Vrrp application (taking ipv4 vrrp for example) – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade LB Cards User Manual
Page 17
9
If the uplink fails, hosts in the LAN cannot access external networks through the router. The state
of the monitored track entry is negative and the priority of the router decreases by a specified
value. Then, a higher priority router in the VRRP group becomes the master to maintain the
proper communication between the hosts in the LAN and external networks.
{
Monitor the master on a backup.
When the master fails, the backup immediately takes over to maintain normal communication.
For more information about track entries, see "Configuring Track."
VRRP application (taking IPv4 VRRP for example)
1.
Master/backup
In master/backup mode, only the master forwards packets. When the master fails, a new master
is elected from the backups. This mode requires only one VRRP group, in which each router holds
a different priority and the one with the highest priority becomes the master.
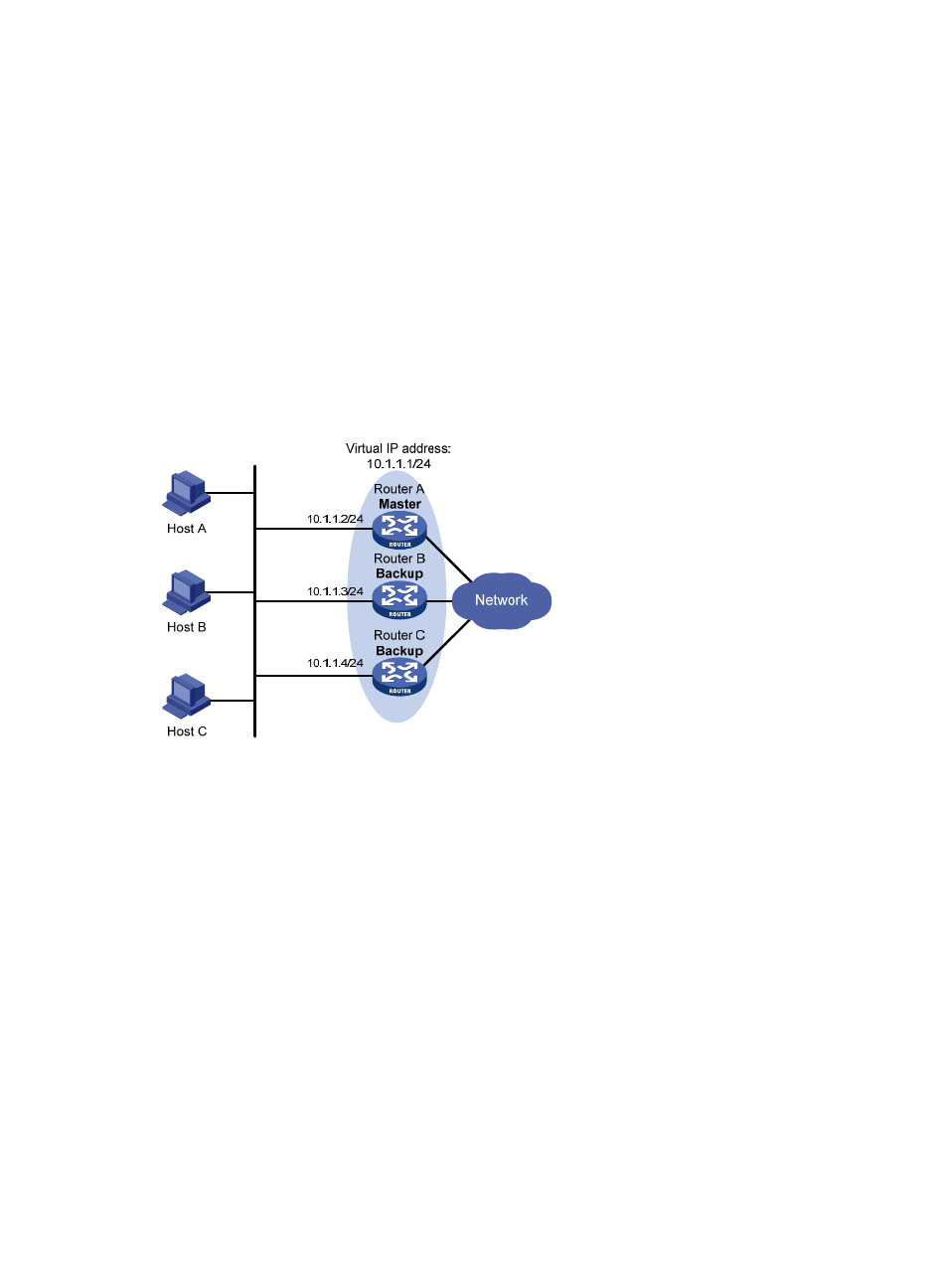
Figure 5 VRRP in master/backup mode
Assume that Router A is acting as the master to forward packets to external networks, and Router
B and Router C are backups in listening state. When Router A fails, Router B and Router C elect a
new master to forward packets for hosts on the LAN.
2.
Load sharing
More than one VRRP group can be created on an interface of a router to allow the router to be the
master of one VRRP group but a backup of another at the same time.
In load sharing mode, multiple routers provide services simultaneously. This mode requires two or
more VRRP groups, each of which comprises a master and one or more backups. The masters of
the VRRP groups are assumed by different routers.
