A.4 binary data representation – Triton Isis User Manual
Page 15
June 2004 Isis® Sonar User's Manual, Volume 2
5
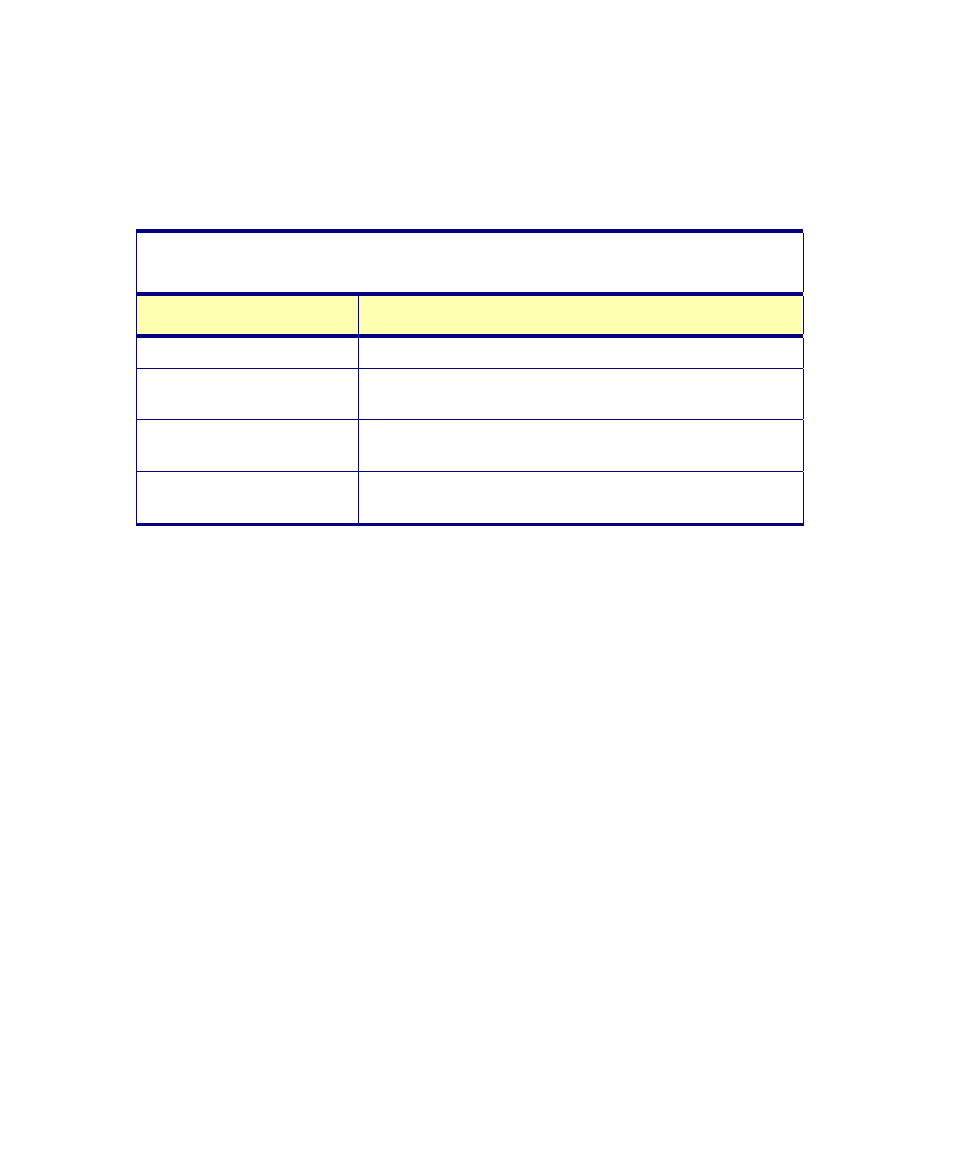
For example, a data file written by Q-MIPS with 3 pings of raw and corrected
imagery for each of two sidescan channels at eight bits per pixel would be
configured as follows:
Table A-3. Sample configuration illustrating file size
Size of Data in Bytes
Description
[1024] Q-MIPS
Header
[1024] [1024] [1024]
[1024] [256]
Ping 1, Four channels, 1024 bytes each; Q-MIPS
footer
[1024] [1024] [1024]
[1024] [256]
Ping 2
[1024] [1024] [1024]
[1024] [256]
Ping 3
The amount of memory all the data would occupy is:
14080 bytes [(1024 x 13) + (256 x 3)]
A.4 Binary Data Representation
The Q-MIPS format header and footer structures are made up of fields in six
number representation schemes or types. For each type shown in Table A-4 on
page 6, the type definition from the C-language Q-MIPS source code is shown in
parentheses and the range of numbers that can be represented by that type is
shown in brackets.
Note:
Q-MIPS and Isis will never store a 12-bit value in a 12-bit field. All sonar
values are stored as 8 or 16 bit.
Appendix A: Q-MIPS File Format
