Comtech EF Data CRS-400 User Manual
Page 19
CRS-400 1:8 Redundancy Switch
Revision 0
Introduction
MN/CRS400.IOM
3
There are several other key operational features of the CRS-400 architecture:
“Bridging” a traffic modulator/demodulator clock and data: A copy of the data and
clock signals feeding a particular modulator/demodulator is selectively routed to the
redundant modulator/demodulator.
“Bridging” a traffic modulator/demodulator IF: RMI Rx IF is tuned to receive any
selected carrier.
Live traffic may be checked on the redundant demodulator when the traffic
demodulator is placed in “bridge” mode.
There are two ways to set up the CRS-400 for IF operation. The first method does not
require an optional IF switch and is used when all modulators/demodulators within a
group are connected to the same up/down converter.
The second method is used when operation with more than one up/down converter is
required. In this case, adding the CRS-280 IF Switch permits connections to as many
converters as traffic modulators/demodulators.
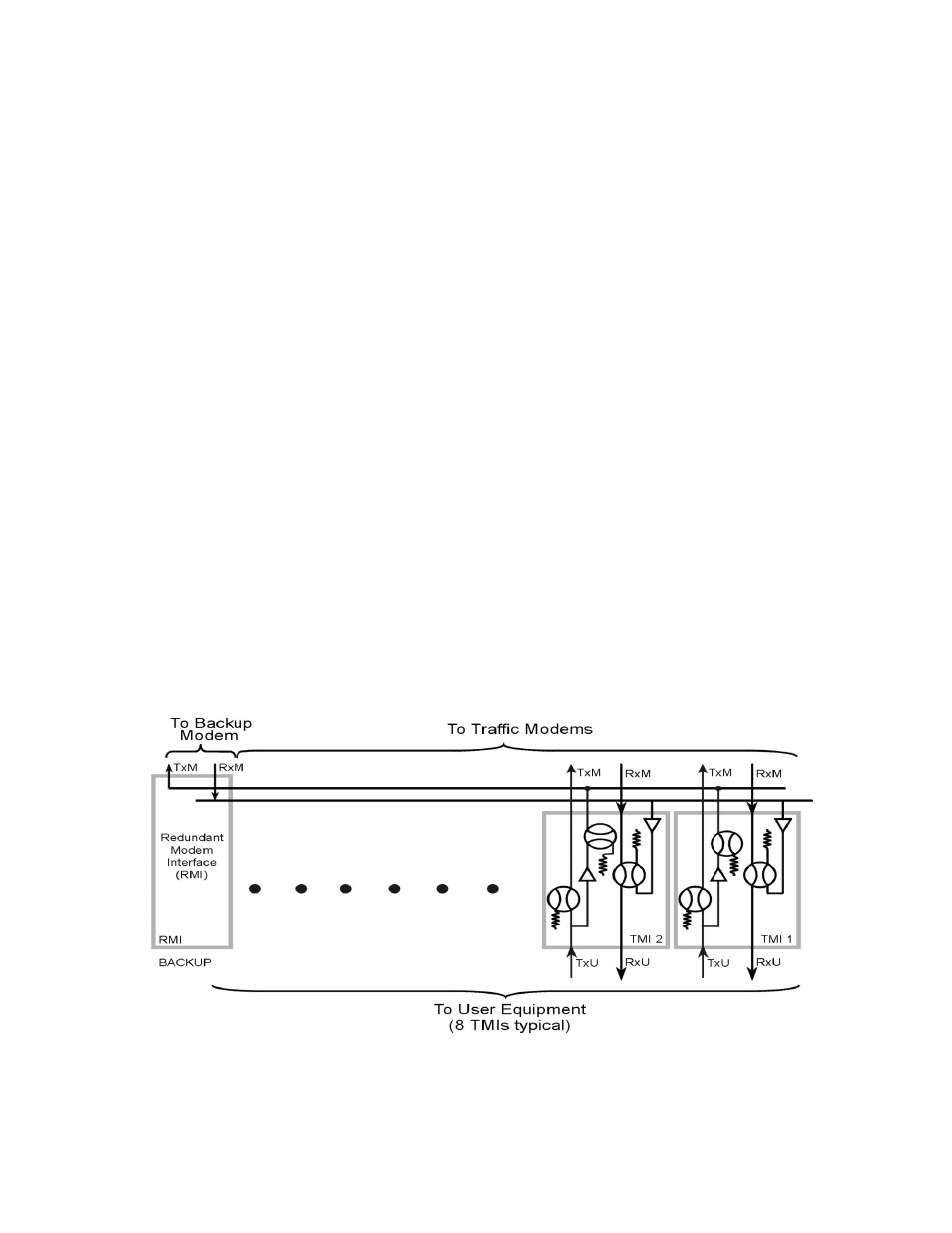
The data switch and IF switch are shown in Figure 1-2 and Figure 1-3, respectively. Data
enters the TMI modules (CH1 - CH8) at the bottom of Figure 1-2. The Tx data entering
each channel is routed through the TMI and sent out to the traffic modulators/de-
modulators. The Tx data and clock are also buffered by an amplifier to make them
available for bridging and routing through the RMI.
Figure 1-2 CRS-400 Data Switch Block Diagram (TMI #1 is Bridged)
