Garmin GPS 12MAP User Manual
Page 33
23
REFERENCE
Satellite Status
Page
The Satellite status Page
shows where the satellites
are and how strong the
signal is from each one.
A solid signal bar means
the satellite is ready to use.
Use the LEFT/RIGHT
keys on the rocker keypad
to adjust the screen con-
trast and the UP/DOWN
keys to adjust the back-
lighting. Press ENTER to
save the settings.
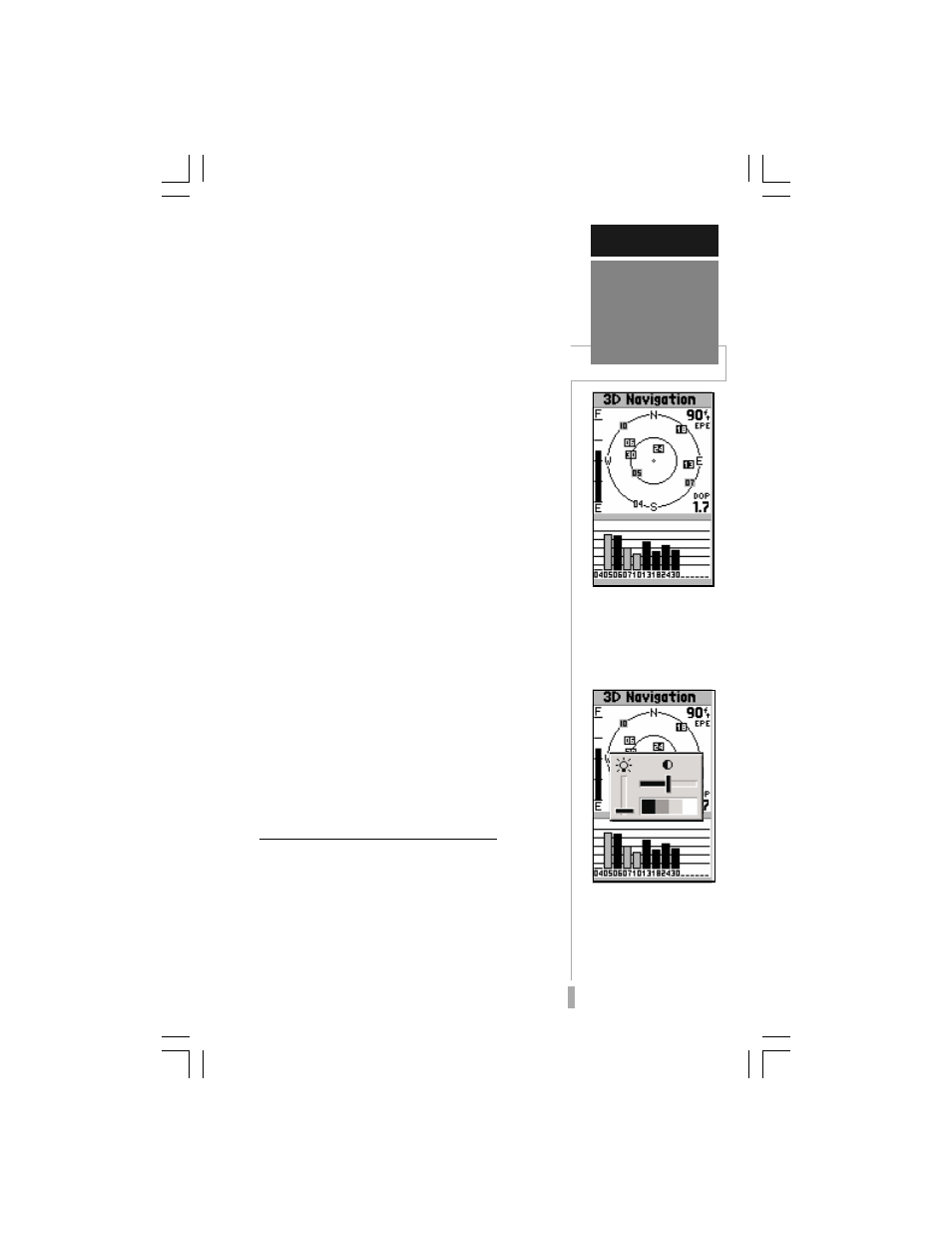
The GPS 12 MAP’s Satellite Status Page
provides a visual reference of various receiver
functions, including current satellite coverage,
receiver operating mode, battery level and
position accuracy. As the receiver locks onto
satellites, a signal strength bar will appear for
each satellite in view, with the appropriate
satellite number (01-32) underneath each bar.
The progress of satellite acquisition is shown in
three stages:
• No signal strength bars— the receiver is
looking for the satellites indicated.
• Hollow signal strength bars— the
receiver has found the satellite(s) and is
collecting data.
• Solid signal strength bars— the receiver
has collected the necessary data and the
satellite(s) is ready for use.
Each satellite has a 30-second data transmis-
sion that must be collected (hollow bar status)
before that satellite may be used for navigation
(solid bar status). Once a fix has been calcu-
lated, the GPS 12 MAP will then update your
position, track, and speed by selecting and
using the best satellites in view. You can also
access the GPS 12 MAP’s backlight and contrast
feature from this or any main page.
To adjust the screen contrast and/or
backlighting:
1. Press LEFT or RIGHT on the rocker keypad to
adjust the level of contrast, and press ENTER to
save the new contrast setting.
2. Press UP or DOWN on the rocker keypad to
adjust the level of backlighting, and press ENTER
to save the new backlight setting.
Sky View and Signal Strength Bars
The sky view and signal strength bars give
you an indication of what satellites are visible to
the receiver, whether or not they are being used
to calculate a position fix, and the signal quality.
The satellite sky view shows a bird’s-eye view of
the position of each available satellite relative to
the unit’s last known position. The outer circle
represents the horizon (north up); the inner
circle 45º above the horizon; and the center
point directly overhead.
