Microcom 438 User Manual
Page 134
Chapter 8
Bar Codes
438 Operator’s Manual - 880052-0100
8-17
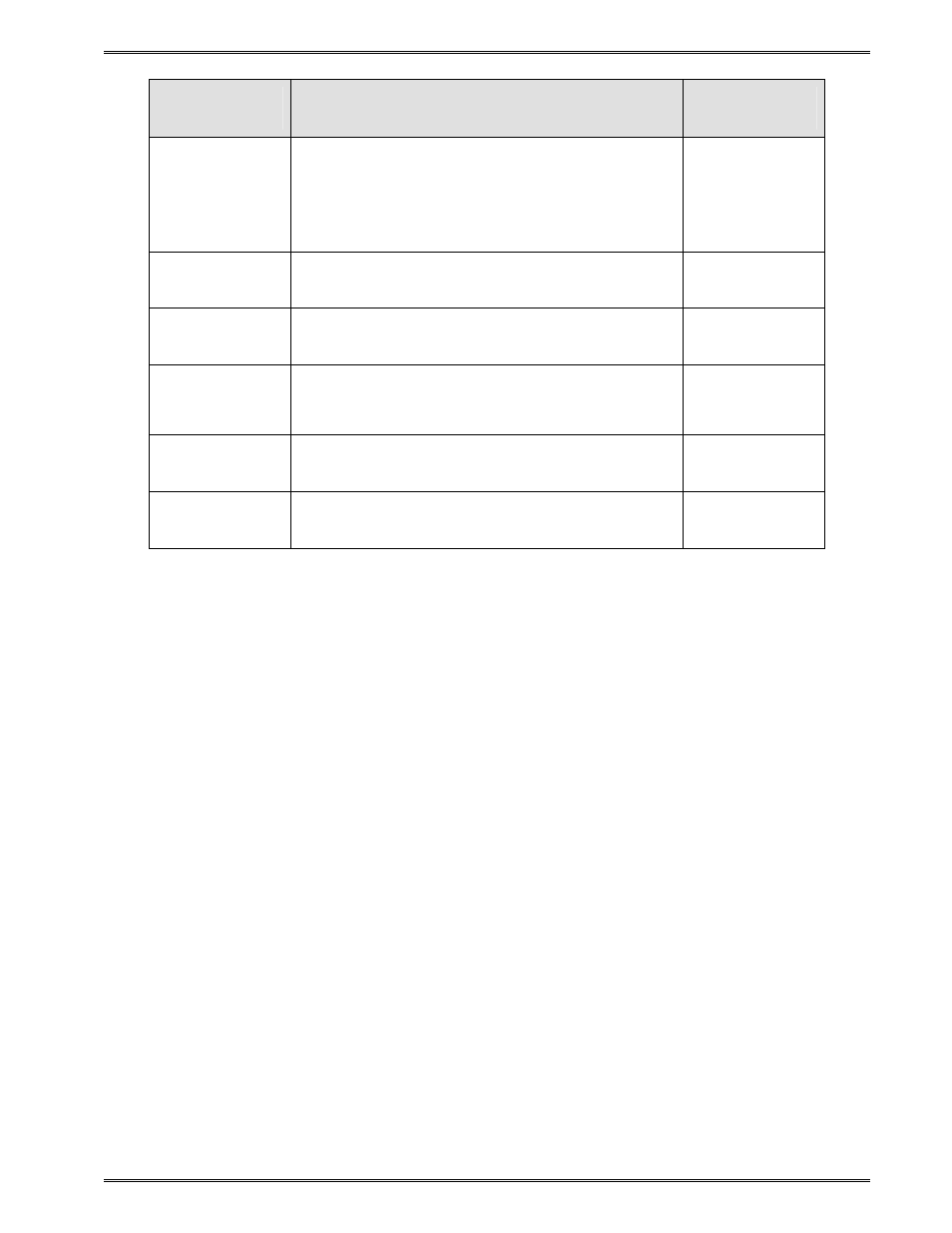
Encoding
Scheme
Characters
Bits per
Character
A- ASCII
Double digit numeric
ACSII values 0 – 127
Extended ASCII values 128-255
4
8
16
C- C40
Primarily Uppercase Alphanumeric
5.33
T- Text
Primarily Lowercase Alphanumeric
5.33
B- Base256
All byte values 0 – 255
8
X- X12
Similar to C40
5.33
E- Edifact
63 ASCII plus un-latch char
6
Table 8-6
Data Matrix Encoding Schemes
ACSII Encoding Scheme
ASCII encoding is the basic scheme that encodes ASCII data, double density numeric data
and symbology control characters. Which means it encodes one alphabetic or two numeric
characters per byte. All other encoding schemes are invoked from ASCII and will then
return to this scheme through the use of code words.
C40 Encoding Scheme
C40 encoding scheme is used to encode uppercase alphabetic, numerical and space
characters. C40 encodes three alphanumeric data characters into two bytes.
Text Encoding Scheme
Text encoding is primarily used to encode lowercase alphabetic and numerical characters.
Text encodes three alphanumeric data characters into two bytes.
Base 256 Encoding Scheme
The Base 256 encoding scheme is used to encode any 8-bit byte data, including extended
channel interpretations (ECI’s) and binary data.
X12 Encoding Scheme
X12 encoding scheme is use to encode the standard ANSI X12 electronic data interchange
characters, which are compacted three data characters to two codewords in a manner
similar to C40 encoding.
Edifact Encoding Scheme
