Invalidation rate graph, Exception rate graph, Pio rate graph – AMD SimNow Simulator 4.4.4 User Manual
Page 38
AMD Confidential
User Manual
September 12
h
, 2008
26
Chapter 3: Graphical User Interface
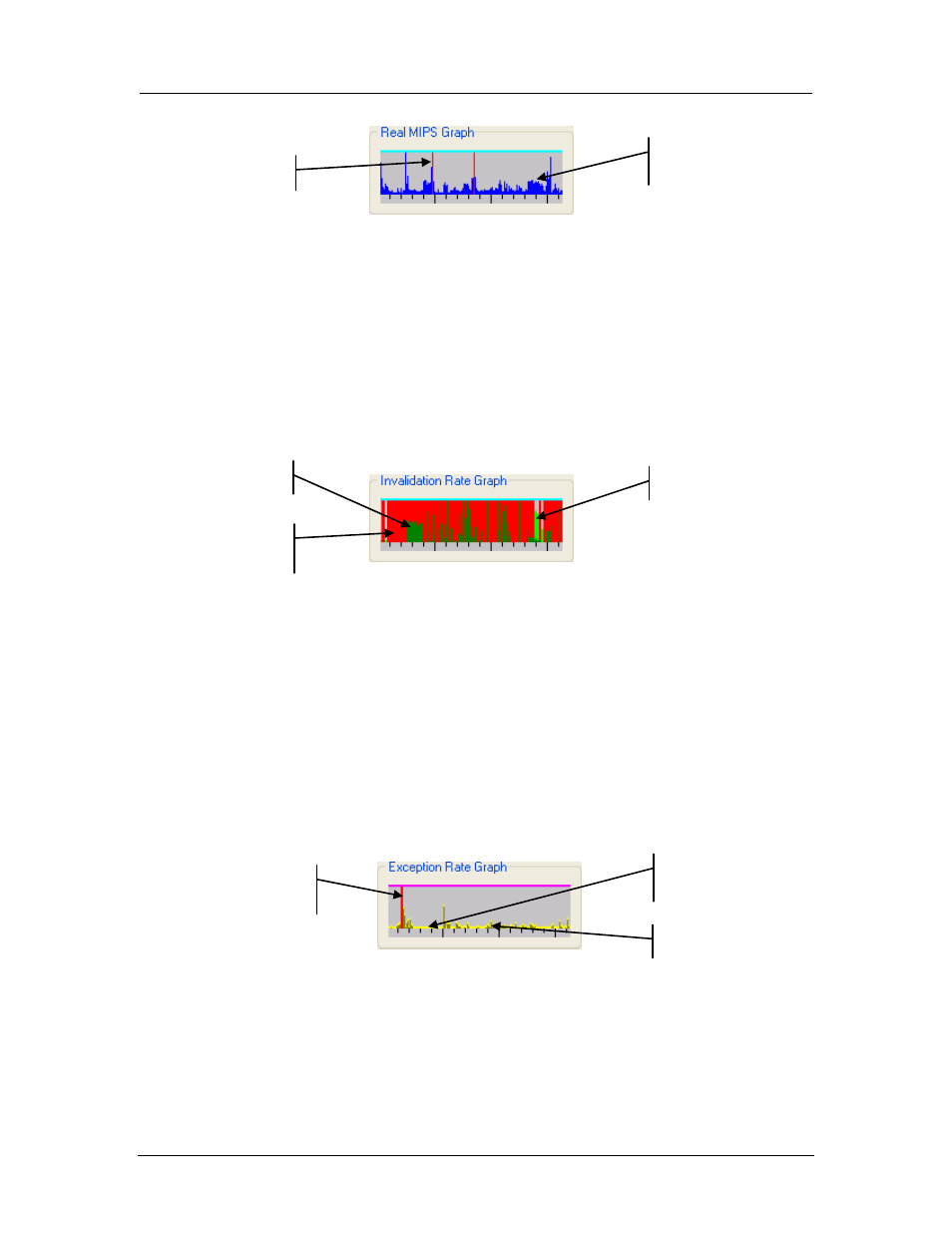
Figure 3-17: CPU Real MIPS Graph
3.4.2.3 Invalidation Rate Graph
The Invalidation Rate Graph updates once a second. If this value exceeds what can be
displayed on this graph, the graph line turns red. A rate of zero will appear as a horizontal
line, one pixel high. Full vertical scale represents one invalidatated translation per
thousand simulated instructions. The lower, darker color represents plain invalidations.
The upper, lighter color represents range invalidations. This upper, lighter color is a
minimum of one pixel high, i.e., a value of zero range invalidations still results in a one-
pixel-high line of the lighter color.
Figure 3-18: CPU Invalidation Graph
3.4.2.4 Exception Rate Graph
The Exception Rate Graph updates once a second. If this value exceeds what can be
displayed on this graph, the graph line turns red. A rate of zero appears as a horizontal
line one pixel high. Full vertical scale represents a rate of one exception taken by the
simulator per ten simulated instructions. These exceptions may be internal to the
simulator and not turn into exceptions in the simulated machine. The lower, darker color
represents all such exceptions other than segmentation violation (SEGV) exceptions. The
upper, lighter color represents all the SEGV exceptions. This upper, lighter color is a
minimum of a one-pixel-high line, i.e., a value of zero SEGV exceptions still shows a
one-pixel-high line of the lighter color.
Figure 3-19: CPU Exception Rate Graph
3.4.2.5 PIO Rate Graph
The PIO Rate Graph updates once a second. If the port I/O (PIO) rate exceeds what can
be displayed on this graph, the graph line turns red. A rate of zero will appear as a
horizontal line one pixel high. Full scale represents one PIO per ten simulated
Plain
Invalidations
Range
Invalidations
Exceeds what
can be
displayed.
Million of
Instructions per
Host CPU second.
Exceeds 100
MIPS.
Exceeded
what can be
displayed.
All exceptions other
than segmentation
violations (SEGV).
Segmentation
violations (SEGV).
