4 flash memory characteristics, Table 10-12, Nts, as shown in – Freescale Semiconductor 56F8122 User Manual
Page 108: Figure 10-1
56F8322 Techncial Data, Rev. 10.0
108
Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
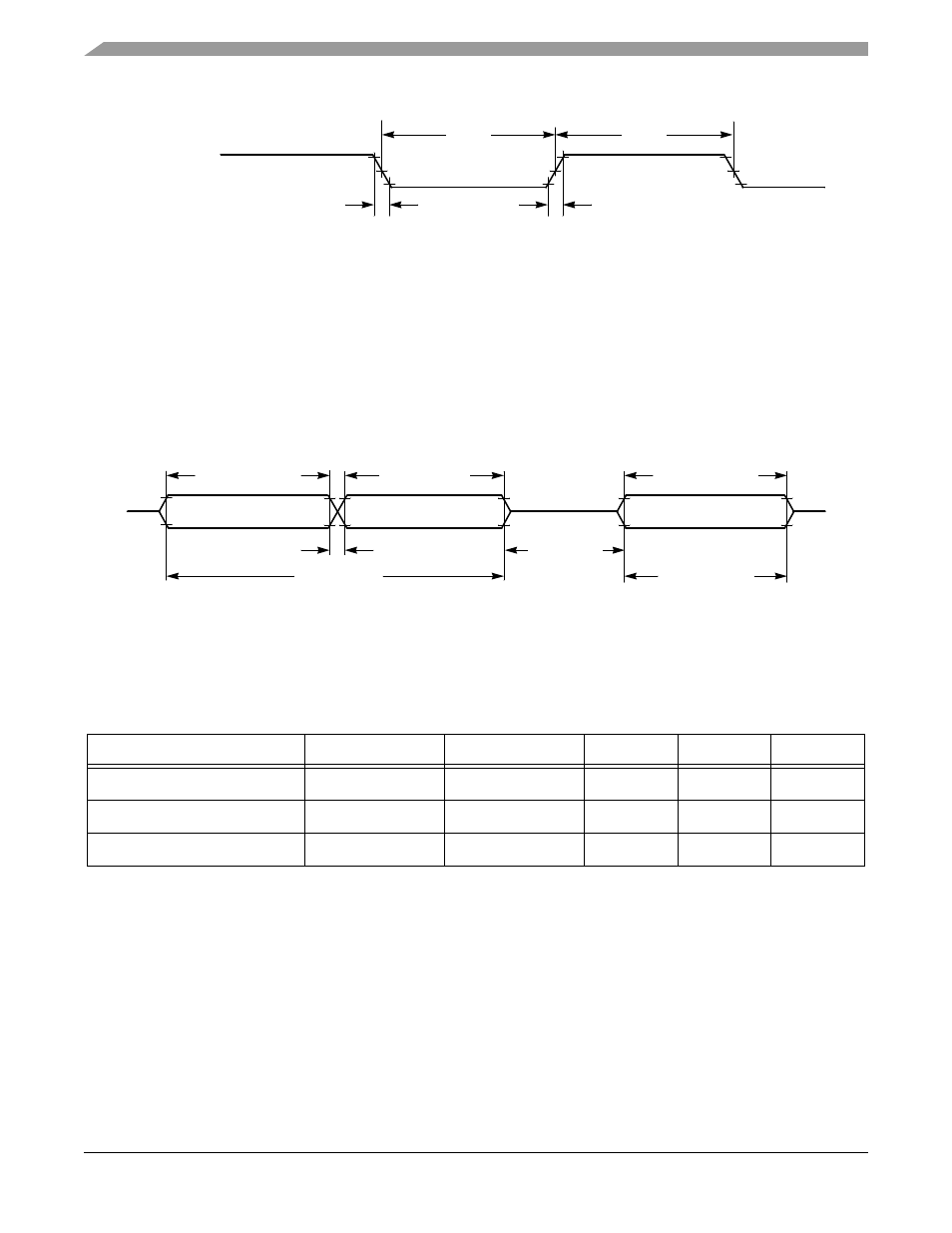
Figure 10-1 Input Signal Measurement References
shows the definitions of the following signal states:
•
Active state, when a bus or signal is driven, and enters a low impedance state
•
Tri-stated, when a bus or signal is placed in a high impedance state
•
Data Valid state, when a signal level has reached V
OL
or V
OH
•
Data Invalid state, when a signal level is in transition between V
OL
and V
OH
Figure 10-2 Signal States
10.4 Flash Memory Characteristics
Table 10-12 Flash Timing Parameters
Characteristic
Symbol
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Program time
1
1. There is additional overhead which is part of the programming sequence. See the 56F8300 Peripheral User Manual for details.
Program time is per 16-bit word in Flash memory. Two words at a time can be programmed within the Program Flash module,
as it contains two interleaved memories.
T
prog
20
—
—
µ
s
Erase time
2
2. Specifies page erase time. There are 512 bytes per page in the Data and Boot Flash memories. The Program Flash module
uses two interleaved Flash memories, increasing the effective page size to 1024 bytes.
T
erase
20
—
—
ms
Mass erase time
T
me
100
—
—
ms
V
IH
V
IL
Fall Time
Input Signal
Note: The midpoint is V
IL
+ (V
IH
– V
IL
)/2.
Midpoint1
Low
High
90%
50%
10%
Rise Time
Data Invalid State
Data1
Data2 Valid
Data
Tri-stated
Data3 Valid
Data2
Data3
Data1 Valid
Data Active
Data Active
