Arbitrary waveform generator, Figure 14. arbitrary waveform ui, Arbitrary waveform gen – Cirrus Logic CS61884 User Manual
Page 43: Erator, Arbitrary, Waveform generator
CS61884
DS485F3
43
15. ARBITRARY WAVEFORM
GENERATOR
Using the Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG)
allows the user to customize the transmit pulse
shapes to compensate for nonstandard cables,
transformers, protection circuitry, or to reduce
power consumption by reducing the output pulse
amplitude. A channel is configured for a custom
pulse shape by storing data representing the pulse
shape into the 24/26/28 phase sample locations and
then enabling the AWG for that channel. Each
channel has a separate AWG, so all eight channels
can have a different customized pulse shape. The
microprocessor interface, is used to read from or
write to the AWG, while the device is in host mode.
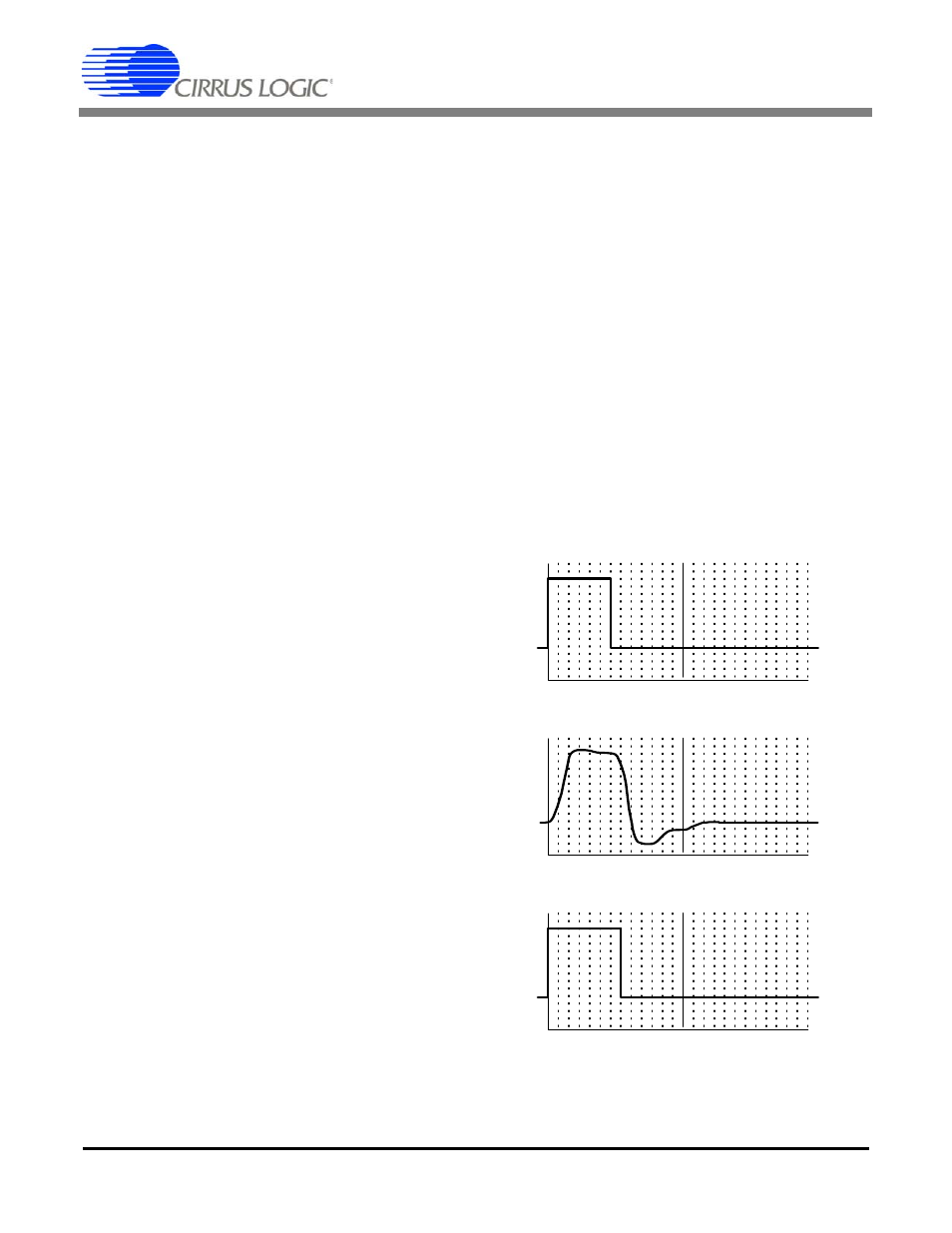
In the AWG RAM, the pulse shape is divided into
two unit intervals (UI). For E1 mode, there are 12
sample phases in each UI, while in T1/J1 mode, the
number of sample phases per UI are either 13 or 14.
The first UI is for the main part of the pulse and the
second UI is for the “tail” of the pulse (Refer to
). A complete pulse-shape is represented
by 24 phase samples in E1 mode or 26/28 phase
samples in T1/J1 mode. In E1 mode, data written in
the first UI represents a valid pulse shape, while
data in the second UI is ignored and should be set
to zero.
The mode of operation is selected using the
Length Channel ID Register (10h)
(See Section 14.18 on page 39). A
phase sample, or cell, is accessed by first loading
the channel address and the phase sample address
into the
AWG Phase Address Register (17h)
Section 14.24 on page 40), and then reading or
writing the
Section 14.25 on page 40). The upper locations in
each channel’s address space are not used; reading
and writing to these registers produces undefined
results.
The data in each phase sample is a 7-bit two’s com-
plement number with a maximum positive value of
0x3f, and a maximum negative value of 0x40. The
terms “positive” and “negative” are defined for a
positive going pulse only. The pulse generation cir-
cuitry automatically inverts the pulse for negative
going pulses. The data stored in the lowest phase
address corresponds to the first phase sample that
will be transmitted in time. When the mode of op-
eration calls for only 24/26 phase samples if the
phase samples that are not used (25 through 28) are
written to, they are ignored and don’t effect the
shape of the customized pulse shape.
The following procedure describes how to enable
and write data into the AWG to produce custom-
ized pulse shapes to be transmitted for a specific
E1 AWG Example
DSX-1 (54% duty cycle) AWG Example
DSX-1 (50% duty cycle) AWG Example
U1
U2
U1
U2
U1
U2
Figure 14. Arbitrary Waveform UI
