Active/standby mode, Load balancing mode – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade LB Cards User Manual
Page 157
149
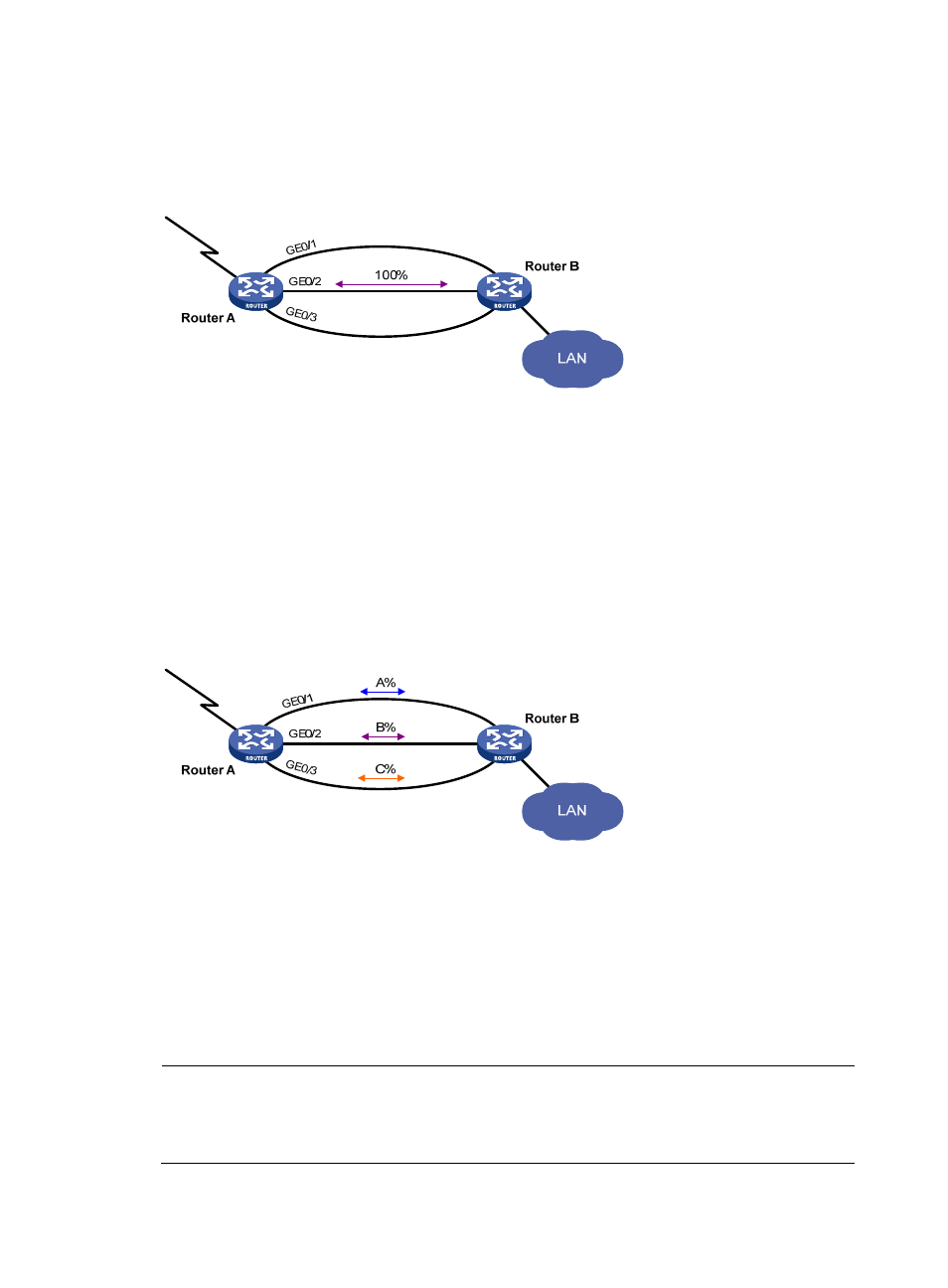
Active/standby mode
As shown in
, interface GigabitEthernet 0/2 on Router A acts as the active interface and
interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/1 and GigabitEthernet 0/3 act as the standby interfaces.
Figure 61 Diagram for active/standby mode
In active/standby mode, only one interface transmits data at any given time.
•
When the active interface is operating properly, even if the traffic is overloaded, the standby
interface is in a backup state. All traffic is transmitted by the active interface.
•
If the active interface fails, the standby interface with highest priority takes over to transmit data.
•
When the active interface is restored, it resumes data transmission.
Load balancing mode
As shown in
, interface GigabitEthernet 0/2 on Router A acts as the active interface, and
interfaces GigabitEthernet 0/1 and GigabitEthernet 0/3 act as the standby interfaces.
Figure 62 Diagram for load balancing mode
In load balancing mode, you can set an upper threshold (enable-threshold) and a lower threshold
(disable-threshold). Traffic can be shared among multiple interfaces:
•
When the traffic on the active interface exceeds the predefined enable-threshold, the highest
priority standby interface is activated. Other standby interfaces are activated in descending priority
order if exceeding traffic still exists.
•
When the traffic on the active interface decreases below the predefined disable-threshold, the
system shuts down the lowest priority standby interface first and then shuts down the other standby
interfaces in ascending priority order depending on traffic size.
NOTE:
Adopt active/standby or load balancing mode depending on whether you have configured an upper or
lower threshold for the active interface traffic. If this threshold is configured, load balancing mode is
adopted. Otherwise, active/standby mode is adopted.
