C.
Finally, we obtain a
PPMC
VD
value of 788.
2.4.3.5 Combining the Coefficients for Temperature Compensation
The TC formula for equation 2 is restated below:
⋅
⋅
⋅
⋅
⋅
−
⋅
⋅
⋅
⋅
=
2
)
2
6
2
4
2
4
1
X
S
X
VD
X
S
VD
C
C
IB
C
C
VA
C
C
IA
C
VA
P
After characterizing all major contributors to the TC of the meter, we have all components at hand to design the
overall compensation.
For simplification purposes, we have decided to ignore C
VD
. For the control of
GAIN_ADJA
, we will need the
following coefficients:
C
S1
: The
PPMC
S
= -3331 determined for the shunt resistor.
PPMC2
S
for the shunt resistor is 0.
C
VD
: The
PPMC
VD
value of 788 determined for the voltage-divider.
C
4X
:
PPMC
4X
= -820 and
PPMC2
4X
= -680
We will find that coefficients can simply be added to combine the effects from several sources of temperature
dependence. Before we do that, we must consider that the equations for temperature compensation are struc-
tured in a special way, i.e.,:
•
If an error source affects both current and voltage measurements, the original
PPMC
and
PPMC2
coeffi-
cients are used.
•
If an error source affects only one measurement, the original
PPMC
and
PPMC2
coefficients are divided
by 2.
Following this procedure, we obtain the coefficients for
GAIN_ADJA
as follows:
•
PPMC
A
=
PPMC
S
/2 +
PPMC
4X
+
PPMC
VD
/2 = -3331/2 - 820 + 788/2 = -2092
•
PPMC2
A
= PPMC2
S
+
PPMC2
4X
=
-680
