Channel cut-off frequency, Figure 3.2 frequency response graphs – Rockwell Automation 1769-OF2 Compact I/O Analog Modules User Manual
Page 57
Publication 1769-UM002B-EN-P - July 2005
Module Data, Status, and Channel Configuration for the Input Modules 3-7
Channel Cut-Off Frequency
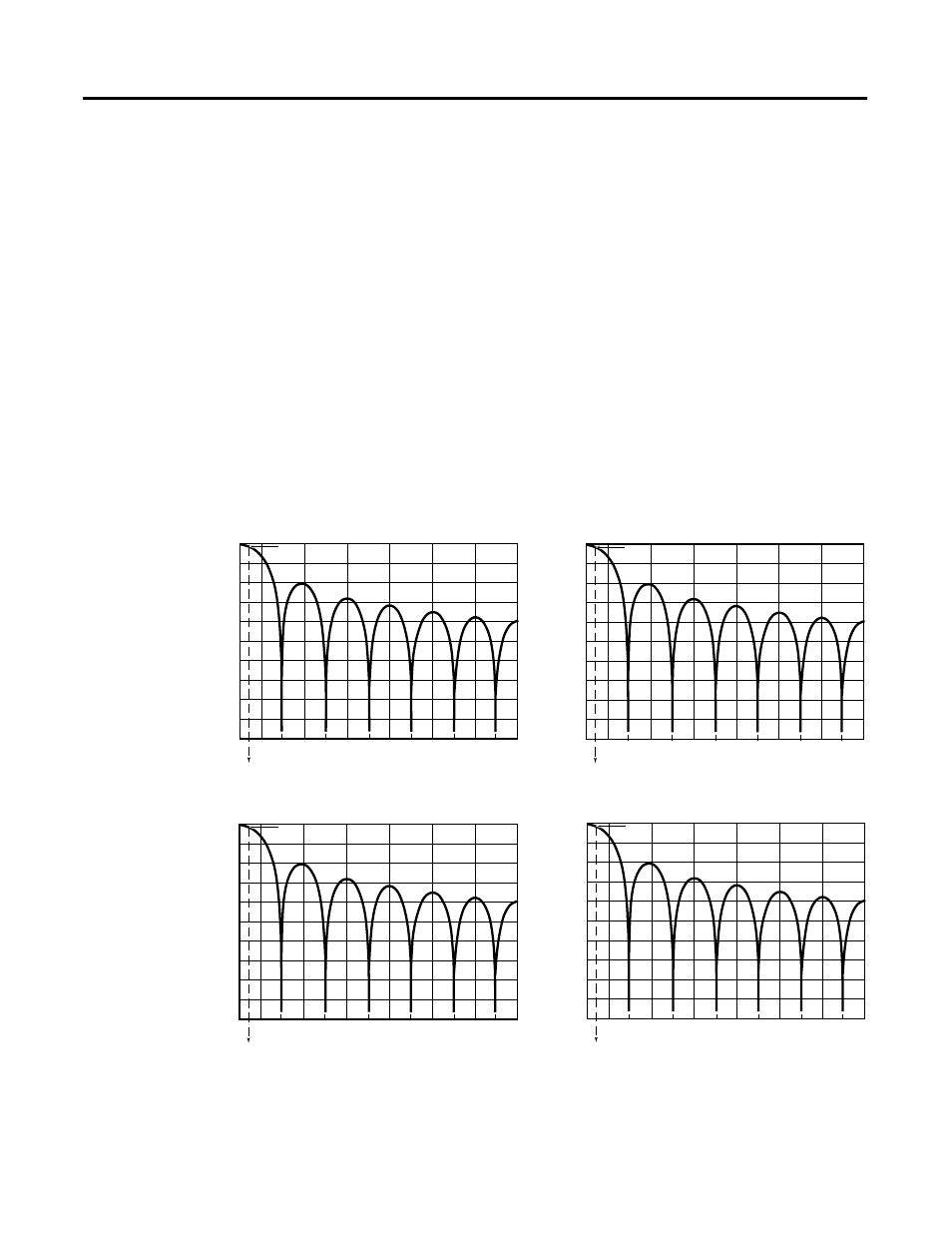
The -3 dB frequency is the filter cut-off frequency. The cut-off frequency is
defined as the point on the frequency response curve where frequency
components of the input signal are passed with 3 dB of attenuation. All input
frequency components at or below the cut-off frequency are passed by the
digital filter with less than 3 dB of attenuation. All frequency components
above the cut-off frequency are increasingly attenuated as shown in the graphs
below.
The cut-off frequency for each channel is defined by its filter frequency
selection. Choose a filter frequency so that your fastest changing signal is
below that of the filter’s cut-off frequency. The cut-off frequency should not
be confused with the update time. The cut-off frequency relates to how the
digital filter attenuates frequency components of the input signal. The update
time defines the rate at which an input channel is scanned and its channel data
word is updated.
Figure 3.2 Frequency Response Graphs
0
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
–200
–20
–3 dB
300
0
250
150
100
50
13.1 Hz
200
0
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
–200
–20
–3 dB
360
0
300
180
120
60
15.72 Hz
240
0
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
–200
–20
–3 dB
1300
0
1150
750
500
250
65.5 Hz
900
0
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
–180
–200
–20
–3 dB
3000
0
2500
1500
1000
500
131 Hz
2000
50 Hz Input Filter Frequency
60 Hz Input Filter Frequency
250 Hz Input Filter Frequency
500 Hz Input Filter Frequency
Frequency (Hz)
Frequency (Hz)
Frequency (Hz)
Frequency (Hz)
Ga
in
(d
B)
Ga
in
(d
B)
G
ain (
dB)
G
ain (
dB)
