Tmpcnv(), 890 appendix a: functions and instructions – Texas Instruments TITANIUM TI-89 User Manual
Page 890
890
Appendix A: Functions and Instructions
tmpCnv()
CATALOG
tmpCnv(
expression1_
¡tempUnit1
,
_
¡tempUnit2
)
⇒
⇒
⇒
⇒
expression _
¡tempUnit2
Converts a temperature value specified by
expression1
from one unit to another. Valid
temperature units are:
_
¡C Celsius
_
¡F Fahrenheit
_
¡K Kelvin
_
¡R Rankine
For example, 100_
¡C converts to 212_¡F:
To convert a temperature range, use
@
@
@
@tmpCnv()
instead.
tmpCnv(100_¡c,_¡f) ¸ 212.ø_¡F
tmpCnv(32_¡f,_¡c) ¸ 0.ø_¡C
tmpCnv(0_¡c,_¡k) ¸ 273.15ø_¡K
tmpCnv(0_¡f,_¡r) ¸ 459.67ø_¡R
Note: To select temperature units from a menu,
press 2
9
@
@
@
@tmpCnv()
CATALOG
@
@
@
@tmpCnv(
expression1_
¡tempUnit1
,
_
¡tempUnit2
)
⇒
⇒
⇒
⇒
expression _
¡tempUnit2
Converts a temperature range (the difference
between two temperature values) specified by
expression1
from one unit to another. Valid
temperature units are:
_
¡C Celsius
_
¡F Fahrenheit
_
¡K Kelvin
_
¡R Rankine
1_
¡C and 1_¡K have the same magnitude, as do
1_
¡F and 1_¡R. However, 1_¡C is 9/5 as large as
1_
¡F.
To get
@
, you can press ¥ c ¤ [
D]
(or 2 ¿
1 5
).
@
tmpCnv(100_¡c,_¡f) ¸
180.ø_¡F
@
tmpCnv(180_¡f,_¡c) ¸
100.ø_¡C
@
tmpCnv(100_¡c,_¡k) ¸
100.ø_¡K
@
tmpCnv(100_¡f,_¡r) ¸
100.ø_¡R
@
tmpCnv(1_¡c,_¡f) ¸
1.8ø_¡F
Note: To select temperature units from a menu,
press 2
9
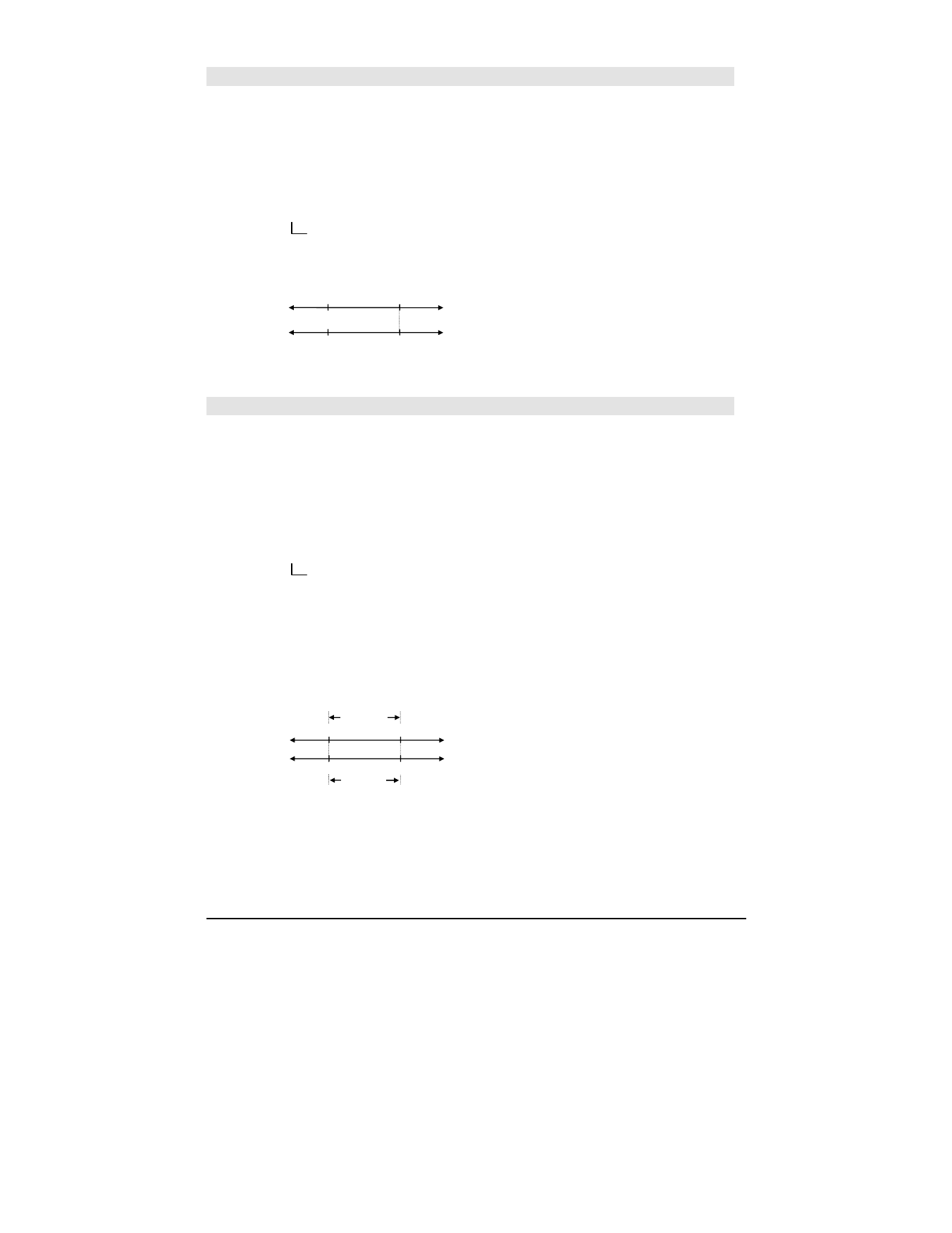
For example, a 100_
¡C range (from 0_¡C to
100_
¡C) is equivalent to a 180_¡F range:
To convert a particular temperature value instead
of a range, use
tmpCnv()
.
For
¡
, press
2 “
.
For _
, press
¥
.
For
¡
, press
2 “
.
For _
, press
¥
.
_
¡
F
_
¡
C
0 100
212
32
_
¡
C
0
100
_
¡
F
212
32
180_
¡
F
100_
¡
C
