Usi – universal serial interface, 1 features, 2 overview – Rainbow Electronics ATtiny43U User Manual
Page 100: Attiny43u
100
8048B–AVR–03/09
ATtiny43U
14. USI – Universal Serial Interface
14.1
Features
•
Two-wire Synchronous Data Transfer (Master or Slave)
•
Three-wire Synchronous Data Transfer (Master or Slave)
•
Data Received Interrupt
•
Wakeup from Idle Mode
•
In Two-wire Mode: Wake-up from All Sleep Modes, Including Power-down Mode
•
Two-wire Start Condition Detector with Interrupt Capability
14.2
Overview
The Universal Serial Interface (USI), provides the basic hardware resources needed for serial
communication. Combined with a minimum of control software, the USI allows significantly
higher transfer rates and uses less code space than solutions based on software only. Interrupts
are included to minimize the processor load.
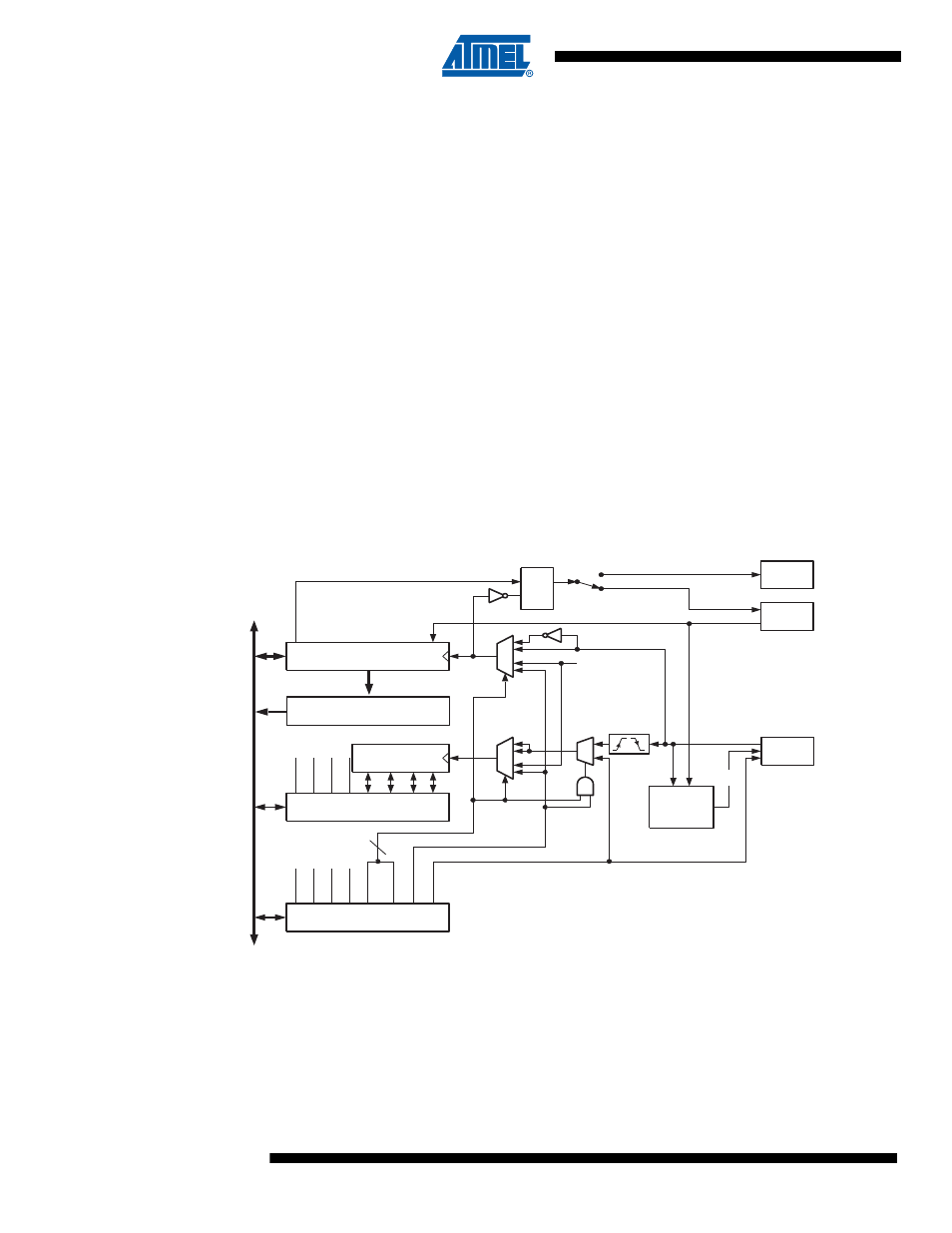
A simplified block diagram of the USI is shown in
. For actual placement
“Pinout of ATtiny43U” on page 2
. CPU accessible I/O Registers, including I/O
bits and I/O pins, are shown in bold. The device-specific I/O Register and bit locations are listed
in the
“Register Descriptions” on page 107
.
Figure 14-1. Universal Serial Interface, Block Diagram
The 8-bit USI Data Register (USIDR) contains the incoming and outgoing data. It is directly
accessible via the data bus but a copy of the contents is also placed in the USI Buffer Register
(USIBR) where it can be retrieved later. If reading the USI Data Register directly, the register
must be read as quickly as possible to ensure that no data is lost.
The most significant bit of the USI Data Register is connected to one of two output pins (depend-
ing on the mode configuration, see
). There is a transparent latch
between the output of the USI Data Register and the output pin, which delays the change of data
DATA BUS
USIPF
USITC
USICLK
USICS0
USICS1
USIOIF
USIOIE
USIDC
USISIF
USIWM0
USIWM1
USISIE
Bit7
Two-wire Clock
Control Unit
DO
(Output only)
DI/SDA
(Input/Open Drain)
USCK/SCL
(Input/Open Drain)
4-bit Counter
USIDR
USISR
D Q
LE
USICR
CLOCK
HOLD
TIM0 COMP
Bit0
[1]
3
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
0
1
2
USIDB
