Triton Isis User Manual
Page 14
June 2004 Isis® Sonar User's Manual, Volume 2
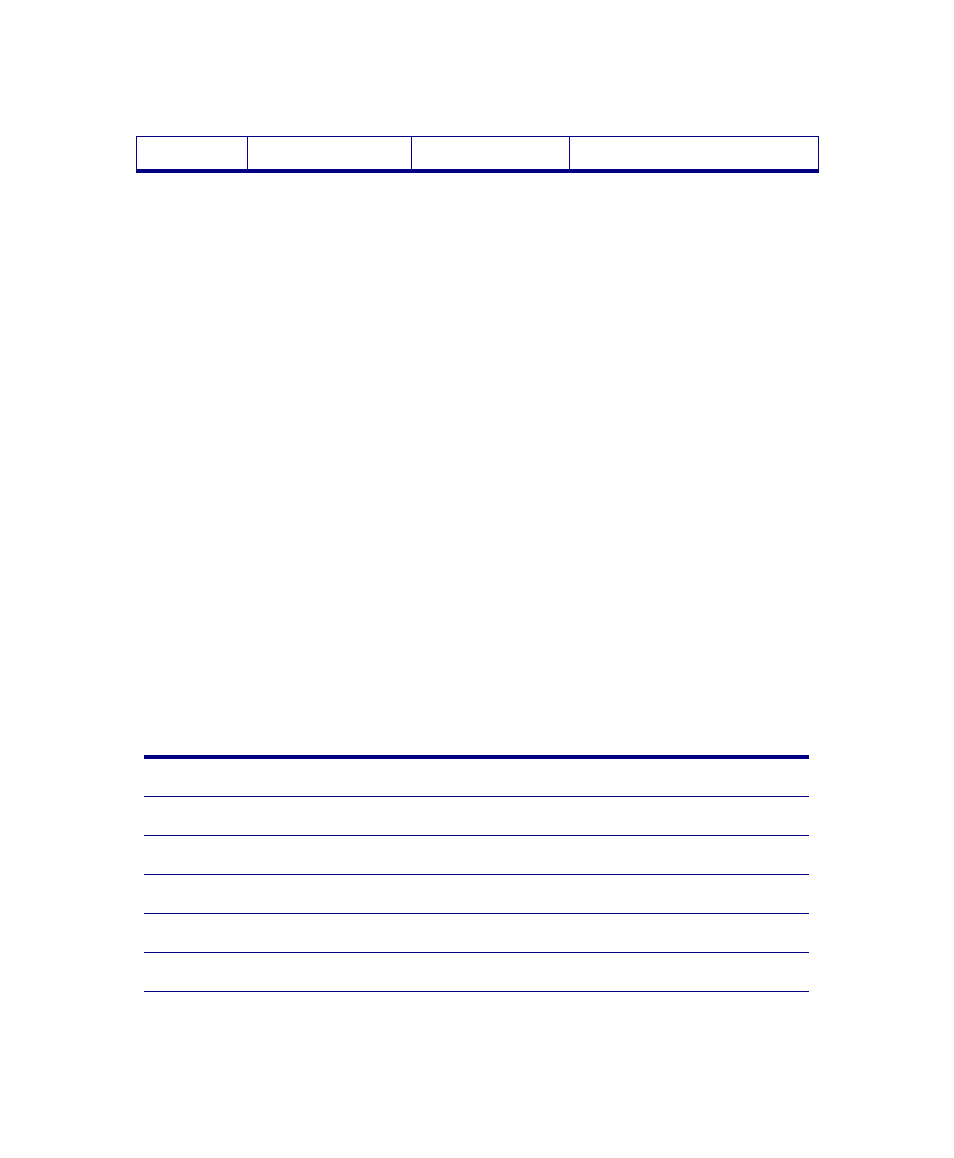
4
CH4
CORRECTED
Write or Read
Starboard or Subbottom
Port channels are stored in pixel order (reverse chronological order) from far
range to nadir and starboard channels are stored from nadir to far range
(chronological order). This convention matches the left-to-right orientation for the
waterfall display on the Q-MIPS high-resolution imagery display. The ping
imagery data are followed by the footer for each ping.
Subbottom pings are normally received asynchronously with respect to side-scan
pings, downsampled differently, and stored with the nearest side-scan ping. A
subbottom channel is termed the asynchronous channel and must be received
on the last (highest number) channel present. The asynchronous ping rate is
generally slower than the side-scan ping rate so the data are replicated ping-by-
ping until a new asynchronous ping is received.
When computing the size of Q-MIPS format files to estimate survey storage
media requirements or throughput rates, use the equations shown in
Equation A-2 on page 4 and Equation A-3 on page 4:
BPP = NIC x PPC x (BPX/8) + PFS in bytes
Equation A-2. Calculating bytes per ping
File Size = 1024 + (NP x BPP) in bytes
Equation A-3. Calculating file size using bytes per ping
where, in Equation A-3, the meaning of the variables are shown in:Table A-2
.
Table A-2. Variables for calculating bytes per ping
BPP
=
Bytes per ping
NIC
=
imagery channels being saved (raw and corrected)
NP
=
number of pings stored in file
PPC
=
pixels per channel per ping (always 1024 for Q-MIPS)
PFS
=
ping footer size = 256
BPX
=
bits per pixel (user-defined as 8 or 16)
Appendix A: Q-MIPS File Format
