HEIDENHAIN TNC 640 (34059x-01) ISO programming User Manual
Page 333
HEIDENHAIN TNC 640
333
1
1
.2 The PLANE F
unction: Tilting the W
o
rk
ing Plane (Sof
tw
ar
e Option 1)
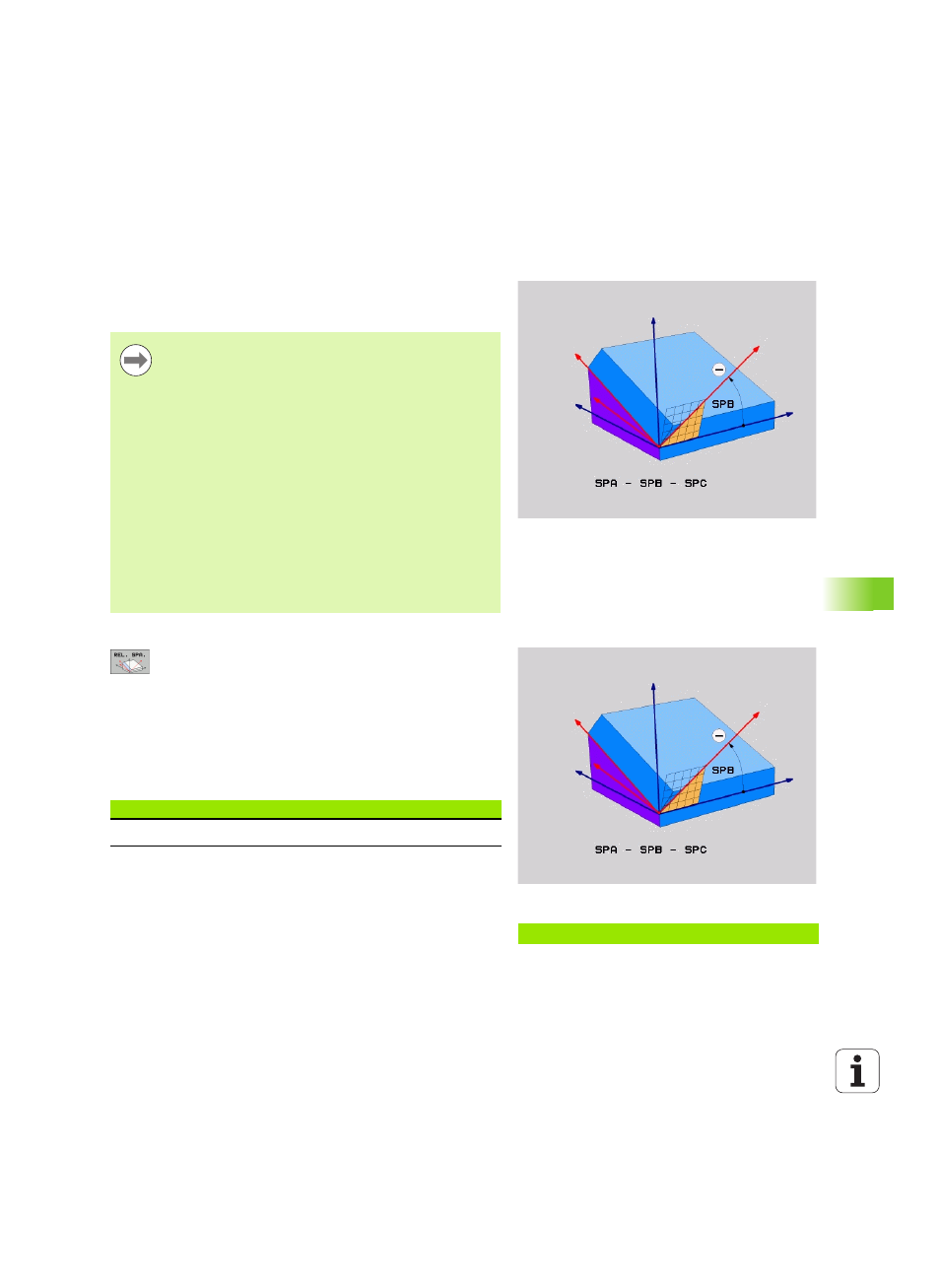
Defining the machining plane with a single,
incremental spatial angle: PLANE RELATIVE
Application
Use an incremental spatial angle when an already active tilted working
plane is to be tilted by another rotation. Example: machining a 45°
chamfer on a tilted plane.
Input parameters
U
Incremental angle?
: Spatial angle about which the
active machining plane is to be rotated additionally
(see figure at right). Use a soft key to select the axis
to be rotated about. Input range: –359.9999° to
+359.9999°
U
Continue with the positioning properties (see
"Specifying the positioning behavior of the PLANE
function" on page 336)
Abbreviations used
Before programming, note the following
The defined angle is always in effect in respect to the
active working plane, regardless of the function you have
used to activate it.
You can program any number of PLANE RELATIVE functions
in a row.
If you want to return to the working plane that was active
before the PLANE RELATIVE function, define the PLANE
RELATIVE
function again with the same angle but with the
opposite algebraic sign.
If you use the PLANE RELATIVE function in a non-tilted
working plane, then you simply rotate the non-tilted plane
about the spatial angle defined in the PLANE function.
Parameter description for the positioning behavior: See
"Specifying the positioning behavior of the PLANE
function" on page 336.
Example: NC block
5 PLANE RELATIVE SPB-45 .....
Abbreviation
Meaning
RELATIVE
Relative to
