Various modes (q406) – HEIDENHAIN iTNC 530 (340 49x-06) Cycle programming User Manual
Page 478
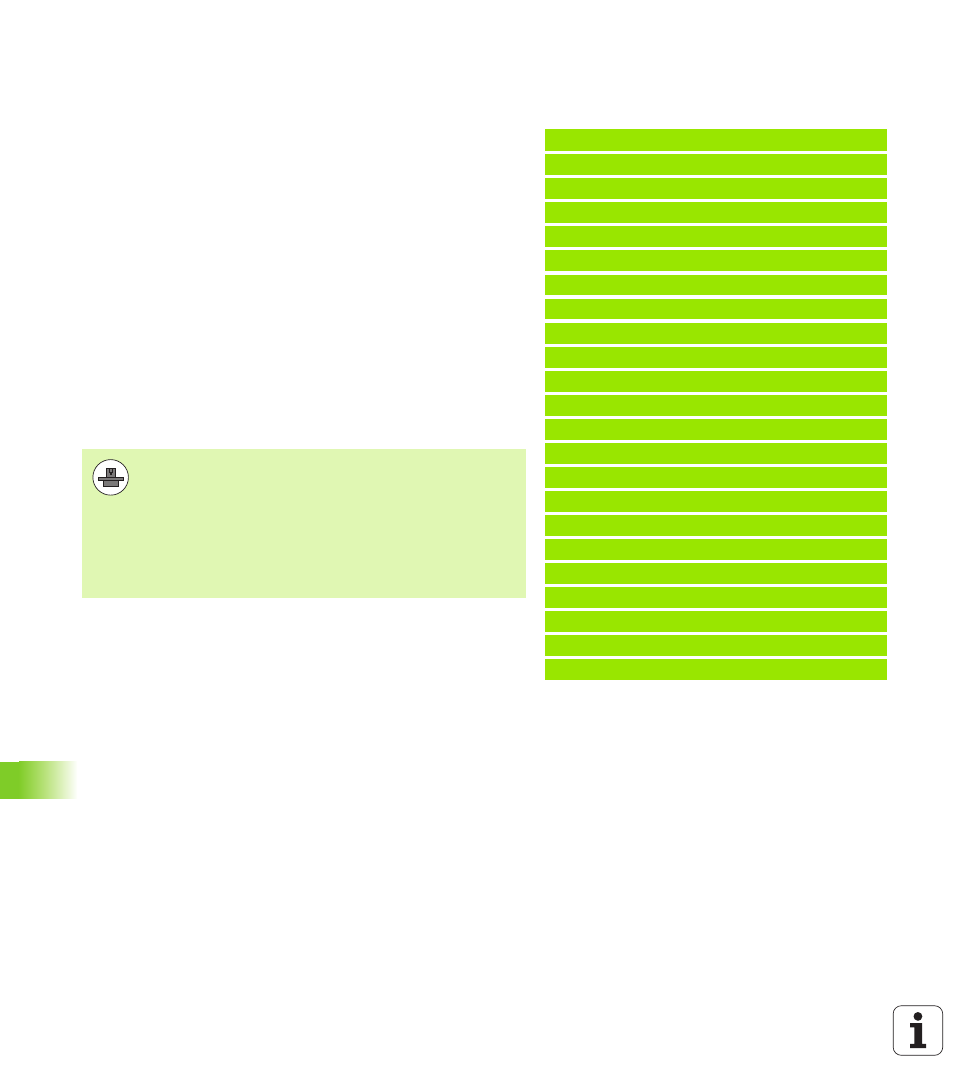
478
Touch Probe Cycles: Automatic Kinematics Measurement
1
8
.4 MEA
S
URE KINEMA
TICS (Cy
c
le 451, DIN/ISO: G451; Option)
Various modes (Q406)
Test mode Q406 = 0
The TNC measures the rotary axes in the positions defined and
calculates the static accuracy of the tilting transformation.
The TNC records the results of a possible position optimization
but does not make any adjustments
Position Optimization mode Q406 = 1
The TNC measures the rotary axes in the positions defined and
calculates the static accuracy of the tilting transformation.
During this, the TNC tries to change the position of the rotary in
the kinematics model in order to achieve higher accuracy.
The machine data is adjusted automatically
Position and Angle Optimization mode Q406 = 2
The TNC measures the rotary axes in the positions defined and
calculates the static accuracy of the tilting transformation.
First the TNC tries to optimize the angular position of the rotary
axis by means of compensation (Option #52, KinematicsComp).
If the TNC was able to optimize the angle, it automatically
optimizes the position in another measurement series.
Example: Angle and position optimization of the
rotary axes after automatic datum setting
1 TOOL CALL “TASTER“ Z
2 TCH PROBE 451 MEASURE KINEMATICS
Q406=2
;MODE
Q407=12.5 ;SPHERE RADIUS
Q320=0
;SETUP CLEARANCE
Q408=0
;RETR. HEIGHT
Q253=750
;F PRE-POSITIONING
Q380=0
;REFERENCE ANGLE
Q411=-90
;START ANGLE A AXIS
Q412=+90
;END ANGLE A AXIS
Q413=0
;INCID. ANGLE A AXIS
Q414=0
;MEAS. POINTS A AXIS
Q415=-90
;START ANGLE B AXIS
Q416=+90
;END ANGLE B AXIS
Q417=0
;INCID. ANGLE B AXIS
Q418=4
;MEAS. POINTS B AXIS
Q419=+90
;START ANGLE C AXIS
Q420=+270 ;END ANGLE C AXIS
Q421=0
;INCID. ANGLE C AXIS
Q422=3
;MEAS. POINTS C AXIS
Q423=3
;NO. OF MEAS. POINTS
Q431=1
;PRESET
Q432=0
;BACKLASH, ANG. RANGE
For angle optimization, the machine manufacturer must
have adapted the configuration correspondingly. You can
ask your machine manufacturer if this is the case, and
whether an angle optimization makes sense. Angle
optimization can be particularly useful on small, compact
machines.
Angle compensation is only possible with Option #52
KinematicsComp.
