Measurement Computing DBK70 User Manual
Page 71
DBK70 User’s Manual
928494
Fundamentals of Obtaining Vehicle Data 6-5
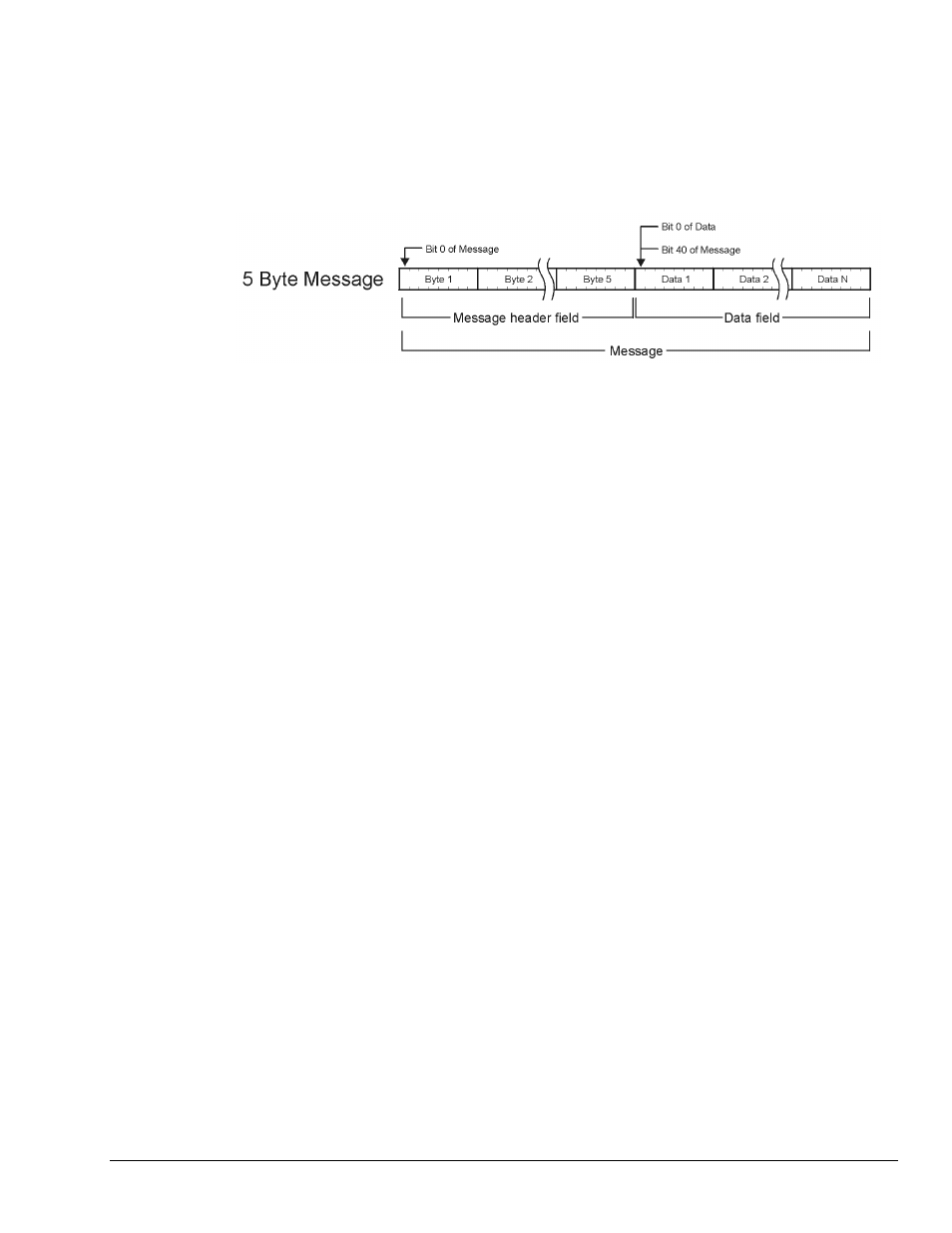
The Index and Length values define where in a received message that has passed the Filter, the desired
data starts and how long it is, respectively. The first bit of a received message, the high order bit of the first
byte of the message, has an Index value of 0. The first high order bit of the second byte has a value of 8.
If the header field is 5 bytes, the data will typically begin at an Index of 40. Length values are typically
in multiples of 8 ( 8, 16, 24, or 32). Occasionally, the data is one or a few bits in size. In these cases the
Length value would be 1, 2, 3, etc. If the length of the data is one byte, the Length value will be 8.
The Storage Type value indicates whether the data should be processed as 2’s complement signed data or
as unsigned data. Most data is unsigned, but once in a while data is signed. Another way to look at this is to
ask if the raw data in the received message can be negative. This does not refer to the scaled value of the
data, only to the raw data in the received message.
Received data is multiplied by the value of the Output Scale field and the result of that multiplication is
added to the value of the Output Offset field (i.e., y = m * x + b, where x is the received data, m is the
Output Scale, b is the Output Offset, and y = the scaled result). The values of Output Scale and Output
Offset depend on the resolution of the received data, the range of the scaled data derived from the received
data, and the desired range and lowest value of the proportional output signal.
