2 ceramic resonator (default), 3 external clock source – Freescale Semiconductor 56F8122 User Manual
Page 27
External Clock Operation
56F8322 Technical Data, Rev. 10.0
Freescale Semiconductor
27
Preliminary
3.2.2
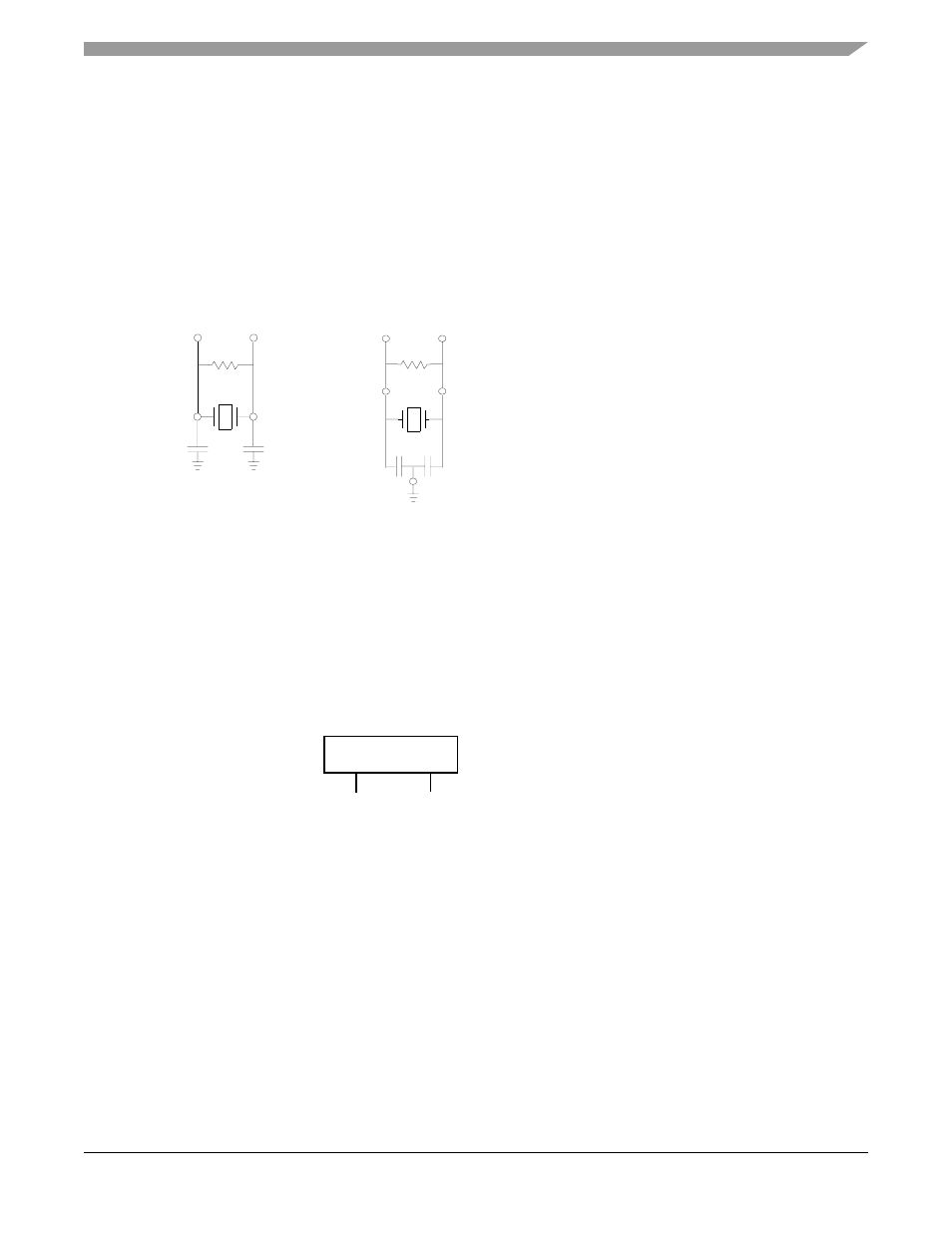
Ceramic Resonator (Default)
It is also possible to drive the internal oscillator with a ceramic resonator, assuming the overall system
design can tolerate the reduced signal integrity. A typical ceramic resonator circuit is shown in
.
Refer to the supplier’s recommendations when selecting a ceramic resonator and associated components.
The resonator and components should be mounted as near as possible to the EXTAL and XTAL pins.
Figure 3-2 Connecting a Ceramic Resonator
Note:
The OCCS_COHL bit must be set to 0 when a crystal resonator is used. The reset condition on the
OCCS_COHL bit is 0. Please see the COHL bit in the Oscillator Control (OSCTL) register, discussed
in the 56F8300 Peripheral User Manual.
3.2.3
External Clock Source
The recommended method of connecting an external clock is illustrated in
. The external clock
source is connected to XTAL and the EXTAL pin is grounded.
Figure 3-3 Connecting an External Clock Register
EXTAL XTAL
R
z
Sample External Ceramic Resonator Parameters:
R
z
= 750 K
Ω
EXTAL XTAL
R
z
C1
CL1
CL2
C2
Resonator Frequency = 4 - 8MHz (optimized for 8MHz)
3 Terminal
2 Terminal
CLKMODE = 0
XTAL
EXTAL
External
V
SS
Clock
Note: when using an external clocking
source with this configuration, the
CLKMODE and COHL bits
of the OSCTL register should be set to 1.
or GPIO
