4 network cabling for profibis dp, 2 token rotation time, 3 bus cycle time – Flowserve MX/QX Profibus DP/PA Field Unit User Manual
Page 16
PB DPV1 / PA Field Unit Installation and Maintenance FCD LMENIM2336-03 – 12/12
16
2.2.3.2 Token Rotation Time
The time required for the rotation of the token to all active nodes is the token rotation time. The Time
Target Rotation (TTR) is adjustable, and is used to specify the maximum allowed time of one rotation.
2.2.3.3 Bus Cycle Time
Based on the number of slaves attached to each master and the amount of data to be transferred, a
Bus Cycle Time is calculated by the master. This is the amount of time required for a master to poll all
slaves. This, along with the Token Rotation Time, makes PROFIBUS network access deterministic.
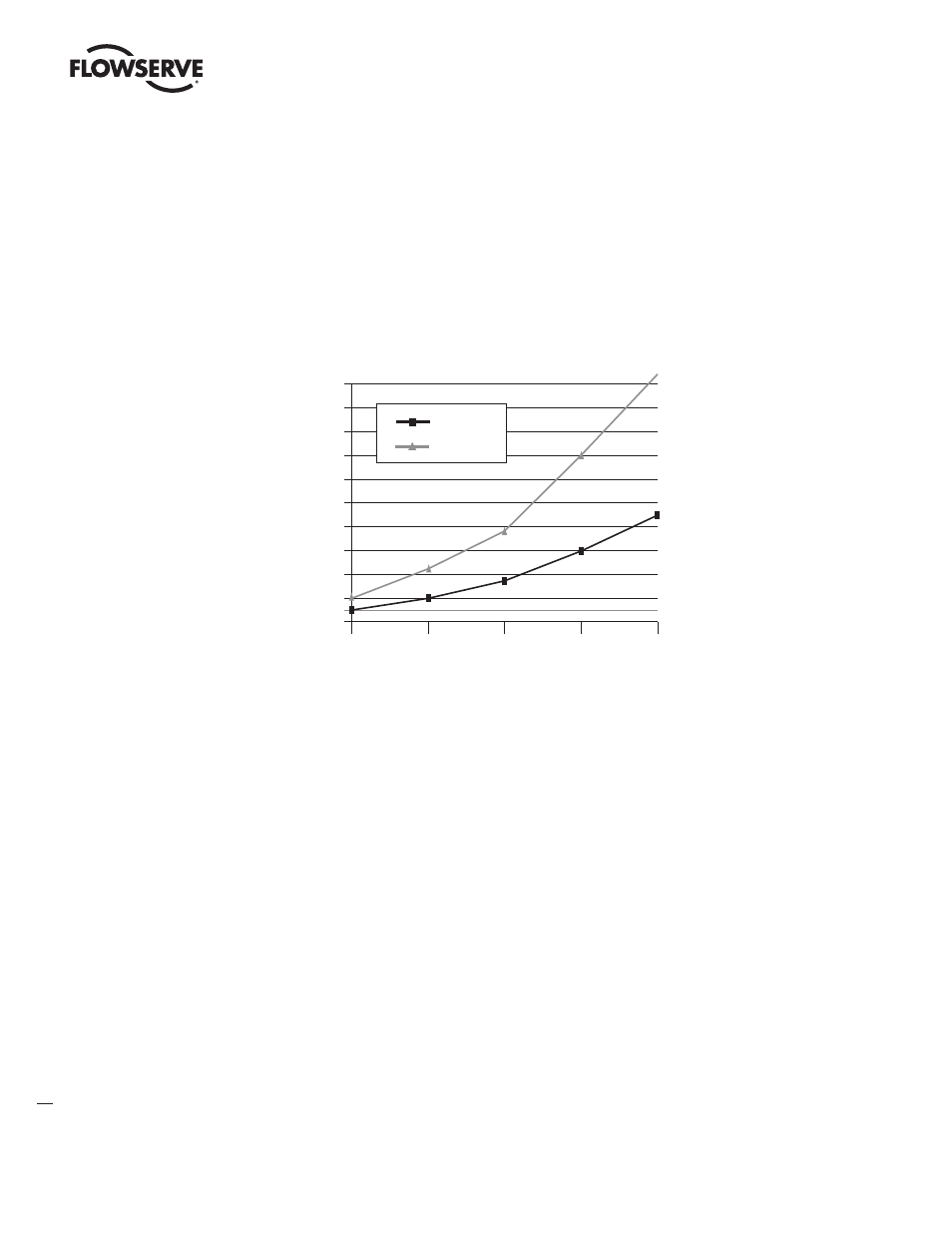
Figure 2.4 – Typical Cycle Time (Each Station with 2 Bytes I/O)
20.0
18.0
16.0
14.0
12.0
10.0
8.0
6.0
4.0
2.0
0.0
5
1
10
20
30
Cycle T
ime (ms)
Number of Slaves
1.5 MBaud
500 kBaud
8.8
14.1
6.1
3.3
7.7
4.6
2.0
0.9
2.0
2.2.4 Network Cabling for PROFIBIS DP
Network cabling should be in accordance with PROFIBUS Decentralized Periphery (DP) guidelines.
To achieve immunity to electromagnetic interference, ensuring high data integrity, certain cables and
guidelines are recommended. Additionally, the following items should be taken into account when
planning the network:
• Transmission rate – Within a network, only one transmission rate can be used; the MX/QX PB DP
works at baud rates up to 1.5 Mbps.
• The level of Master and Slave redundancy, if any.
• The required number of nodes.
• The type of network components needed – terminals, connectors, connecting cables, termination.
• The type of cable to be used and its characteristics.
• The number of segments and/or repeaters.
• The overall span of the network – adding repeaters and long cable lengths can increase transmis-
sion time.
• Cable termination – active termination resistors are required at the ends of all segments.
In general, the following rules apply for PROFIBUS networks:
• The higher the baud rate, the shorter the distance allowed between nodes.
• The higher the baud rate, the shorter the maximum distance of a segment.
• The higher the baud rate, the shorter the maximum distance of an entire network.
